Online Gather.town Pitches
Heart I
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
4116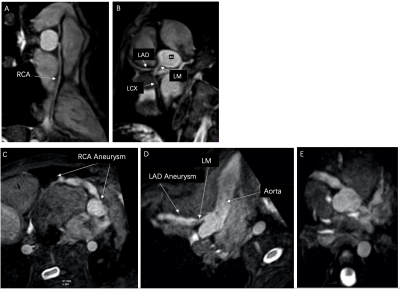 |
1 | Diagnostic value of NCE-CMRA in detection of inflammatory factors related coronary artery damage in Kawasaki disease
Juan Liang1, Yurong Ma1, Na Han1, Kai Ai2, and Jing Zhang1
1Department of Magnetic Resonance, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Xi'an, China
This study mainly uses the non-contrast whole-heart magnetic resonance coronary angiography (NCE-CMRA) to evaluate coronary artery lesion (CAL) in children with Kawasaki disease (KD), and analyze the mechanism of inflammatory factors in the occurrence and development of coronary artery lesions in KD. Multiple linear regression was used to analyze the correlation between inflammatory factors and the severity of CAL. Platelet, PCT, ESR, CRP, D-dimer, albumin, and leukocyte have certain diagnostic value for KD, among which ESR is the most sensitive. Therefore, NCE-CMRA combined with inflammatory indicators is helpful for early diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of CAL in children with KD.
|
||
4117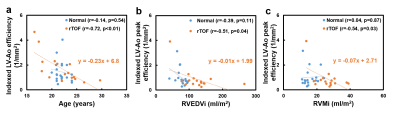 |
2 | Left ventricular-aorta energy efficiency in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot
Yu-Ru Yang1, Meng-Chu Chang1, Ming-Ting Wu2, Ken-Pen Weng3, and Hsu-Hsia Peng1
1Department of Biomedical Engineering and Environmental Sciences, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 2Department of Radiology, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
In this study, we defined a ratio of aortic KE and LV KE to represent LV-Ao efficiency. We aimed to evaluate LV-Ao energy efficiency in rTOF patients and evaluate the relationship between LV-Ao efficiency and RV hypertrophy. The aortic root KE, LV KE, and LV-Ao efficiency in rTOF group were comparable with normal group. The indexed LV-Ao efficiency was negatively correlated with age and RV volumetric parameters. The association between LV-Ao efficiency and age and RV hypertrophy suggested that the adverse interaction between RV and LV was expanded to the aorta in rTOF patients with preserved LV function.
|
||
4118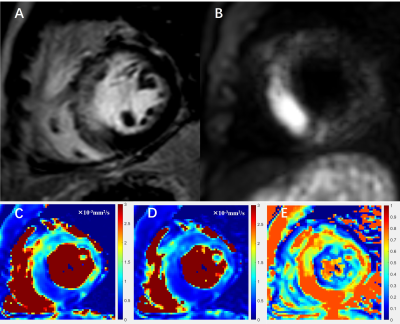 |
3 | Diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute myocardial infarction Video Permission Withheld
Zhenfeng Lv1, Lianming Wu2, Jilei Zhang3, Weibo Chen3, and Haikun Qi1
1School of Biomedical Engineering, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China, 2Department of Radiology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai 200040, P. R. China, Shanghai, China Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), being able to detect the diffusion of water molecules in the tissue, is one of the potential techniques for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction without contrast agent administration. In this study, we investigated the diagnostic value of the mono-exponential and stretched exponential DWI model in the assessment of acute myocardial infarction. The preliminary results from 10 patients showed that the diffusion parameters were significantly lower in the infarcted region, and both models had capability of diagnosing acute myocardial infarction with the stretched exponential model performing slightly better. |
||
4119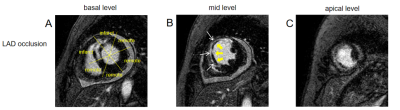 |
4 | Infarct size and strain by cardiac magnetic resonance predict adverse remodeling after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Jianing Cui1, Tao Li1, Yanan Zhao1, and Xiuzheng Yue2
1Department of Radiology, the First Medical center, Chinese People's Liberation Army Hospital, Beijing, China., Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Over the past few decades, all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events have remained high in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients. One of the reasons for this is that adverse LV remodeling of the heart that occurs in many patients after myocardial infarction. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging has become a beneficial imaging modality to assess myocardial morphology, LV function and infarct characteristics simultaneously. This study analyzed the value of LV volumes, LV function and infarct characteristics by CMR predicting adverse LV remodeling after STEMI. Our data showed that total enhanced volume was the most accurate prediction parameter.
