Online Gather.town Pitches
Genitourinary & Women's Imaging II
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
3701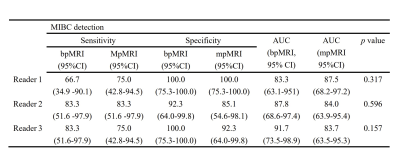 |
1 | Simplified VI-RADS based on biparametric MRI for the detection of muscle-invasive bladder cancer Video Permission Withheld
Lei Ye1, Xiaoyong Zhang2, Yuntian Chen1, and Hui Xu1
1Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, 2Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
There are different opinions about the importance of dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) in VI-RADS among patients with bladder cancer (BCa), for the limited contribution for identifying muscle invasiveness and gadolinium-related toxicity. This study head-to-head compared the diagnostic accuracy between simplified VI-RADS excluding DCE sequence and conventional VI-RADS including DCE sequence. Our results showed that the diagnostic performance was comparable between these two MRI protocols.
|
||
3702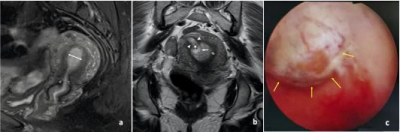 |
2 | MRI in the differential diagnosis of angular pregnancy and interstitial pregnancy during the first trimester
Wenjuan Liu1, Weili Xie2,3, and Zhenchang Wang1
1Beijing Friendship Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2School of Clinical Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining, China, 3Jining No. 1 Peoples’ Hospital, Jining, China
The study evaluated the accuracy of MRI in the diagnosis of 22 angular pregnancy cases and 37 interstitial pregnancy cases retrospectively during the first trimester. Two senior obstetrics radiologists reviewed the MR images and analyzed several features. The study found two key features were useful to diagnose angular pregnancy, namely, “medial free edge” and “medial free edge plus above-cutoff endometrial thickness”. One key feature to diagnose interstitial pregnancy was “intact lateral junctional zone”. MRI is a novel imaging approach to make the precise differential diagnosis of angular pregnancy and interstitial pregnancy.
|
||
3703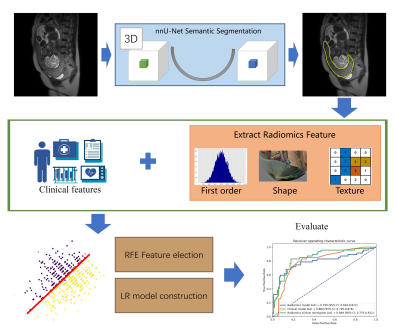 |
3 | An automatic pipeline combining deep learning and radiomics to predict placenta accrete spectrum disorders from T2W MR images
Haijie Wang1, Yida Wang1, Lei Ling2, Jue Wang3, Xiaotian Li3, Hao Zhu3, He Zhang2, and Guang Yang1
1Shanghai key lab of magnetic resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2Department of Radiology, Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 3Department of Obstetrics, Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Placenta accrete spectrum (PAS) disorders may lead to common complication like catastrophic perinatal hemorrhage. T2W is the most useful MRI sequence for identification of PAS disorders, but the diagnosis of PAS is often difficult and highly subjective. To overcome this problem, we automatically segmented the placental regions by nnU-Net and used radiomics features extracted from the segmented region to build a radiomics-clinical model for identification of placenta invasion. 512 pregnant women were enrolled in this study. Our segmentation model achieved a mean Dice coefficient of 0.890 and the classification model achieved an AUC of 0.849 on the independent validation cohort.
