Digital Poster
MRS & Hyperpolarization I
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Computer # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
1797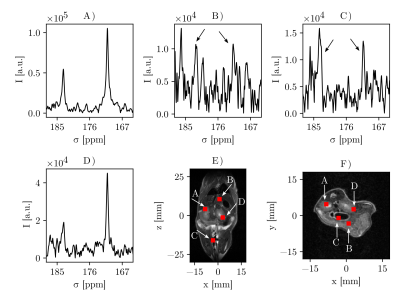 |
67 | Multi-voxel PRESS for fast and sensitive static MRS of hyperpolarized nuclei
Wolfgang Gottwald1, Luca Nagel1, Geoffrey J. Topping1, and Franz Schilling1
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, TUM School of Medicine, Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany
A multi-voxel point resolved spectroscopy (MV-PRESS) sequence was developed for measuring hyperpolarized 13C-labelled compounds, on a 7T preclinical small animal scanner. MV-PRESS allows to excite selected imaging voxels within a 3D volume with high sensitivity (i.e. 90° excitation angle). This method was compared to both single-voxel PRESS of a thermal 1H phantom and CSI with a hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate phantom. MV-PRESS was then used to detect both pyruvate and lactate in healthy mouse kidneys after hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate injection, using 2x2x2 mm3 voxels for a total of 4 voxels.
|
||
1798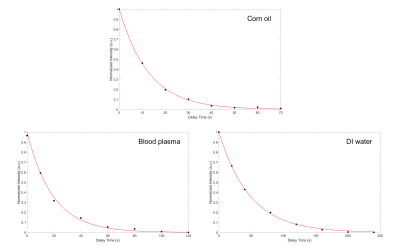 |
68 | Dissolved-phase 129Xe longitudinal relaxation times at low and high magnetic field strengths
Nicholas Bryden1, Michele Kelley1, Christian T McHugh1, and Rosa T Branca1
1University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, United States We provide longitudinal relaxation measurements of hyperpolarized (HP) 129Xe gas dissolved in a variety of solvents at both low and high magnetic field strengths. The method of measuring T1 presented here is less sensitive than more commonly used methods to RF flip angle miscalibration, which has caused the significant variation in dissolved-phase 129Xe T1 values reported in the past. A field dependent study of gas depolarization by hollow membrane fibers commonly used to dissolve xenon in blood or other solvents is also included, which provides insight to experimental limitations on their use in both field regimes. |
||
1799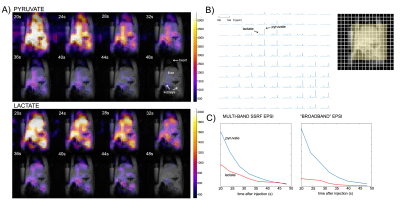 |
69 | Multi-band echo-planar spectroscopic imaging of hyperpolarized 13C probes in a compact preclinical PET/MR scanner
Cornelius von Morze1, Tyler Blazey1, Richard Baeza2, Ruslan Garipov2, Timothy Whitehead1, Galen D Reed3, Joel R Garbow1, and Kooresh I Shoghi1
1Washington University, St Louis, MO, United States, 2MR Solutions, Guildford, United Kingdom, 3GE Healthcare, Dallas, TX, United States Hyperpolarized (HP) 13C MRI requires advanced pulse sequences to capture the dynamic, localized metabolic information. We developed an echo planar spectroscopic imaging (EPSI) pulse sequence incorporating multi-band spectral-spatial radiofrequency (SSRF) pulses for rapid and efficient HP 13C MRI on a new cryogen-free simultaneous PET/MR molecular imaging platform with compact footprint. Excitation profiles were measured in phantoms, and the SSRF-EPSI sequence was tested in rats using two HP 13C probes. We also obtained simultaneous 18F-FDG-PET data for comparison. In conclusion, advanced 13C SSRF imaging approaches are feasible on the new PET/MR platform, facilitating direct comparison with PET. |
||
1800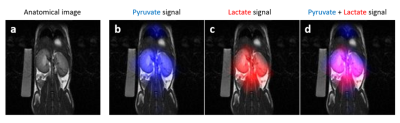 |
70 | Improving the biocompatibility of parahydrogen hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate
Francesca Reineri1, Oksana Bondar1, Carla Carrera2, Eleonora Cavallari1, Erika Cerutti1, Ginevra Di Matteo1, and Silvio Aime1
1Molecular Biotechnology, University of Torino, Torino, Italy, 2Institute of Biostructure and Bioimaging, Nation Research Council, Torino, Italy
ParaHydrogen Induced Polarization is a hyperpolarization method much less technically demanding and affordable than d-DNP. The Side Arm Hydrogenation method allowed to obtain hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate that can be used for metabolic studies, but concerns about the safety and bio-compatibility of the final aqueous solution of the HP products may be present, due to organic solvents and metal complex. In this work, a method to remove all the traces of toxic solvents and metal complex from the final product will be presented, together with the 13C-MR images obtained using the metabolite thus hyperpolarized.
