Online Gather.town Pitches
Cancer II
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
4278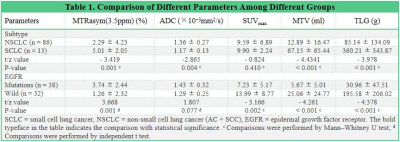 |
1 | Lung cancer in multi-parametric PET/MRI: assessment of subtype and EGFR status based on amide proton transfer-weighted imaging and 18F-FDG PET
Nan Meng1, Fangfang Fu2, Pengyang Feng3, Ziqiang Li4, Zhun Huang3, Ting Fang1, Yaping Wu2, Jianmin Yuan5, Yang Yang6, Hui Liu7, and Meiyun Wang*1
1Department of Medical Imaging, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital & Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Department of Medical Imaging, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 3Department of Medical Imaging, Henan University People’s Hospital & Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 4Department of Medical Imaging, Xinxiang Medical University Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 5Central Research Institute, UIH Group, Shanghai, China, 6Beijing United Imaging Research Institute of Intelligent Imaging, UIH Group, Beijing, China, 7UIH America, Houston, TX, United States
18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (18F-FDG PET/MRI) allows multimodal quantitative MRI sequences to be scanned in parallel with PET imaging, providing a more multidimensional reflection of lesion information. Our results showed that amide proton transfer-weighted imaging (APTWI), and metabolism related parameters can be beneficial for the non-invasive assessment of subtype and EGFR status in patients with lung cancer.
|
||
4279 |
2 | Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Different Diffusion Times for Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors
Jie Ding1, Yishi Wang2, Zhen Zhang1, Xiuzheng Yue2, Rongrong Zhu1, and Ruoshui Ha1
1Medical Imaging Center, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Some novel biomarkers has emerged from the fact that apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) depends strongly on the diffusion time, such as the rate of ADC change using two diffusion times for the differentiation of breast tumor types and a cell size modeling. In this study, we propose to use Multiband (MB) SENSE to accelerate the data acquisition of OGSE and PGSE sequences and compare the diagnostic value of ADC at different diffusion times for breast tumor. Our data showed superior diagnostic performance between benign and malignant breast lesions using ADC at a short diffusion time.
|
||
4280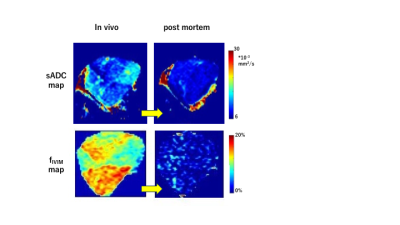 |
3 | Time-dependent IVIM and non-Gaussian parameters in breast cancer and melanoma xenograft models; correlation with histological markers
Yuko Someya1, Mami Iima1,2, Hirohiko Imai3, Tomomi Nobashi1, Akihiko Yoshizawa4, Masako Kataoka1, Hiroyoshi Isoda1, Denis Le Bihan5,6,7, and Yuji Nakamoto1
1Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 2Institute for advancement of clinical and translational science, Kyoto University Hospital, Kyoto, Japan, 3Department of Systems science, Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 4Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 5NeuroSpin/Joliot, CEA-Saclay Center, Paris-Saclay University, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 6Human Brain Research Center, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, 7National Institute for Physiological Sciences, Okazaki, Japan
Time-dependent IVIM and non-Gaussian diffusion parameters might provide additional information over conventional DWI to evaluate features linked to tissue microstructure. Time-dependent IVIM and non-Gaussian diffusion parameters were evaluated both in-vivo and post-mortem in MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer) and B16 (melanoma) models. As expected, fIVIM values significantly dropped from in-vivo to post-mortem conditions with both models at two different diffusion times, confirming the association between fIVIM and tumor perfusion, but did not reach 0, suggesting limitations in the IVIM/non-Gaussian Kurtosis model. ADCo values significantly decreased at long diffusion times and upon sacrification while Kurtosis moderately increased.
|
||
4281 |
4 | Magnetic resonance elastography imaging for the evaluation of MVI of T1 staging renal clear cell carcinoma preoperatively
Hanmei Zhang1, Daguang Wen1, Jie Chen1, Yi Wang1, Yuntian Chen1, Yige Bao2, and Bin Song1
1Radiology, Sichuan University, West China Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, 2Urology, Sichuan University, West China Hospital, Chengdu,Sichuan, China
This prospective study evaluated the performance of 3D magnetic resonance elastography imaging for predicting microvascular invasion(MVI) of T1 staging renal clear cell carcinoma. 80 consecutive patients were enrolled. The mean MRE stiffness value has significant difference between the tumor with MVI (5.4±0.6 Kpa) or without MVI (4.1±0.3 Kpa) (p<0.05). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, AUC of stiffness value to predict MVI were 100%, 75%, 63%, 96%, 0.87, respectively. 3D MRE imaging has promising diagnostic performance for T1 staging renal clear cell carcinoma MVI.
