Online Gather.town Pitches
Body: GU & Breast I
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
3656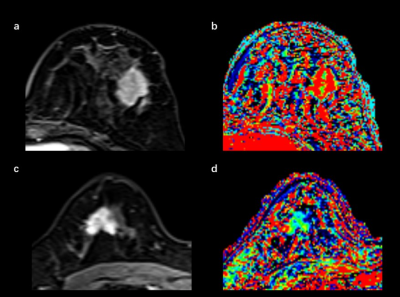 |
1 | Quantitative CAIPIRINHA-Dixon-TWIST-VIBE parameters correlate with molecular subtypes of invasive ductal carcinoma Video Not Available
Tianwen Xie1, Tingting Jiang1, Caixia Fu2, Marcel Dominik Nickel3, Weijun Peng1, and Yajia Gu1
1Radiology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China, 2MR Applications Development, Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 3MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
In this study, we analyzed the relationship between CAIPIRINHA-Dixon-TWIST-VIBE (CDTV)-derived DCE parameters and clinicopathological factors, including molecular subtypes of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). Our results showed that the values of semi-quantitative parameters were similar for various prognostic factors and molecular subtypes of IDC. However, the values of quantitative inline pharmacokinetic kinetic parameters, kep_minimum and kep_difference, were significantly different for the luminal A and HER2-positive subtypes. AUC value for accurately distinguishing luminal A and HER2-positive subtypes based on combined kep_minimum and kep_difference values was 0.820. Therefore, our study demonstrates that CDTV-derived quantitative parameters are associated with molecular subtypes of IDC.
|
||
3657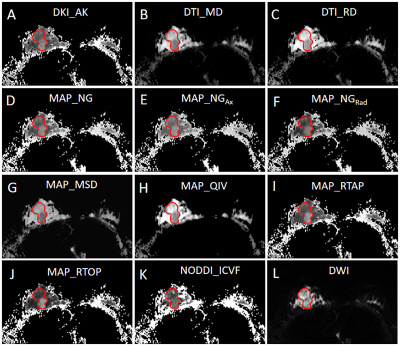 |
2 | Applying Multiple Diffusion Models to Predict HER-2 Status in Patients with Breast Cancer: a preliminary study using Diffusion Spectrum Imaging Video Permission Withheld
Chunping Mao1, Mengzhu Wang2, Xu Yan2, Guang Yang3, Xiang Zhang1, and Jun Shen1
1Department of Radiology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Guangzhou, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, School of Physics and Electronic Science, Shanghai, China
This study explored the feasibility of applying multiple diffusion models based on the same diffusion spectrum imaging (DSI) data into preoperative prediction of HER-2 status in patients with breast cancer (BC). The results showed that some diffusion parameters can discriminate HER-2 positive BC patients, but apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) based on conventional mono-exponential model can not. This study suggests that the simultaneously application of multiple diffusion models from DSI data is feasible for diagnosis of patients with BC, which has certain clinical value of preoperative prediction of HER-2 status and is worthy of further research.
|
||
3658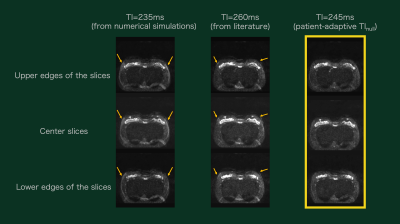 |
3 | Breast DWIBS with patient-adaptive STIR inversion delay (TI) optimization utilizing dynamic TI scout scan (DynTI)
Mana Kato1, Kazuo Kodaira1, Yasuhiro Goto1, Yasutomo Katsumata2, Mai Nishihara2, Masami Yoneyama2, Isao Shiina1, Yutaka Hamatani1, Takumi Ogawa1, Michinobu Nagao3, and Shuji Sakai3
1Radiological Services, Tokyo Woman's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 3Diagnostic imaging & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Woman's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
DWI provides beneficial information that has high diagnostic potential of breast lesions. DWIBS can suppresses the background signals including fat tissues effectively, but there are often insufficient fat suppression cases because of non-adaptation TInull were used. In this study we demonstrated that the actual TI for nulling breast fat in DWI is patient-specific and dynamic TI scout scan (DynTI) is useful to explore patient-adaptive TI that can provide more beneficial to increase the robustness of breast DWIBS.