|
||
3704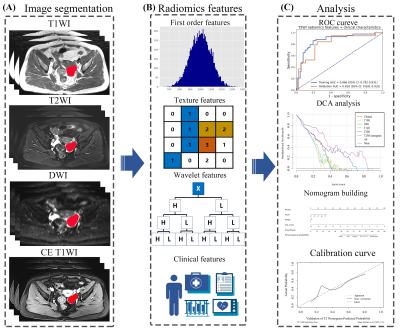 |
4 | MR-based radiomics-clinical nomogram in epithelial ovarian tumor prognosis prediction: a comparison of effectiveness of multiple MR sequences
Haijie Wang1, Yida Wang1, Tianping Wang2, Xuefen Liu2, Lei Ling2, Guofu Zhang2, He Zhang2, and Guang Yang1
1Shanghai key lab of magnetic resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2Department of Radiology, Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
To compare radiomics-clinical nomograms based on various sequence MR images in predicting epithelial ovarian tumor prognosis status. A total of 186 patients with epithelial ovarian cancer pathologically proven by invasive procedure were enrolled. The single-sequence and paired-sequence radiomics signatures were constructed for T2W, T1W, DWI and CE-T1W images. And the T2W radiomic-clinical nomogram achieved a favorable prediction performance in the validation cohort with an AUC of 0.818. And it was also found the T2W radiomic-clinical nomogram was better than other models with a greater clinical net benefit.
|
||
3705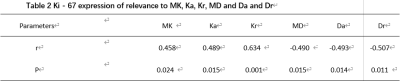 |
5 | Correlation between Ki67 expression and DKI in ovarian cancer
Xianglin Guo1, Qinglin Song1, Ye Li1, Yulin Chen1, and Ailian Liu1,2
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Dalian Engineering Research Center for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging, Dalian, China
Symptoms of ovarian cancer are concealed, it is difficult to diagnose early, and the mortality rate is very high. DKI imaging can sensitively detect microstructure changes in tumor tissue and help preoperative assessment of Ki67 expression. This paper aims to study the correlation between Ki67 expression and DKI in ovarian cancer. The results show that the MK, Ka, Kr, MD, Da and Dr values in the DKI parameters have obvious correlation with Ki-67 expressions, and that the MK, Ka, and Kr values in DKI parameters were positive correlation with Ki-67 expression levels, and the difference was statistically significant.
|
||
3706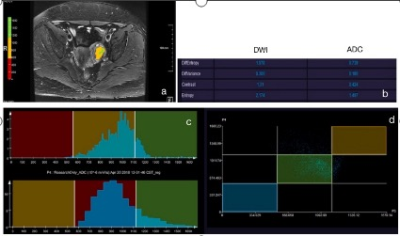 |
6 | Texture analysis of multiparametric MRI in the diagnosis of the ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors (SCSTs)
hui zhang1,2 and hui zhang1
1Beijing Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Nanjing Meishan Hospital, Nanjing, China
The accurate diagnosis of malignant SCSTs is still a challenge. We retrospectively analyzed the MRI texture features of 69 cases, and used t-test, one-way ANOVA, the Mann-Whitney U-test and ROC curve to evaluate these parameters. The results showed that the derived texture parameters may be valuable tool in predicting malignant SCSTs.
|
||
3707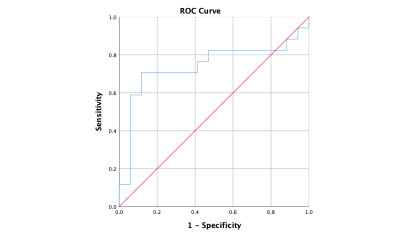 |
7 | Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) DiffusionWeighted imaging in quantitatively evaluation of WT-1 expression in Ovarian Cancer Video Not Available
Jiajun Guo1, Ye Li1, Ailian Liu1, and Yulin Chen1
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Dalian, China
Ovarian cancer (OC) behaves more aggressively and has a worse prognosis than any other cancer involving the female genital tract. WT-1 was significantly upregulated in human OC tissues and closely associated with OC type, grade and FIGO stage. This worked aimed at exploring the value of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) quantitative parameters for diagnosis of WT-1 positive OC. The results showed that D value provided a promising performance (AUC = 0.740, sensitivity= 88.2%, specificity= 70.6 %) in quantitatively evaluating WT-1 positive OC.