|
||
4282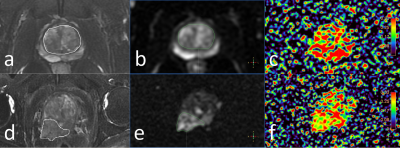 |
5 | Application of ultra-high b value diffusion weighted aquaporin imaging for discrimination of prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia Video Not Available
Yunsong Liu1, Lihua Chen1, Jiazheng Wang2, Liangjie Lin2, Zhigang Wu2, and Ailian Liu1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
In this study, the ADC value (AQP-ADC) fitted by ultra-high b value diffusion weighted images (UHB-DWI) was used for discrimination between prostate cancer (PCa) from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The AQP-ADC value was observed to significantly higher in PCa than in BPH. And AQP-ADC may serve as a potential biomarker for differentiation between benign and malignant prostate lesions.
|
||
4283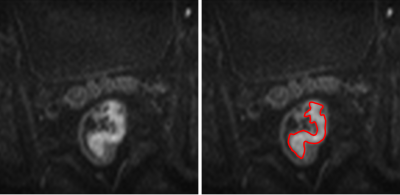 |
6 | Can whole-tumor histogram based on zoomed EPI diffusion-weighted imaging help predict perineural invasion in rectal cancer? Video Not Available
Lijuan Wan1, Hongmei Zhang2, and Qinglei Shi3
1Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China
Perineural invasion (PNI) is a strong prognostic indicator in rectal cancer. Timely and accurate assessment of PNI status can assist in making individualized treatment plans. Histogram features can reflect the heterogeneity of tumors with better reproducibility than higher-order texture features. The zoomed DWI can provide a higher-spatial-resolution with fewer artifacts and distortions. We aim to evaluate the ability of histogram parameters derived from zoomed DWI to identify patients with positive PNI. The results demonstrated that histogram parameters could be used for assessing PNI status in RC, and skewness achieved the highest AUC.
|
||
4284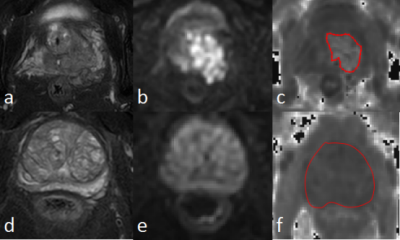 |
7 | Diffusion-kurtosis based texture features for differential diagnosis between prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia Video Not Available
Yunsong Liu1, Ailian Liu1, Lihua Chen1, Jiazheng Wang2, Liangjie Lin2, and Xiaoxiao Zhang2
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
The differential diagnosis between prostate cancer (PCa) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) remains challenging due to their overlapping atypical clinical symptoms and MRI features. This study aims to explore the performance of mean kurtosis (MK) based texture features in differentiation between PCa and BPH. Results show that the MK texture features can help distinguish PCa and BPH. The 90Percentile MK value show the best diagnostic performance (AUC: 0.93; sensitivity: 88%; specificity: 100%).
|
||
4285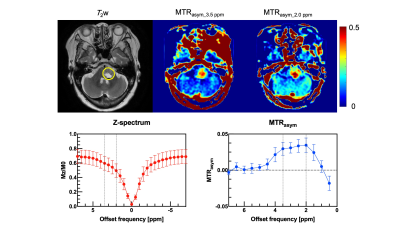 |
8 | Evaluation of brain tumor and surrounding tissue activity using multi-pool CEST imaging on 3 Tesla scanner
Yuki Kanazawa1, Masafum Harada1, Mitsuharu Miyoshi2, and Yuki Matsumoto1
1Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 2Global MR Applications and Workow, GE Healthcare Japan, Hino, Japan
We evaluated amide- and amine-CEST signal of brain tumors on a 3 Tesla MR scanner with conventional Z-spectrum and MTRasym analysis. Subjects were eight patients with brain tumor. There were significant differences between mean MTRasym values at 0.2 and 0.35 ppm offset frequencies (P < 0.05). Our findings was able to evaluate brain tumor characteristics with multi-pool analysis on the positive side of offset frequency on a 3 Tesla MRI scanner.