|
||
3659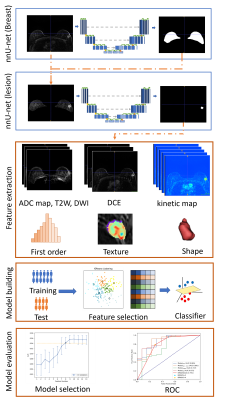 |
4 | Combine nnU-Net and radiomics for automated classification of breast lesion using mp-MRI
Jing Zhang1, Chenao Zhan2, Xu Yan3, Yang Song3, Yihao Guo4, Tao Ai2, and Guang Yang1
1East China Normal University, Shanghai key lab of magnetic resonance, shanghai, China, 2Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, shanghai, China, 4Siemens Healthcare, MR Collaboration, Guangzhou, China
Multi-parametric MRI (mp-MRI) radiomics can distinguish breast mass effectively, but requires breast lesion segmentation first, which is subjective and laborious for radiologists. To overcome this problem, we combined nnUnet and radiomics analysis as an automatic model for breast lesion classification. In the test cohort, the breast lesion segmentation model achieved mean dice of 0.835, and the classification model achieved an AUC of 0.891. We found that the nnU-Net can delineatey lesions accurately based on dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE, TWIST-VIBEs)), and mp-MRI radiomics features extracted from the auto-segmented lesions can be used to classfy breast lesions accurately.
|
||
3660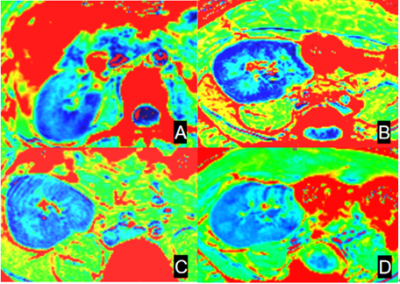 |
5 | Combination of Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI to Evaluate Chronic Kidney Disease in Renal Transplants Video Not Available
Pan Wang1, Min Li1, Xiangnan Li1, Jiyang Zhang1, Xin Zheng2, Chen Zhang3, Stemmer Alto4, and Tao Jiang1
1radiology department, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Urinary Surgery, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Beijing, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4] MR Application Development, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany
Kidney transplantation is currently considered as the preferred treatment for end-stage renal disease, this study aims to explore the performance of BOLD-fMRI and IVIM of renal transplants kidney patients with CKD. The results showed the D value in renal cortical could well identify and distinguish normal kidney and diseased kidney. The R2* value could indirectly reflect deoxyhemoglobin to assess the degree of renal function impairment. BOLD-fMRI and IVIM can provide a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the functional information of the chronic kidney metabolism.
|
||
3661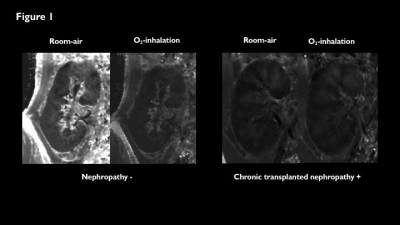 |
6 | O2-inhalation T2* BOLD and dual-VENC 4D flow MRI: hypoxic evaluation of pediatric transplanted kidneys
Michinobu Nagao1, Taro Ando1, Yasuhiro Goto1, Isao Shiina1, Kazuo Kodaira1, Masami Yoneyama2, Kenichiro Miura1, Motoshi Hattori1, and Shuji Sakai1
1Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan
For pediatric patients with end-stage renal failure, kidney transplantation is the only treatment that can provide growth and long-term survival. Although rejection is the common cause of renal dysfunction, there are other causes of chronic transplant nephropathy, in which the transplanted kidney develops fibrosis. Hypoxia is considered as possible causes of this order. We used O2-inhalation T2*-BOLD and dual-VENC 4D flow MRI to assess hypoxia in pediatric transplanted kidneys. In patients with chronic transplant nephropathy, hypoxia was found in the renal medulla and small vessel’s flow was reduced. This analysis is an effective means of monitoring hypoxia in transplanted kidneys.
