Online Gather.town Pitches
Body: GU
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
4233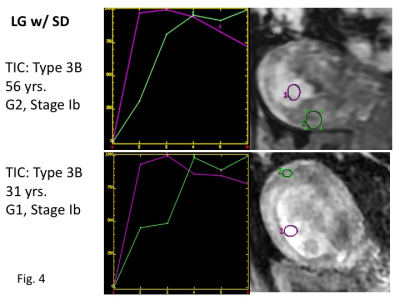 |
1 | Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of endometrial cancer with/without squamous differentiation
Mayumi Takeuchi1, Kenji Matsuzaki2, Yoshimi Bando3, and Masafumi Harada1
1Department of Radiology, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 2Department of Radiological Technology, Tokushima Bunri University, Sanuki-city, Japan, 3Division of Pathology, Tokushima University Hospital, Tokushima, Japan
DCE-MRI of endometrial cancer including 41 low-grade type I cancers without squamous differentiation (LG) and 39 with squamous differentiation (LG_w/SD), and 20 high-grade type II cancers (HG) was retrospectively evaluated. Significant difference in the time-intensity curves was found between LG and HG, and LG and LG_w/SD, whereas no significant difference was seen between HG and LG_w/SD. Curve type 3 (initial signal rise which is steeper than that of the myometrium) was more frequent in HG (60%) and LG_w/SD (77%) than in LG (34%). It should be recognized as a pitfall that HG and LG_w/SD may show similar early strong enhancement.
|
||
4234 |
2 | Reliability Assessment of IVIM Imaging with Different b-values in Evaluating Myometrium Invasion of Endometrial Cancer Video Permission Withheld
Fang Wang1, Ying Liu 1, Chen Zhang2, and Zhaoxiang Ye1
1Department of Radiology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Tianjin, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China
The incidence of Endometrial Carcinoma (EC) has occupied the first place among malignant tumors of the female reproductive system. This study aims to explore the reliability of different b-values of IVIM-MRI in evaluating the myometrial invasion of endometrial cancer using advanced ZOOMit technique. The results showed that group A was the highest, group B was the second, and group C was the lowest in evaluating consistency and repeatability of D value, D* value and fp value. It indicated diagnostic is related to b values combinations of IVIM imaging for EC.
|
||
4235 |
3 | Low Variance ADC Technique Reduces Bias of Kidney ADC Values Video Not Available
Qiao Li1, Xiance Zhao2, and Peng Wu2
1Radiology, Jiangsu Provincial People’s Hospital,Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Low variance (LOVA) ADC technique could compensate for gradient linearity errors, delivering consistent ADC values with high accuracy in large FOV. This work aims to investigate if gradient nonlinearity bias can be corrected in evaluating the ADC values of kidney using LOVA ADC technique. Our results verified that the corrective effect exists in both health volunteers and patients with common kidney diseases. With the corrected ADC, we could better estimate the unbiased difference between marginal lesions and central lesions, to better predict biological behavior of tissues and provide useful information for diagnosis and treatment.
|
||
4236 |
4 | Reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted MRI improving diagnostic value in cervical cancer
Huihui Wang1 and Jianxing Qiu1
1Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
This study was aimed to investigate the image quality and signal intensity (SI) of reduced field-of-view (r-FOV) DWI in patients with cervical cancer in comparison with full FOV (f-FOV) DWI. The subjective image quality, quantitative tumor conspicuity and quantitative normal tissue contrast were better for the r-FOV DWI images than for f-FOV DWI. The tumour diameters measured from the r-FOV DWI images experienced less bias than those from the f-FOV DWI. Those suggest that r-FOV DWI improving diagnostic value in cervical cancer than f-FOV DWI.
|
||
4237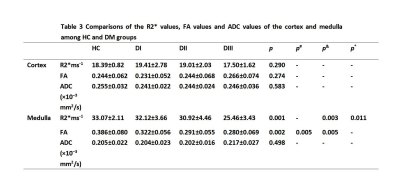 |
5 | Alterations of renal function in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A BOLD and DTI study Video Permission Withheld
Xiaobao Wei1, Runyue Hu2, Xiaoli Zhou2, Dongqing Zha1, Haibo Xu2, Xiaoyan Wu1, and Weiyin Liu3
1Nephrology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2Radiology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Renal damage varies in patients with diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Our study aims to determine the patterns of renal oxygenation changes and microstructural changes by blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-MRI) and diffusion tensor imaging magnetic resonance imaging (DTI-MRI) with the deteriorating kidney function.
