Online Gather.town Pitches
Heart II
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Booth # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
4557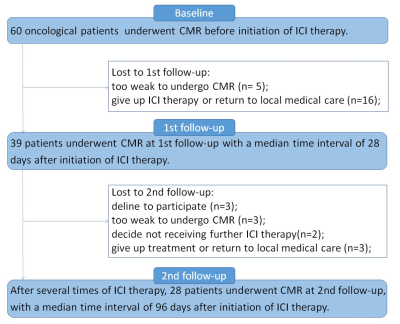 |
1 | Evaluation of cardiotoxicity in chest tumor patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors by cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Jia Liu1, Yukun Cao1, Kuikui Zhu1, Sheng Yao2, Mei Yuan1, Xiangchuang Kong1, Xiaoming Liu1, Yumin Li1, Yue Cui1, Xiaoyu Han1, Xiaoyue Zhou3, Rui Meng1, and Heshui Shi1
1wuhan union hospital, wuhan, China, 2wuhan tongji hospital, wuhan, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, shanghai, China
In our study, we conducted a prospective study to investigate the subclinical cardiotoxicity by serial cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI). Some functional parameters and global strains of bi-ventricles revealed significant decrease at the early stage on ICI therapy, and ejection fraction as well as global strain values of both ventricles all showed a decline trend. Tissue characterization is an extra advantage of CMR technique. While in our study, parameters (T1 mapping, T2 mapping and late gadolinium enhancement) regarding tissue characterization of global myocardium showed no significant differences, compared with baseline data.
|
||
4558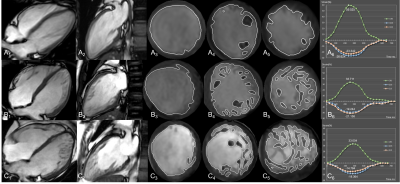 |
2 | Correlation between LV fractal dimension and impaired strain in patients with excessive trabeculation and normal LV ejection fraction
Shiqin Yu1, Xiuyu Chen1, Kai Yang1, Jiaxin Wang1, Kankan Zhao2, Wenhao Dong1, Weipeng Yan1, and Shihua Zhao1
1Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, SZ University Town, Shenzhen, China
In patients with prominent excessive trabeculation, left ventricular systolic dysfunction was detected early by cardiac MRI feature tracking despite the presence of normal left ventricular ejection fraction and was associated with excessive trabecular complexity assessed by fractal dimension.
|
||
4559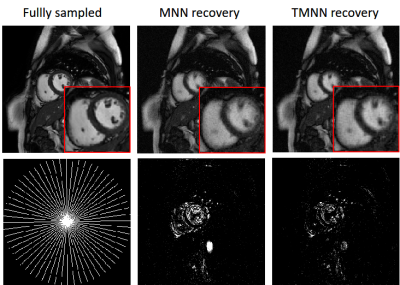 |
3 | Dynamic MRI Reconstruction Combining Tensor Nuclear Norm and Casorati Matrix Nuclear Norm
Yinghao Zhang1, Yue Hu1, and Xin Lu2
1School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2School of Computer Science and Informatics, De Montfort University, Leicester, United Kingdom
Low-rank tensor models have been applied in accelerating dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI). Recently, a new tensor nuclear norm based on t-SVD has been proposed and applied to tensor completion. Inspired by the different properties of the tensor nuclear norm (TNN) and the Casorati matrix nuclear norm (MNN), we introduce a novel dMRI reconstruction method combining TNN and Casorati MNN, which we term as TMNN. Moreover, we convert the the TMNN dMRI reconstruction problem into a simple tensor completion problem, which can be efficiently solved by the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM).