|
||
3662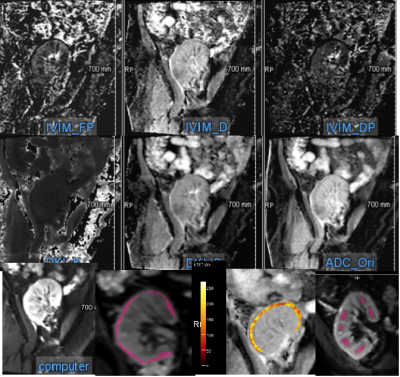 |
7 | ASL and multi-b-value DWI for longitudinal renal function evaluation of renal allografts Video Permission Withheld
lihua chen1, jianmin cui2, jinxia zhu3, and wen shen2
1Tianjin First Center Hospital, tianjin, China, 2Tianjin First Center Hospital, Tianjin, China, 3MR collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Beijing, China
Early evaluation and treatment of delayed graft function due to renal cold ischemia reperfusion injury has important clinical significance for prolonging donor kidney preservation times and improving the survival rates of allografts. Arterial spin labeling (ASL) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) have been accepted for microstructure change evaluations of renal function. In this study, transplant recipients were collected for fMRI examination at 14d, 30d and 90d after transplantation. The parameters were compared to evaluate renal microstructure changes among different time points. The results showed ASL and DWI can reflect longitudinal changes of diffusion and perfusion properties for allografts after kidney transplantation .
|
||
3663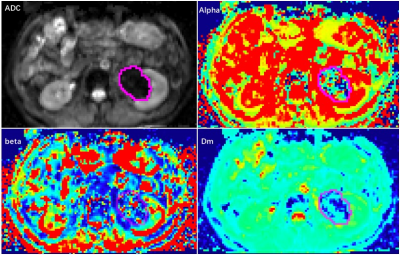 |
8 | Differentiating Benign from Malignant Renal Cystic Masses Using Continuous-time Random-walk diffusion model
Xiaojun Yang1, Xiaohui Duan1, Mengzhu Wang2, Xu Yan2, Lingjie Yang1, Weike Zeng1, Wei Jiang1, Yaojun Hu1, Guang Yang3, and Jun Shen1
1Department of Radiology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China, 22MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Guangzhou, China, 3Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
This study evaluated whether continuous-time random-walk (CTRW) diffusion model could be used to distinguish benign from malignant renal tumors, as well as compared the diagnostic effectiveness between the diffusion parameters of CTRW and apparent dispersion coefficient (ADC). The results demonstrated that CTRW diffusion model as a new noninvasive MR technique, was able to differentiate benign from malignant renal masses in vivo, and further improve the diagnostic efficiency of renal malignant masses compared with conventional diffusion imaging.
|
||
3664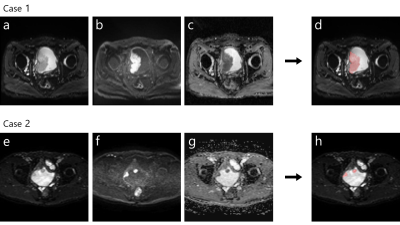 |
9 | Automatic segmentation of bladder cancer on MRI using a convolutional neural network and reproducibility of radiomics features.