|
||
3708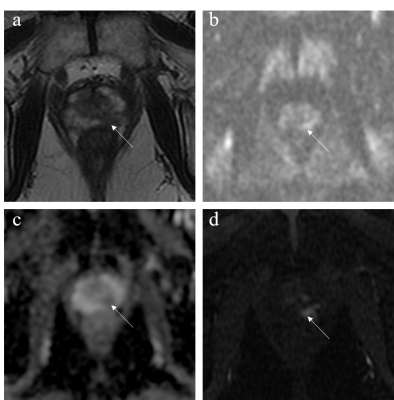 |
8 | Comparison between Biparametric and Multiparametric MRI for Detection of Prostate Cancer in the Peripheral Zone using PI-RADS Version 2.1
Jiahui Zhang1, Lili Xu2, Gumuyang Zhang2, Hao Sun2, and Zhengyu Jin2
1Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China This study aimed to compare and analyse the diagnostic value of PI-RADS v2.1 when used with bpMRI versus mpMRI, DWI versus T2WI to detect peripheral-zone prostate cancer (pzPCa) and clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa). The diagnostic efficiencies of mpMRI and bpMRI as well as DWI and T2WI in pzPCa and csPCa were compared using a PI-RADS score of ≥4 as the positive threshold and pathologic results as the gold standards. MpMRI and bpMRI as well as DWI and T2WI using PI-RADS v2.1 exhibited similar diagnostic efficiency in pzPCa and csPCa, whereas bpMRI demonstrated increased diagnostic specificity compared with mpMRI. |
||
3709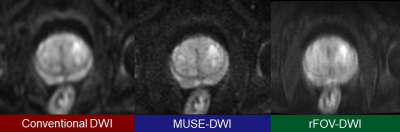 |
9 | Comparison of Multiplexed Sensitivity Encoding and Reduced Field-of-view Technique for Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Prostate
Atsushi Nakamoto1, Hiromitsu Onishi1, Takahiro Tsuboyama1, Takashi Ota1, Hideyuki Fukui1, Kazuya Ogawa1, Keigo Yano1, Kengo Kiso1, Toru Honda1, Mitsuaki Tatsumi1, and Noriyuki Tomiyama1
1Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Suita, Japan
The image quality and diagnostic performance of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) using multiplexed sensitivity encoding (MUSE) and DWI using reduced field-of-view (rFOV) technique in detecting prostate cancer were compared. Visual scores of MUSE-DWI regarding the visibility of prostate anatomy and overall image quality were significantly higher than those of rFOV-DWI. The diagnostic performance in detecting prostate cancer was not significantly different between MUSE-DWI and rFOV-DWI. MUSE yielded high quality DWI without reducing FOV and is expected to be more useful than rFOV technique for evaluation of the prostate including lymph node metastasis.
|
||
3710 |
10 | CEST vs. DWI: Capability for Distinguishing Malignant from Benign Prostatic Areas in Patients with Prostatic Cancer Video Permission Withheld
Takahiro Ueda1, Yoshiharu Ohno1,2, Kaori Yamamoto3, Masao Yui3, Masato Ikedo3, Saki Takeda4, Akiyoshi Iwase4, Yuka Oshima1, Nayu Hamabuchi1, Satomu Hanamatsu1, Yuki Obama1, Hiroyuki Nagata1, Hirotaka Ikeda1, Kazuhiro Murayama2,
and Hiroshi Toyama1
1Radiology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 2Joint Research Laboratory of Advanced Medical Imaging, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan, 4Radiology, Fujita Health University Hospital, Toyoake, Japan
We hypothesize that CEST is at least as valuable as DWI and may have a potential to improve differentiation capability of malignant from benign prostatic areas as one of the combined quantitative discriminators on prostatic MR imaging. The purpose of this study was to compare the capability for distinguishing malignant from benign areas among CEST, DWIs at standard and super high b values and combined quantitative discriminator in suspected prostatic cancer patients.