|
||
4560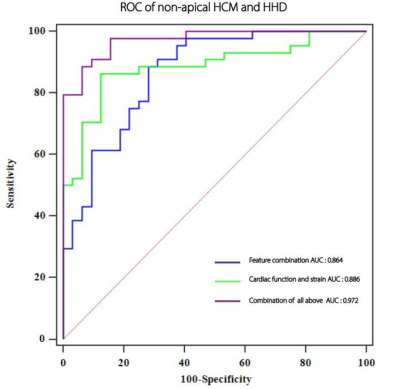 |
4 | Native T1 mapping texture analysis discriminates hypertensive heart disease vs non-apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Mei Yuan1, Jia Liu1, Huan Liu2, Xiaoyue Zhou3, and Heshui Shi1
1Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Shanghai, China
本研究探索了原生T1映射的纹理分析(TA),以便检测非apic肥大性心肌病(HCM)、心肌梗塞和高血压心脏病(HHD)的特定模式,具有良好的诊断效果,可反映心肌纤维化。结果表明,TA能够有效地区分和显示与心脏功能相媲美的诊断精度,并结合菌株分析。TA、心脏功能和应变分析的结合,使非 apical HCM 或 apical HCM 与 HHD 的区分具有最佳诊断精度。这表明,将 TA 与心脏功能和应变参数相结合,比单独使用 TA 具有增量值。
|
||
4561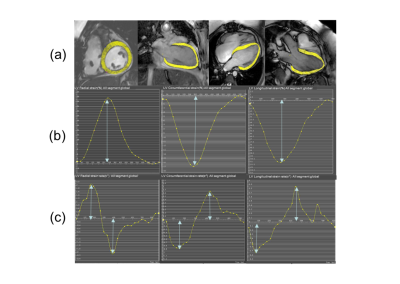 |
5 | Left Ventricular Strain is associated with Outcomes of Pulmonary Valve Replacement in Patients with Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot
Baiyan Zhuang1, Minjie Lu1, and Shihua Zhao1
1Fuwai Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease,PUMC, Beijing, China
Given the fact that patients who have underwent repair of tetralogy of fallot (rTOF) further need pulmonary valve replacement (PVR) due to pulmonary regurgitation, but the effect of PVR is mixed. We prospectively enrolled 45 asymptomatic rTOF patients who required PVR due to moderate or severe pulmonary regurgitation and measured their pre-operative strain and strain rate. After follow-up and analysis, we found that the radial strain (RS), circumferential strain (CS), longitudinal strain (LS), systolic radial strain rate (RSRs), early diastolic radial strain rate (RSRe) and early diastolic longitudinal strain rate (LSRe) before PVR are important prognostic factors for adverse events.
|
||
4562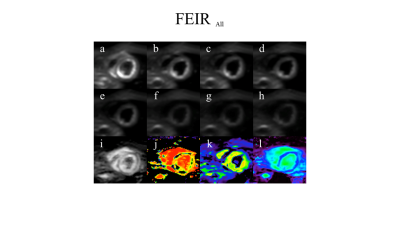 |
6 | Improvement of distortion-free cardiac IVIM-DWI using motion-compensated single-shot turbo spin echo DWI with fast elastic image registration
Yasuhiro Goto1, Nagao Michinobu2, Masami Yoneyama3, Johannes M Peeters4, Isao Shiina1, Kazuo Kodaira1, Yutaka Hamatani1, Takumi Ogawa1, Mana Kato1, and Shuji Sakai2
1Department of Radiological Services, Tokyo Woman's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic imaging & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Woman's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands
We evaluated the feasibility of the combined use of MoSE CINE imaging (to determine exact TD as a preparation procedure), MoCo-TSE-DWI acquisition and FEIR post-processing (to register the respective diffusion images) for improving the robustness of quantitative cardiac IVIM mapping. Combined use of the MoSe-CINE procedure for determining the exact cardiac trigger delay, MoCo-TSE-DWI acquisition, and FEIR post-processing to register among all source images, could be useful to increase the robustness of image quality and improve the quantitative accuracy in myocardial IVIM mapping.
|
||
4563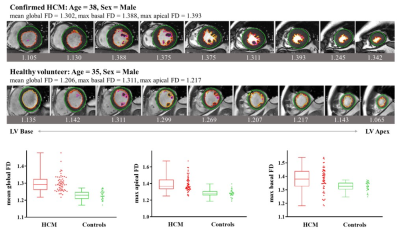 |
7 | Feasibility of fractal analysis in the diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients using strain analysis as reference
xin Zhang1, Lianggeng Gong1, jingyang Wen1, long Qian2, and Weiyin Vivian Liu2
1The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2MR Research, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Pathological changes vary in the morphology and function during the process of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In this study, we compared the diagnostic value of fractal analysis and tissue tracking on cardiovascular magnetic resonance images to characterize the trabecular complexity as myocardial strain alteration for HCM.