|
||
4238 |
6 | A comparative study of non-PTX‑zoom‑DWI with conventional DWI in bladder cancer lesion display and muscular invasion diagnosis
Zhenming Zhang1, Naiming Xue2, Yueluan Jiang3, Lulu Guo2, Mengchao Zhang2, Bo Gao4, Shishun Zhao5, Lin Liu2, and Thomas Benkert6
1China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2Radiology, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China, 4Jilin Metering Center, State Grid Corporation of China, Changchun, China, 5College of Mathematics of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 6MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
The value of non-parallel-transmission zoom-diffusion weighted imaging (non-PTX zoom-DWI) compared with conventional DWI in the diagnosis of bladder cancer muscular invasion is investigated. Results show that non-PTX zoom-DWI improves sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy. Additionally, it has good diagnostic consistency across different readers, and shows better display of bladder than conventional DWI sequence. Non-PTX zoom-DWI may be superior to conventional DWI in predicting the muscular invasion in bladder cancer.
|
||
4239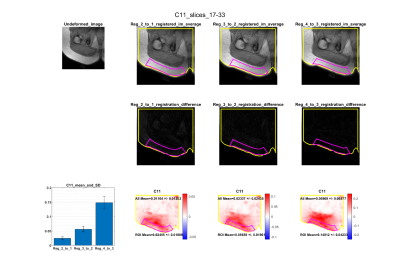 |
7 | Non-rigid registration of DIXON images is an accurate method for calculating physiological strain in adipose tissue
Alice Hatt1, Robert Lloyd1,2, Bart Bolsterlee1,3, and Lynne E. Bilston1,4
1NeuRA, Sydney, Australia, 2School of Medical Sciences, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, 3Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering, University of New South Wales, 2052, Australia, 4Faculty of Medicine, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
To accurately map the large deformation properties of soft tissues, accurate, in-vivo measurements of internal strain are essential. In this study, the Right Cauchy Green strain of adipose tissue was calculated from displacements generated through the non-rigid registration of mDIXON images under increasing compression. The method was validated by synthetically deforming an uncompressed image with compression. Five real-world datasets were acquired of adipose tissue under increasing compression, which resulted in significant increases in the maximum principal strain (one-way ANOVA, p<0.001). The described method provides an accurate quantification of physiological strains in adipose tissue that is essential for mapping strain-varying viscoelasticity.
|
||
4240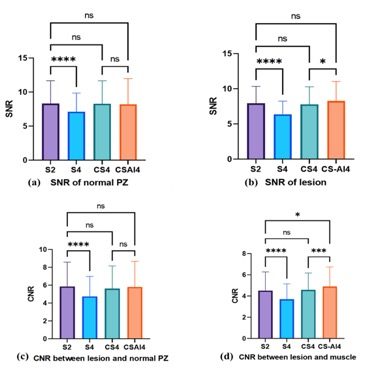 |
8 | The Value of Clinical application of T2WI with CSAI - a deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE reconstruction on prostate cancer Video Permission Withheld
Xiaobo Ding1, Xiang Qiu1, Zhuo Wang1, Ying Qiu1, Xu Zhang1, Yi Zhu2, and Ke Jiang2
1Radiology department, First Hospital of JiLin University, ChangChun, China, 2Philips Healthcare, BeiJing, China
Image quality of T2WI suffers from long scanning time. Compressed SENSE (C-SENSE) allow for Shorter scanning time and Ensuring good image quality,Image quality can be further optimized with CSAI . A total of 20 patients with prostate cancer (PC) underwent MRI including T2WI with SENSE-2(S2)and SENSE-4 (S4)、CS4 and CSAI4. SNR was significantly higher in CSAI4 than CS4 and S4. In comparison CNR between of S4、CS4 and CSAI4 of clinically insignificant PC, only CSAI4 had significant difference. CSAI4 improves the image quality and may contribute to increased diagnostic performance of tumor and clinicians’ confidence in the detection and diagnosis of prostate cancer.
|
||
4241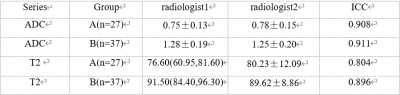 |
9 | The differential value of the combination of DWI and T2 mapping in the identification of prostatic hyperplasia from prostatic cancer.