|
||
4120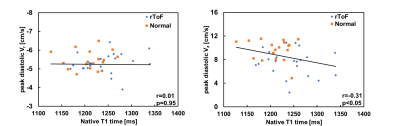 |
5 | Left ventricular myocardial motion and fibrosis in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot
Hung-Wei Wei Wang1, Ming-Ting Wu2, Ken-Pen Weng3,4, and Hsu-Hsia Peng5
1National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 2Department of Radiology, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 4Department of Pediatrics, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering and Environmental Sciences, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
Repaired tetralogy of Fallot (rTOF) caused diffuse fibrosis due to adverse ventricular reconstruction. T1 mapping was employed to observe the diffuse fibrosis. In patients, the native T1 and peak diastolic longitudinal velocity (Vz) were found to be different from the normal group. We aimed to investigate the relationship between left ventricular myocardial motion and myocardial fibrosis in patients with rTOF.
|
||
4121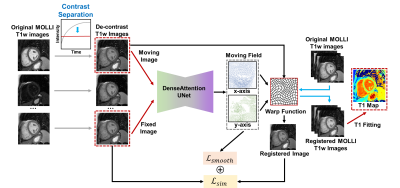 |
6 | Motion Correction for Myocardial T1 Mapping using Self-supervised Deep Learning Registration with Contrast Separation
Yuze Li1, Chunyan Wu1, Haikun Qi2, Dongyue Si1, Haiyan Ding1, and Huijun Chen1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2School of Biomedical Engineering, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China
A motion correction method for myocardial T1 mapping using Self-supervised Deep learning based Registration with contrAst seParation (SDRAP) was proposed. A sparse coding based method was firstly proposed to separate the contrast component from T1w images. Then, a self-supervised deep neural network was developed to register contrast separated images, followed by the signal fitting to generate motion corrected T1 maps. Models were trained and tested in 47 healthy volunteers using MOLLI sequence, and compared with Free Form Deformation method. Results showed the proposed method can achieve better performance in registration and T1 mapping with higher efficiency (7x acceleration).
|
||
4122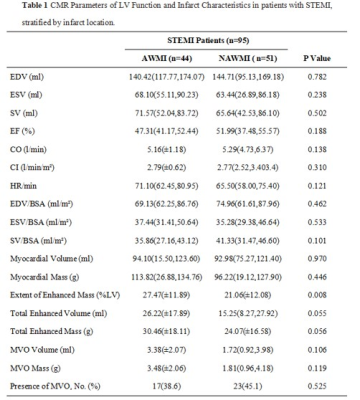 |
7 | Relationship between Infarct size, strain and infarct site in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Jianing Cui1, Tao Li1, Yanan Zhao1, Wei Wang1, Wenjia Liu1, Yundai Chen2, Geng Qian2, Xiuzheng Yue3, and Yishi Wang3
1Department of Radiology, the First Medical center, Chinese People's Liberation Army Hospital, Beijing, China., Beijing, China, 2Department of Cardiology, The Six Medical Center, Chinese People's Liberation Army Hospital , Beijing, China., Beijing, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Effective risk assessment and stratification are essential for the clinical management of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients. CMR imaging has become a beneficial imaging modality to assess myocardial morphology, function and infarct characteristics simultaneously. This study quantitatively evaluated the relationship between infarct size, regional myocardial function by cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking strain analysis and infarct location in patients with STEMI treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Our data showed that myocardial damage was more extensive and regional myocardial function in infarct zone was lower in the anterior wall myocardial infarction group compared to non-anterior wall myocardial infarction group.