|
||
4564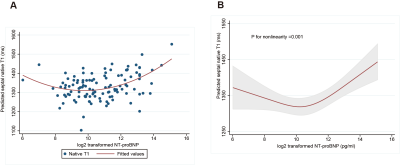 |
8 | Non-linear Association Between NT-proBNP and Septal Native T1 in Non-ischaemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Yujie Gao1, Xiaoyue Zhou2, Shengen Liao3, and Yi Xu1
1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
This study investigated the relationship between cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) T1 mapping parameters and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) patients. The results showed that, in DCM, a non-linear relationship existed between NT-proBNP and septal native T1, indicating a complex relationship between the secretion of NT-proBNP and myocardial diffuse fibrosis. When NT-proBNP is greater than the inflection point(1105 pg/ml), NT-proBNP may provide additional value for the judgment of myocardial diffuse fibrosis.
|
||
4565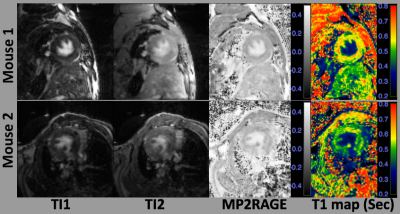 |
9 | Simultaneous late-gadolinium enhancement and T1 mapping to detect diffuse myocardial fibrosis in 1K/DOCA/salt-induced mice using MP2RAGE
Gang Zheng1, Yifang Li2, Ekaterina Salimova 1, Hong X Wang1, Shenjun Zhong 1, Chrishan S Samuel 2, Michael de Veer1, and Gary Egan 1
1Monash Biomedical Imaging, Monash University, Clayton, Australia, 2Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute and Department of Pharmacology, Monash University, Clayton, Australia
The detection and localization of diffuse myocardial fibrosis is for the non-invasive evaluation of therapeutic strategies in murine cardiac disease models. Cardiac late-gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and T1 mapping are two techniques for non-invasive cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. This abstract demonstrates that the magnetization prepared 2 rapid acquisition gradient echo (MP2RAGE) can simultaneously acquire LGE and T1 maps for the detection of diffuse myocardial fibrosis in a 1K/DOCA/salt-induced murine model of hypertensive disease.
|
||
4566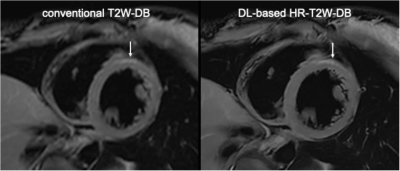 |
10 | Clinical assessment of high spatial resolution myocardial T2-weighted dark blood imaging based on deep learning
Lingping Ran1, Lu Huang1, Xianghu Yan1, Yi Luo1, Shuheng Zhang2, Shiyu Zhang2, Yuan Zheng3, Jian Xu3, and Liming Xia1
1Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3UIH America, Inc., Houston, TX, United States
High resolution T2-weighted dark blood (HR-T2W-DB) imaging is not always robust for clinical use because of low SNR and long scan time. The purpose of this study was to evaluate a novel deep learning (DL) based reconstruction method in T2W-DB sequence that achieves higher spatial resolution and same scan duration compared with traditional reconstruction method. Quantitative and qualitative image assessment demonstrated that DL based HR-T2W-DB sequence showed better CNR in region of edema and LV free wall visibility, which might help detecting myocardial edema.