Yusaku Moribata1, Yasuhisa Kurata1, Mizuho Nishio1, Aki Kido1, Satoshi Otani1, Yuki Himoto1, Naoko Nishio2, Akihiro Furuta2, Kimihiko Masui3, Takashi Kobayashi3, and Yuji Nakamoto1
1Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, 2Department of Radiology, Japanese Red Cross Osaka Hospital, Osaka, Japan, 3Department of Urology, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan
This multi-center retrospective study performed automatic segmentation of bladder cancer (BC) on MRI with a convolutional neural network and evaluated the reproducibility of radiomics features. Of the total 170 patients, 140 were used to train our U-net model and 30 were used to evaluate the segmentation performance of the model. Our U-net model achieved a median Dice similarity coefficient of 0.811 in the test dataset and most of the automatically extracted radiomics features showed high reproducibility (median intraclass correlation coefficient: 0.83-0.86). Our model would lead to efficient medical image analysis of BC using the radiomics approach.
|
||
3665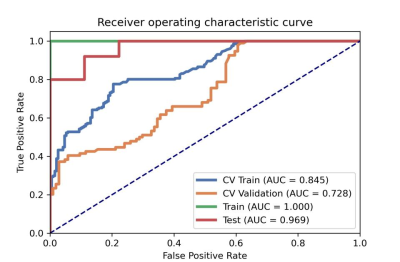 |
10 | Optimize and Evaluate the Efficacy of Pairwise AE Model in Predicting the Prognosis of Concurrent Chemo-radiotherapy for Cervical Cancer
Miao Liu1, Qi Wang1, Gaofeng Shi1, Li Yang1, and Qinglei Shi2
1The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shi Jiazhuang, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing , Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China
To overcome the small data set problems in clinical situations, this paper proposed a pairwise auto encoder (AE) model, which can learn more relationship information among samples to enhance the generalization ability, in predicting the prognosis of concurrent chemo-radiotherapy for LACC and demonstrated potential in this field.
|
||
3666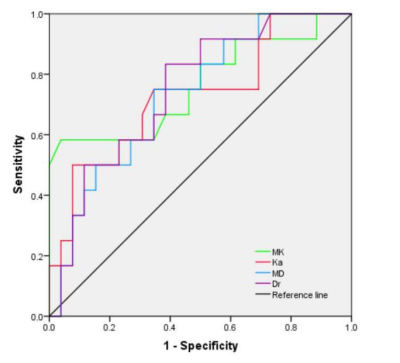 |
11 | Diffusion kurtosis imaging with multiple quantitative parameters for predicting microsatellite instability status in endometrial carcinoma Video Not Available
Wan Dong1, Shifeng Tian1, Lihua Chen2, and Ailian Liu2
1Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Immunohistochemistry is considered the most common method to determine the MSI status of EC, but this method is usually performed after surgery. Here, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) with multiple quantitative parameters was used to predict microsatellite instability (MSI) status of endometrial carcinoma (EC). Results showed that there were good efficiency of DKI to distinguish MSI status of EC (The AUC of MK, Ka, MD, and Dr values was 0.763,0.729,0.731, 0.748, respectively).
|
||
3667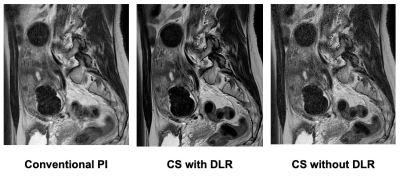 |
12 | Compressed Sensing and Deep Learning Reconstruction: Efficacy for Women’s Pelvic MRI at 1.5 T MR System in Routine Clinical Practice
Takahiro Ueda1, Yoshiharu Ohno1, Kaori Yamamoto2, Natsuka Yazawa2, Ikki Tozawa3, Masayuki Sato3, Motohiro Katagiri3, Masato Ikedo2, Masao Yui2, Hiroyuki Nagata1, Kazuhiro Murayama4, and Hiroshi Toyama1
1Radiology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 2Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan, 3Radiology, Fujita Health University Bantane Hospital, Nagoya, Japan, 4Joint Research Laboratory of Advanced Medical Imaging, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan
We hypothesized that compressed sensing (CS) with deep learning reconstruction (DLR) can improve image quality and shorten examination time on not only T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), but also T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) on women’s pelvic MRI, when compared with PI at 1.5T MR system. The purpose of this study was to compare the utility of CS and DLR for shortening examination time and improving image quality on MRI at 1.5T system in patients with various female pelvic diseases.
