Weekday Course
Breast MRI Basics for Diagnosis & Screening
ISMRM & SMRT Annual Meeting • 15-20 May 2021

| Concurrent 1 | 13:45 - 14:30 | Moderators: Elizabeth Morris |
| BI-RADS Mass
Pascal Baltzer
|
||
 |
Breast MRI for Treatment Response
Fiona Gilbert
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is standard of care in women who are found to have clinical stage T2-4 N0 breast cancer or any T1-3 with HER2 positive breast cancer. Although ultrasound is frequently used in clinical settings MRI has been shown to be the most accurate technique in monitoring response and is used in measurement of initial volume and for assessing response. Residual disease can be over or underestimated in around 20% of cases. DWI and ADC are used in early measures of response as well as pharmacokinetic measurements such as ktrans.
|
|
 |
Beyond BI-RADS
Laura Martincich
DWI when associated with DCE-MRI may improve the diagnostic accuracy of the examination.
|
|
 |
Breast MRI for Screening
Ritse Mann
The use of breast MRI for screening enables earlier detection of relevant breast cancer than with other imaging techniques (particularly mammography). It has been initially tested in women with a very high (hereditary) risk for the development of breast cancer, but indications are expanding and now may include, for example, women with a personal history of breast cancer and women with very dense breasts. To optimize the value of MRI for screening the use of dedicated screening protocols and optimized hangings is required.
|
|
 |
Understanding the Commonly Used Sequences of Breast MRI
Min Sun Bae
This course will outline the commonly used sequences of breast MRI, along with emerging and novel techniques. Standard breast MRI includes T2-weighted imaging, precontrast T1-weighted imaging, and dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging. Abbreviated MRI of the breast includes one precontrast and one postcontrast T1-weighted sequences and maximum intensity projection. Abbreviated MRI shows promise for breast cancer screening, as it can reduce the examination time and the interpretation time as well as the cost associated with MRI studies. Multiparametric MRI, including DWI and ultrafast imaging, has a potential to improve diagnostic accuracy. |
|
 |
Management of High-Risk Patients & Implant Imaging
Wendy DeMartini
Breast MRI is an important tool, with applications including screening asymptomatic women at high risk for breast cancer, and assessment of silicone breast implants for rupture or other complications. MRI use and outcomes for high risk screening and implant assessment will be reviewed.
|
|
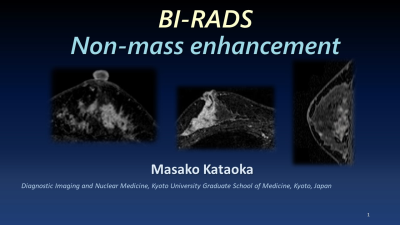 |
BI-RADS Non-Mass Enhancement
Masako Kataoka
This talk first explains the definition of non-mass enhancement (NME), as an area that is neither a mass nor a focus. Internal enhancing characteristics of NME are discrete from the normal surrounding background parenchymal enhancement. NME is described in terms of “distribution” and “internal enhancement patterns”. Linear and segmental distribution, with heterogeneous and clustered ring enhancement are associated with malignant lesions. Various lesions and conditions present as NME. Malignant lesions include ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), intraductal component of invasive carcinoma, and invasive lobular carcinoma. Benign lesions include fibrocystic change. These knowledge helps to diagnose lesions presenting as NME.
|
|
 |
Category & Management Based on BI-RADS (Case-Based)
Maria Adele Marino
MRI of the breast has been established worldwide as a highly accurate imaging modality for breast cancer management in both the symptomatic and screening setting. The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) lexicon contains a structured common language for interpretation and reporting of mammography, ultrasound, and MRI facilitating the communication among physicians through the use of a standardized terminology. The MRI BI-RADS lexicon includes a variety of features from lesion morphology, such as margins, to functional contrast enhancement kinetics. The aim of this talk is to show the basics of the use of BI-RADS on breast MRI.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.