Xiwei Li1, Lihua Chen1, Qingwei Song1, Peng Sun2, and Ailian Liu1
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
DWI plays an important role in the diagnosis of prostate cancer by detecting water molecules diffusion noninvasively, which reflects the microstructure of tumor tissue. However, only DWI might be limited by low sensitivity and specificity. T2 mapping imaging is a quantitative imaging technology to map the transverse relaxation time of tissues with good repeatability and stability. T2 mapping is also sensitive to tissue components (such as edema, fibrosis) without a contrast agent. This study aims to differentiate prostate cancers from hyperplasia by combining DWI and T2 mapping.
|
||
4242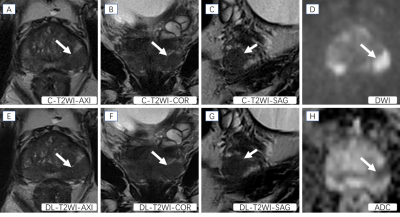 |
10 | T2-weighted imaging with deep learning reconstruction as an alternative method for prostate imaging: a preliminary study
Hao Cheng1, Jinxia Zhu2, Marcel Dominik Nickel3, Ming Liu4, Chunmei Li1, and Min Chen1
1Department of Radiology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Beijing, China, 3MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 4Department of Urology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
The purpose of this research is to explore the clinical performance of T2-weighted imaging with deep learning reconstruction (DL-T2WI) for prostate imaging. We compared DL-T2WI and conventional T2WI using TSE (C-T2WI) in terms of image quality, ghosting and tumor conspicuity. The results showed that compared with C-T2WI, DL-T2WI has comparable image quality, ghosting, and tumor conspicuity. The acquisition time of the complete examination using DL-T2WI is 9 minutes shorter than C-T2WI per patient, which suggests that DL-T2WI could replace C-T2WI in clinical settings, with a significantly shorter examination time.
|
||
4243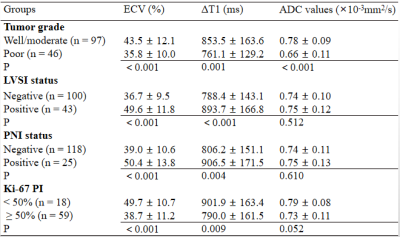 |
11 | T1 mapping with extracellular volume fraction measurement to evaluate histological features of cervical squamous cell carcinoma
Shujian Li1, Jie Liu1, Marcel Dominik Nickel2, Jingliang Cheng1, and Jinxia Zhu3
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 3Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China This study investigated the feasibility of extracellular volume fraction (ECV) measurement using T1 mapping to evaluate histological grade, lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI) status, perineural invasion (PNI) status, and Ki-67 proliferation index (PI) of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC), and to compare T1 mapping with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Results showed that T1 mapping-derived parameters (ΔT1, ECV) can effectively grade and predict CSCC LVSI status, PNI status, and Ki-67 PI, and ADC values can stratify CSCC grading. ECV may represent an effective quantitative imaging biomarker indicating the poor-prognosis histological features of CSCC and may provide incremental diagnostic value beyond qualitative MRI features. |
||
4244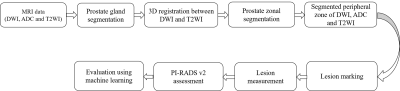 |
12 | Development and validation of a semi-automated framework for PI-RADS v2.1 assessment
Dharmesh Singh1, Virendra Kumar2, Chandan J Das3, Anup Singh1,4, and Amit Mehndiratta1,4
1Centre for Biomedical Engineering (CBME), Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi, New Delhi, India, 2Department of NMR, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Delhi, New Delhi, India, 3Department of Radiodiagnosis, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Delhi, New Delhi, India, New Delhi, India, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Delhi, New Delhi, India, New Delhi, India
Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System version 2.1 (PI-RADS v2.1) was developed to standardize the interpretation of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) for prostate cancer (PCa) detection. However, a significant inter-reader variability among radiologists has been found in the PI-RADS assessment. An automated or semi-automated PI-RADS assessment system could be beneficial in the screening process of PCa and could improve the consistency of scoring. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of an in-house developed semi-automatic framework for PI-RADS assessment using machine learning classifiers.
|
||
4245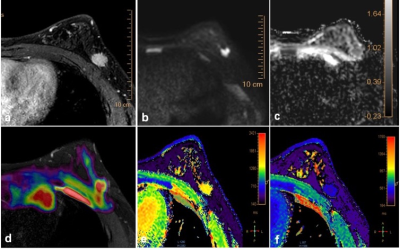 |
13 | Application of synthetic MRI to diagnose benign and malignant breast masses: APTw imaging combined with T1 Mapping and DWI imaging
Jie Ding1, Zhen Zhang1, Rui Wang 1, Xiuzheng Yue2, Rongrong Zhu1, and Ruoshui Ha1
1Medical Imaging Center, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Breast cancer has surpassed lung cancer to become the world's largest cancer for the first time, and the cancer mortality rate ranks second, showing a younger trend in recent years. APTw imaging, as a noninvasive molecular imaging technique, can measure the concentration of free proteins and polypeptides in tissues without the use of exogenous contrast agents, based on a chemical exchange between amide protons and water protons. The aim of study was to explore the diagnostic efficacy for benign and malignant breast tumor by using synthetic MRI. | ||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.