|
||
3668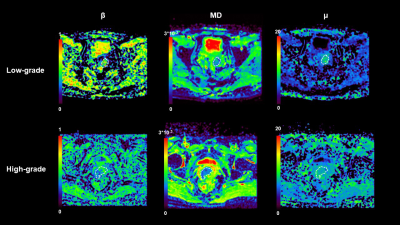 |
13 | Cervical carcinoma: Evaluation using diffusion MRI with a fractional order calculus model and its correlation with histopathologic findings Video Not Available
Hui Liu1, Liyun Zheng2, Dongmei Wu3, Yongming Dai2, and Gaofeng Shi1
1Department of Radiology, Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, Department of Physics, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China Clear insights into histological subtype and differentiation grade are essential in cervical carcinoma diagnosis and management. In current study, we demonstrated the feasibility of using high-b-value non-Gaussian diffusion model fractional order calculus (FROC) model to differentiate the tumor subtype and grade of cervical carcinoma. FROC model provided a set of novel diffusion parameters and the combination of these parameters contributed to the best diagnostic performance in differentiation between low-grade and high-grade cervical carcinoma. |
||
3669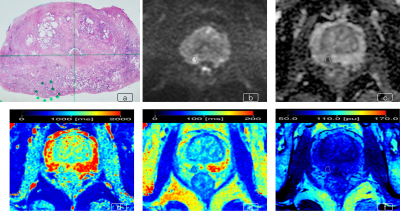 |
14 | Texture Analysis of Synthetic MRI Combined with DWI and ADC for Characterization of Lesions of the Prostate
Hao Cheng1, Pu-Yeh Wu2, Ming Liu3, Chunmei Li1, and Min Chen1
1Department of Radiology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3Department of Urology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
We extracted 104 texture features from relaxation maps of synthetic MRI, DWI and ADC in each of 603 prostate lesions from 297 patients, and compared the diagnostic performance of models based on texture features with mean quantitative values in discriminating PCa from benign lesions and in discriminating csPCa from clinically insignificant lesions. Models of synthetic MRI+DWI+ADC has the highest diagnostic performance in discriminating PCa from SH and noncancerous PZ, and in discriminating csPCa from SH+Gl6 and noncancerous PZ+Gl6. This suggested that texture analysis of synthetic MRI combined with diffusion images can provide better performance in the characterization of prostate lesions.
|
||
3670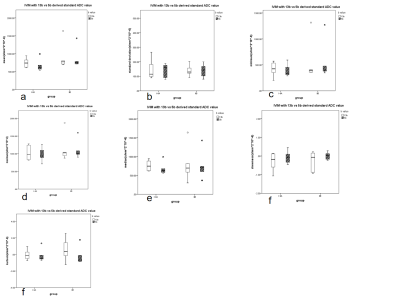 |
15 | A preliminary study of optimized b-value scheme in diagnosis of cervical cancer using reduced field-of-view diffusion weighted imaging Video Not Available
Qian Tang1, Weiyin Vivian Liu2, Qiqi Zhou3, Yu Xing3, Chao Liu3, and Lin Xu3
1Biomedical Engineering College, Hubei University of Medicine, Hubei, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3Department of Radiology,Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Hubei, China
The number of used b values and the b values themselves prolong scan time. Longer scan time deprives patient tolerance, increase more possibility of involuntary movement, and thus limits the application value of IVIM technology. Therefore, we aimed to explore the optimal scheme of rFOV DW imaging with multiple b-values. We found no significant difference of mean ADC, D* and f values but mean D value in our patients between two different b-value schemes, suggesting optimized b-value setting was appropriate in diagnosis of cervical cancer especially for cervical squamous carcinoma.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.