|
||
3711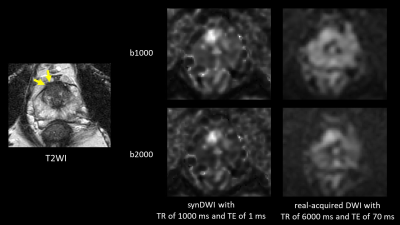 |
11 | Feasibility of synthetic short TR and short TE DWI in prostate cancer
Yu Ueda1, Tsutomu Tamada2, Hiroyasu Sanai2, Kazunori Moriya2, Ayumu Kido2, Makoto Obara1, Tetsuo Ogino1, and Marc Van Cauteren3
1Philips Japan, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Radiology, Kawasaki Medical School, Okayama, Japan, 3Philips Healthcare, Asia Pacific, Tokyo, Japan
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with shorter echo time (TE) could be exploited to improve diffusion contrast by minimizing T2 shine-through due to longer T2 in normal prostate. However, clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner has limitation in shortening TE in conventional DWI. It would be beneficial to generate additional DWI with short TE from DWIs with two different TE, in addition to short repetition time (TR) which improvement of diffusion contrast has been reported. The synthetic DWI with shorter TR (1000 ms) and TE (1 ms) tended to show better diffusion contrast than real-acquired DWI with conventional TR and TE.
|
||
3712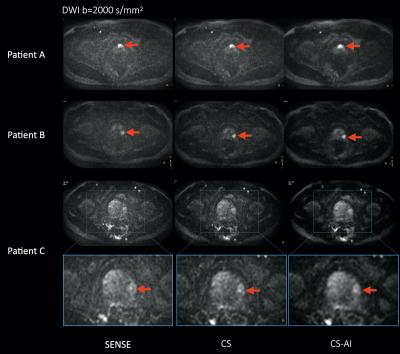 |
12 | SNR enhancement in rapid high b-value prostate single-shot DW-EPI utilizing deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE reconstruction
Masami Yoneyama1, Takashige Yoshida2, Jihun Kwon1, Yasutomo Katsumata3, Shuo Zhang4, and Marc Van Cauteren3
1Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Tokyo Metropolitan Police Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands, 4Philips GmbH Market DACH, Hamburg, Germany
DWI is a key component of the prostate MRI examination, but current prostate DWI images acquired with high b-value DWI using SENSE often suffer from increased noise artifacts. We propose to utilize a deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE (CS-AI) for reducing the noise artifacts in single-shot DW-EPI images. CS-AI DWI clearly reduces noise-like artifacts, boosts the overall SNR and significantly improves the accuracy and robustness of ADC values in rapid high b-value prostate DWI compared with conventional SENSE- and CS-DW-EPI, without any penalty for scan parameters.
|
||
3713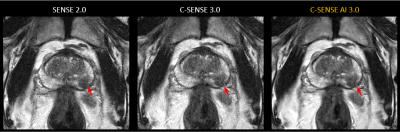 |
13 | Accelerated high-resolution T2-weighted imaging for prostate with a deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE reconstruction
Jihun Kwon1, Takashige Yoshida2, Masami Yoneyama1, and Marc Van Cauteren3
1Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Tokyo Metropolitan Police Hospital, Nakano, Japan, 3Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands
T2-weighted (T2W) imaging is used to depict prostate anatomy. However, T2W imaging with high spatial resolution, which is required by PI-RADSv2, is not always performed because of the long scan time. In this study, we investigated the use of Compressed SENSE AI (CS-AI) reconstruction to accelerate high-resolution T2W imaging of the prostate. The image quality of CS-AI reconstruction, conventional Compressed-SENSE (C-SENSE), and SENSE were compared qualitatively and quantitatively. Clinical cases demonstrated a significant noise reduction in accelerated CS-AI. CS-AI also showed a significantly higher contrast-to-noise ratio in CS-AI compared to SENSE and C-SENSE.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.