|
||
4123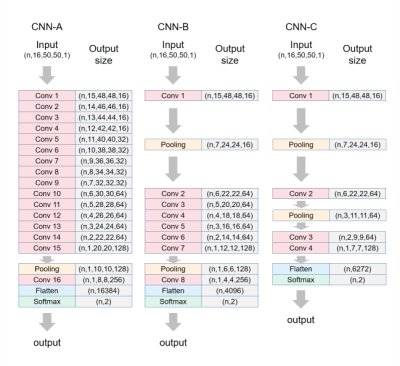 |
8 | Convolutional neural networks to differentiate hypertrophic cardiomyopathy from hypertensive heart disease based on cardiac cine imaging
Qiming Liu1, Yezi Chai1, Meng Jiang1, and Chenxi Hu2
1Department of Cardiology, Ren Ji Hospital,Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Institute of Medical Imaging Technology, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, shanghai, China
Differentiating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) from hypertensive heart disease (HHD) is important yet challenging. In this study, we compared 9 convolutional neural network (CNN) models based on cardiac MR cine imaging only for differentiation of the two diseases. We show that the dynamic information contained in cine about myocardial contraction and relaxation is crucial for accurate differentiation. By leveraging this information, we achieved a testing accuracy of 86.8% ± 3.5% in a cohort including 190 HCM and 113 HHD subjects. The results show that cine-based CNN is reasonably accurate for differentiation of HCM and HHD.
|
||
4124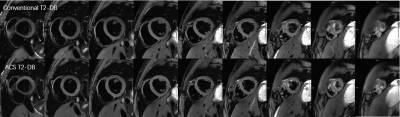 |
9 | Deep learning based whole heart T2-weighted dark blood imaging in a single breath hold
Xianghu Yan1, Lu Huang1, Lingping Ran1, Yi Luo1, Yuwei Bao1, Shuheng Zhang2, Shiyu Zhang2, Yongquan Ye3, Jian Xu3, and Liming Xia1
1Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3UIH America, Inc., Houston, TX, United States
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) T2-weighted dark blood (T2W-DB) imaging has great diagnostic value for detecting myocardial edema. In this study, a novel deep learning based acceleration framework (AI-assisted Compressed Sensing, ACS) was applied to a single-shot T2W-DB sequence for single breath-hold whole heart (9 slices) imaging. Both quantitative and qualitative assessment of the images suggested that the ACS T2-DB sequence offered better image quality with greatly reduced total scan time and the simplified scanning workflow.
|
||
 |
4125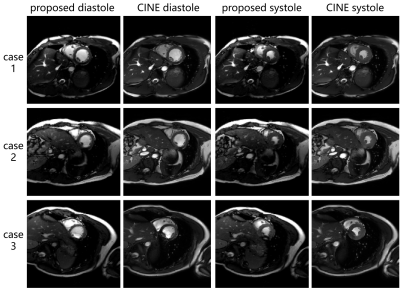 |
10 | Real-time free-running cardiac imaging with ultra-fast reconstruction technique Video Not Available
Zhongsen Li1, Hanyu Wei1, Shuo Chen1, Chuyu Liu1, Mingzhu Fu1, Wei Qiu1, Shuai Wang1, Haining Wei1, Haozhong Sun1, Xihai Zhao1, and Rui Li1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
In this study we have realized a real-time free-running cardiac imaging technique which can provide a continuous high-temporal-resolution movie of the heart during the whole acquisition process. This technique is based on the constrained partial separable model, which has been elaborately designed and optimized to achieve maximum reconstruction speed. Over two thousands dynamic frames of the heart can be acquired and reconstructed in just only 1 minute, without any ECG or respiratory monitoring devices needed. This technique has great potential for the cardiac imaging for patients with arrhythmia.