|
||
4286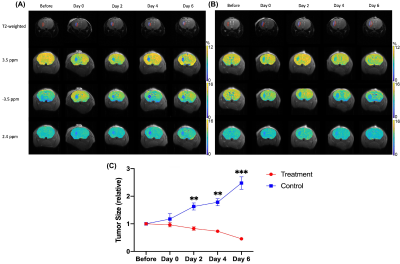 |
9 | Developing CEST-detectable liposomal hydrogel for monitoring local brain tumor treatment
Se Weon Park1,2, Joseph H.C Lai1, Xiongqi Han3, Jianpan Huang1, Peng Xiao1, and Kannie W.Y. Chan1,4,5
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2Hong Kong Centre for Cerebro-Cardiovascular Health Engineering (COCHE), Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 3SiBionics, Shenzhen, China, 4Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 5City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen, China
Glioblastoma is a malignant form of brain tumors, which has a high recurrence even with combined treatments. Here, we developed anti-cancer drugs loaded liposomal hydrogels for sustainable drug release to treat brain tumors locally under MRI guidance. These anti-cancer drugs are CEST-detectable. We observed a continuous decrease in tumor size and CEST contrast at 3.5 and -3.5 ppm compared to control group, where drug-free liposomal hydrogel was injected. The therapeutic efficacy of local drug delivery using liposomal hydrogel was evidenced and can be monitored using CEST multiple-contrast approach. This could serve a robust theranostic application for local brain tumor treatment.
|
||
4287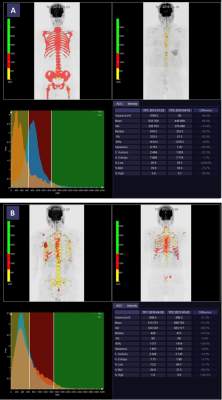 |
10 | Whole-Body Tumor Load ADC Histogram Analysis for Therapy Response Prediction and Evaluation for Multiple Myeloma Video Not Available
Yuhan Gao1, Qin Wang1, Lu Zhang1, Shuang Xia2, Jinxia Zhu3, Rober Grimm4, Alto Stemmer4, Shuo Li1, Dong Liu1, Huadan Xue1, and Zhengyu Jin1
1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
This study aimed to explore the value of histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps for whole-body tumor load(WBTL) in predicting and evaluating the treatment response based on International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) 2016 consensus criteria in patients with multiple myeloma (MM).Histogram analysis of ADC maps extracted eight parameters: mean, median, standard-deviation, entropy, skewness, kurtosis, ADC_5%, and ADC_95%. Seven parameters at baseline were significantly associated with therapy response. Three parameters in treatment percentage change were significantly associated with therapy response. ADC histogram analysis may be considered as an adjunct tool to the MM therapy response evaluation and prediction.
|
||
4288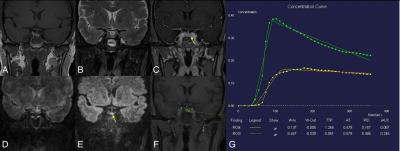 |
11 | Golden-angle radial sparse parallel (GRASP) and simultaneous multi-slice RESOLVE DWI MRI in evaluation of postoperative pituitary adenomas
Zecheng Chen1, Kai Niu2, Xinrui Liu1, Simin Yang3, Yueluan Jiang4, Zechen Yu5, Hongchao Wang3, Huimao Zhang3, and Chunjie Guo3
1Neurosurgery, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 3Radiology, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 4Siemens Healthineers ., Beijing, China, 5Siemens Healthineers Digital Technology., Harbin, China
MRI is a primary imaging method for the evaluation of pituitary adenomas (PAs). However, it is challenging to identify the postoperative residual tumors using traditional techniques. A recent approach Golden-angle Radial Sparse Parallel (GRASP)-DCE, and the novel simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) readout-segmented EPI technique (RESOLVE) procedures were performed to assess the residual tumors of postoperative PAs. And the residual tumors were observed as slow enhancement in GRASP images while manifesting as hyperintense in SMS-RESOLVE images. Thus, both of them are promising techniques for the evaluation of postoperative residual PAs.
|
||
4289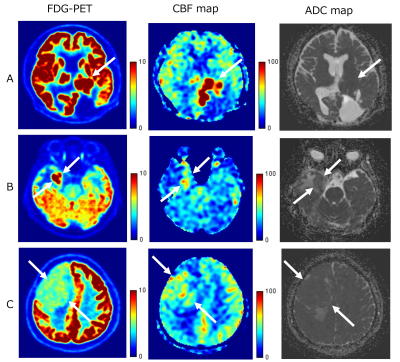 |
12 | Correlation between SUV, tumor blood flow and ADC of extra-axial tumors on FDG-PET/MRI Video Permission Withheld
Sayo Otani1, Yasutaka Fushimi1, Satoshi Nakajima1, Akihiko Sakata1, Sachi Okuchi1, Takuya Hinoda1, Azusa Sakurama1, Krishna Pandu Wicaksono1, Hiroshi Tagawa1, Yang Wang1, Satoshi Ikeda1, and Yuji Nakamoto1
1Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan
PET/MRI shows high accuracy of fused images by simultaneously acquired PET and MR images. We can obtain spatially and temporally consistent information on metabolic and anatomic information from PET/MRI. We evaluated each quantitative value in 12 patients with extra-axial tumor in this study. We manually placed the same regions of interest (ROIs) of the tumor on FDG-PET, CBF map and ADC map, and performed ROI analysis of SUV, TBF (tumor blood flow) and ADC. There were correlations between SUV and TBF, and between SUV and ADC among patients with TBF less than 110 ml/100g/min.