|
||
1801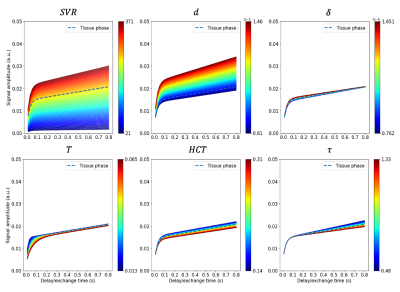 |
71 | Sensitivity analysis of the MOXE model of gas exchange for lung hyperpolarised 129Xe MRS and MRI
Yohn C.G. Taylor1, Frederick J. Wilson2, and Geoff J.M. Parker1,3
1Centre for Medical Image Computing, Quantitative Imaging Group, Department of Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2GlaxoSmithKline R&D, Stevenage, United Kingdom, 3Bioxydyn Limited, Manchester, United Kingdom
Univariate sensitivity analysis was used to determine parameter importance within the model of gas exchange (MOXE) for lung hyperpolarised 129Xe MRS/MRI. Sensitivity of the model to parameter variation across a range of saturation recovery delay times within the chemical shift saturation recovery (CSSR) technique was assessed. Simulated parameter values spanned those in healthy and patient groups. MOXE is found to be most sensitive to changes in surface-area-to-volume ratio and in septal wall thickness. MOXE is negligibly sensitive to alveoli-capillary barrier thickness. CSSR measurements taken within delay periods between 0 - 200 ms provide optimum parameter sensitivity.
|
||
1802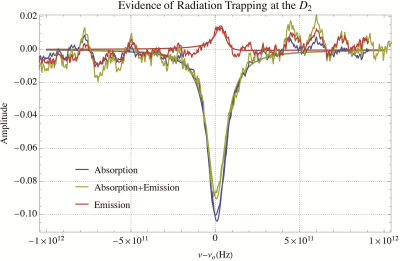 |
72 | In situ evidence of radiation trapping limiting Rb polarization in common SEOP setups
Michele Kelley1 and Rosa Tamara Branca1
1Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, United States
To increase the 129Xe polarization for emerging biomedical applications, the Rb polarization on which the 129Xe directly depends must be first optimized. Radiation trapping is a form of Rb depolarization thought to be quenched by the N2 added to SEOP gas mixtures. Here we use absorption spectroscopy to measure the Rb density, optical spectroscopy to monitor the fraction of Rb atoms involved in radiation trapping, and field cycling to measure the Rb polarization. We find that radiation trapping is still present during spin-exchange optical pumping and appears to limit the achievable Rb polarization.
|
||
1803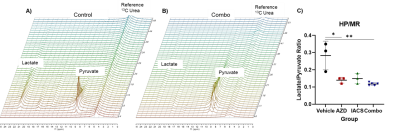 |
73 | Assessment of treatment efficacy in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia models with Hyperpolarized MR and NMR metabolomics
Jose Santiago Enriquez1,2, Natalia Baran3, Shivanand Pudakalakatti1, Marina Konopleva2,3, and Pratip Bhattacharya1,2
1Cancer Systems Imaging, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, United States, 2UT MD Anderson Cancer Center UT Health Science Center Houston Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Houston, TX, United States, 3Leukemia, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, United States
Metabolic reprogramming is one of the key hallmarks in acquiring aggressive phenotype and chemoresistance in many cancers including T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). To combat chemoresistance, we treated patient-derived xenografts with two metabolic drugs that target two different pathways for T-ALL: IACS-010759, a Complex I inhibitor for OXPHOS pathway and AZD3965, a monocarboxylate transporter-1 (MCT1) inhibitor. Hyperpolarized metabolic imaging in vivo and NMR metabolomics ex vivo was utilized to observe the difference in metabolism with single treatment and in combination. Our results demonstrate that metabolic intervention utilizing OXPHOS blockade can be potentiated by targeting the MCT1 transporter.
|
||
1804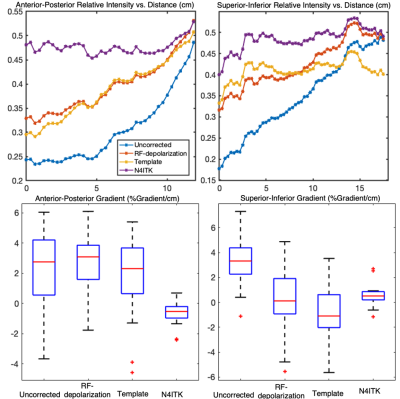 |
74 | Evaluating physiological gradients after bias field correction of Hyperpolarized 129Xe Gas Ventilation MRI
Junlan Lu1, Suphachart Leewiwatwong2, David Mummy3, and Bastiaan Driehuys2
1Medical Physics, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 2Biomedical Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 3Radiology, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States
Quantitative analysis of hyperpolarized 129Xe ventilation imaging requires overcoming the ill-posed problem of accurately correcting for bias field. The standard solution of N4ITK bias field correction removes not only bias field, but also physiologic gradients of interest. An alternative approach is applying RF depolarization mapping in a cohort of subjects to construct a bias field template. Here, we compare the effect that these different bias field correction techniques have on the 129Xe MRI ventilation gradients in a cohort of healthy patients (n=18).
|
||
1805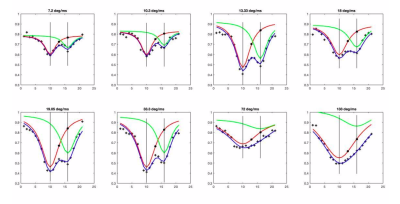 |
75 | Refining selectivity of XTC saturation pulse parameters through spectroscopic analysis
Tahmina Achekzai1, Luis Loza1, Stephen Kadlecek1, Kai Ruppert1, Faraz Amzajerdian1, and Rahim Rizi1
1University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States In Xenon Polarization Transfer Constant (XTC) imaging, saturation pulses are applied at DP Xe frequencies for red blood cell (RBC) and tissue plasma (TP), but, due to their high power, are not perfectly selective, often depolarizing both DP frequencies instead of only the one intended. We used XTC spectroscopy to explore how various saturation pulse parameters, primarily pulse power, affects saturation selectivity. The generated graphs plot depolarization as a function of saturation frequency. They demonstrate that as pulse power increases, the contribution of gas-phase depolarization due to off-resonance saturation increases, compromising selectivity. |
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.