|
|
4126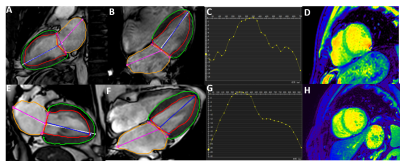 |
11 | The feasibility of cardiac magnetic resonance myocardial feature tracking in evaluating patients with atrial fibrillation
Jianhui Li1, Yanzhen Liu1, Yanhe Ma1, Anhong Yu1, Yapeng Yang1, Jiwei Sun1, Jianxiu Lian2, and Hong Zhang1
1Department of Radiology, Tianjin Chest Hospital, Tianjin, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Atrial fibrillation increases mortality and is an independent risk factor for heart failure and stroke. Cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT) is a post-processing technique that can quantitatively assess myocardial deformation. The result showed that patients with Atrial fibrillation had lower left ventricle longitudinal strain (LVLS) and left atrial longitudinal strain(LALS)compared with healthy control,which may due to impaired function and myocardial injury. Therefore, measuring the longitudinal strain of the left atrium and left ventricle can be used as an important method to evaluate the function of patients with atrial fibrillation.
|
||
4127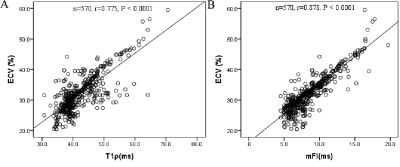 |
12 | T1ρ dispersion imaging on 3T MRI detects diffuse fibrosis in subtypes of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Keyan Wang1, Wenbo Zhang1, Shuman Li1, Hongrui Jin1, Yanan Jin1, Yanan Jin1, Li Wang2, Ran Li3, Yang Yang4, Jingliang Cheng1, Jie Zheng5, and Jing An6
1MRI department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2Pathology department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 3Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States, 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 5Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, MO, United States, 6Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China
This study evaluated a cardiac T1ρdispersion mapping technique, termed as myocardial fibrosis index (mFI), to distinguish various levels of fibrosis in different subtypes of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). These subtypes included patients with or without obstructive HCM, and with or without hypertrophic myocardial segments. Our data demonstrated that the mFI is equal to or significantly better than other cardiac fibrosis index, contrast-derived extracellular volumes, and native T1 values.
|
||
4128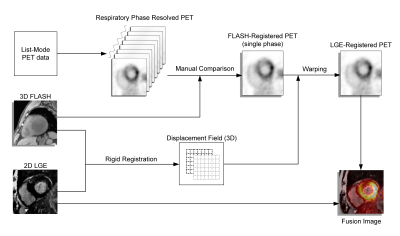 |
13 | Co-registration of cardiac PET and late gadolinium enhancement MRI for integrated PET/MR
zheng zhang1,2, Xing Chen3, Zhiwen You3, Jianmin Yuan2, Lingzhi hu4, Jun Zhao3, and Chenxi Hu1
1Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China, 3Shanghai East Hospital, Shanghai, China, 4United Imaging Healthcare Co. Ltd., Houston, TX, United States A two-stage cardiac PET/late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) co-registration method proposed here significantly improved the co-registration between PET and LGE in integrated PET/MR imaging. The two-stage method led to increased registration score (4.93±0.89) versus no-registration (3.49±0.84, p<0.001) and a single-stage method (4.23±0.81, p<0.001), an increased SUV value in the normal myocardium (3.87±2.56) compared with the no-registration (3.14±1.92, p<0.001) and the single-stage method (3.32±2.16, p<0.001). The technique may improve diagnostic accuracy of non-ischemic cardiomyopathies via better image co-registration. |
||
4129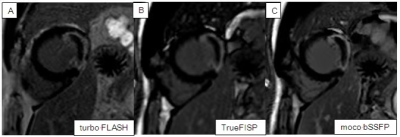 |
14 | The Reliability of CMR Fast Late Gadolinium Enhancement Sequence in The Evaluation of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
li jinshui1 and he yi1
1Beijing Friendship Hospital, bei jing, China
By comparing the three kinds of LGE images of 110 patients with AMI, and taking the current standard turbo FLASH imaging sequence as reference, this study verified the accuracy of using moco bSSFP and TrueFISP to evaluate the lesions in patients with AMI. The research covers image quality evaluation and qualitative diagnosis accuracy evaluation. The results show that moco bSSFP sequence and TrueFISP sequence have equivalent effect as turbo FLASH sequence in the qualitative diagnosis, but their image quality is better than that of turbo FLASH sequence.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.