|
||
4290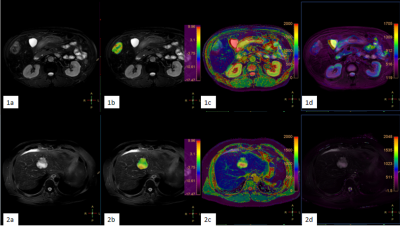 |
13 | Improved differentiation of Primaray liver cancer by combination of Amide Transfer weighted imaging(APTw) and T2 mapping Video Not Available
Tao Lin1, Jiazheng Wang2, Zhigang Wu2, Lihua Chen 1, Qingwei Song1, Renwang Pu1, Ying Zhao1, Xue Ren1, Qihao Xu1, and Ailian Liu1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) are the most common types of primary liver cancer, which differ greatly in terms of pathogenesis, biological behavior, histological morphology, treatment and prognosis. The accurate diagnosis of HCC and ICC is important for treatment options. In this retrospective study, we revealed that APTw combined with T2 mapping could improve the differential diagnosis of HCC and ICC. Results showed that APTw combined with T2 mapping had higher efficacy (AUC:0.910). Further analysis also implied moderate correlations between APTw and T2 mapping.
|
||
4291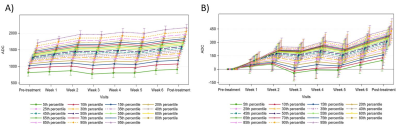 |
14 | Changes in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) in Serial Weekly MRI During Radiotherapy in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer (PREDICT-HN study) Video Not Available
Sweet Ping Ng1, Carlos Cardenas2, Houda Bahig3, JiHong Wang4, Jason Johnson4, Ying Yuan4, Amy Moreno4, and Clifton Fuller4
1Austin Health, Heidelberg, Australia, 2University of Birmingham Alabama, Birmingham, AL, United States, 3Centre hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 4MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, United States
We evaluated the weekly ADC kinetics of tumour during radiotherapy for head and neck cancer in the PREDICT-HN study. of 41 patients, 36 had intact primary tumours, and 31 patients had nodal disease with 46 nodes assessed. For primary tumours, a steep increase in ADC values from pre-treatment to week 2, and from weeks 5 to post-treatment was observed. For nodes, ADC values increased from pre-treatment to week 4, and then decreased thereafter. A discrepancy in the trajectory of ADC changes between primary and nodal sites suggesting that they exhibit different treatment responses.
|
||
4292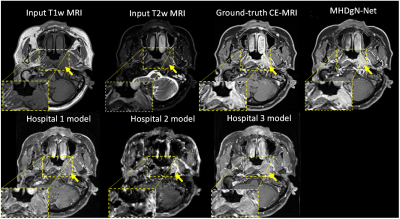 |
15 | Gadolinium-free Contrast-enhanced MRI (GFCE-MRI) Synthesis via Generalizable MHDgN-Net for Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Wen Li1, Saikit Lam1, Haonan Xiao1, Tian Li1, Ge Ren1, Shaohua Zhi1, Xinzhi Teng1, Chenyang Liu1, Jiang Zhang1, Francis Kar-ho Lee2, Kwok-hung Au2, Victor Ho-fun Lee3, Amy Tien Yee Chang4, and Jing Cai1
1The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, HONG KONG, Hong Kong, 2Queen Elizabeth Hospital, HONG KONG, Hong Kong, 3The University of Hong Kong, HONG KONG, Hong Kong, 4Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, HONG KONG, Hong Kong
We have developed and validated a MHDgN-Net for gadolinium-free contrast-enhanced MRI (GFCE-MRI) synthesis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). The developed MHDgN-Net was featured with high generalizability. We first modelled the MHDgN-Net using three hospital datasets to improve the diversity of training samples. Then, the external hospital data was matched to the distribution of training dataset by EDM. Compared to traditional models, the proposed MHDgN-Net can accurately enhance tumor and significantly improve the quality of GFCE-MRI when applying to external hospital data. This technique holds great potential in providing a generalizable gadolinium-free tumor enhancement alternative on data from other hospitals.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.