|
||
4567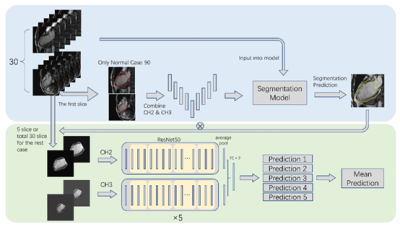 |
11 | Deep-learning for automatic assessment of paradoxical movement in left ventricular aneurysm after myocardial infarction using CMR cine imaging
Binghua Chen1, Jilei Zhang2, Weibo Chen2, Yihong Zhang2, Jianrong Xu1, and Lianming Wu1
1Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
We propose an automatic diagnostic model for left ventricular aneurysm after myocardial infarction. A epicardium segmentation model was established by mixing 2- and 3-chamber images of 90 healthy volunteers, and the dice in all cohorts exceeded 0.95. Five heartphaseimages around end-systolic and end-diastolic stages, multiplied by the predicted mask using the segmentation model were used as the input of the classification model. Data from 259 AMI patients were divided into training cohort (206) and independent testing cohort (53). ResNet was selected to extract the features of 2- and 3- chamber data. Finally, AUC achieved on 0.987/0.946 in training and testing cohort. The automtic deep learning model can be used as a scheme to dignose LVA after AMI, and has potential clinical value for early detection of the risk of the ventricular aneurysm in AMI patients.
|
||
| 4568 | 12 | The predictive value of intravoxel incoherent motion in the assessment of adverse cardiovascular events of athletes heart Video Permission Withheld
Yujiao Deng1,2 and Jing Chen2
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, chengdu,sichuan, China, 2Department of Radiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Regular exercise can have a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, but more and more reports of sudden cardiac deaths in athletes and general people during exercise had made people gradually pay attention to the damage effect of exercise on the heart.There is currently lack of imaging examination methods for early and accurate judgment of athletes’ myocardial injury.This study intended to use intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging to evaluate the myocardial microcirculation of athletes to early predict the incidence of adverse cardiac events such as cardiac remodeling and delayed enhancement of the myocardium.
|
||
4569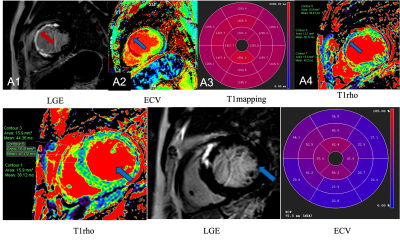 |
13 | Prediction of the changes in myocardial of patients with cardiomyopathy using T1rho mapping
Fang Wang1, Zhen Zhang1, Xiuzheng Yue2, Xiaowei Ruan1, Rongrong Zhu1, Ruoshui Ha1, and Yanbin Yang1
1Medical Imaging Center, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
The study is to determine clinical utility of T1rho to detect patients with cardiomyopathy. In the LGE positive group, the T1 mapping values and ECV values in the lesion area were significantly higher than those in the LGE negative group and the normal control group, while the T1rho values in the lesion area were significantly lower than those in the LGE negative and normal groups, and the display range of lesions was in good consistency with LGE and ECV. It can be used as an endogenous diagnostic index when myocardial structure changes.
|
||
4570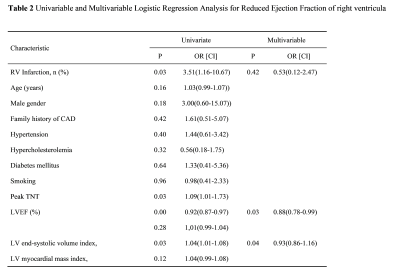 |
14 | The Clinical value of Left ventricle and Septum for Right ventricular function in Patients with Left Ventricle Acute Myocardial Infarction
Yanan Zhao1, Tao Li1, Jianing Cui1, Xueqian Liu2, and Xiuzheng Yue3
1Department of Radiology, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Qinhuangdao Workers' Hospital, Qinhuangdao, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
The reduced right ventricular ejection fraction (RVEF) has prognostic value for predicting cardiovascular mortality in patients with left ventricular acute myocardial infarction (LVAMI). Previous studies have shown that interaction between left ventricular (LV) and right ventricular (RV). This study used CMR to further explore what factors affect the RVEF. The results shown that the incidence of reduced RVEF was 40% in LVAMI patients and the occurrence of reduced RVEF was associated with LVEF, LV end-systolic volume index and RV end-systolic volume index.
|
||
4571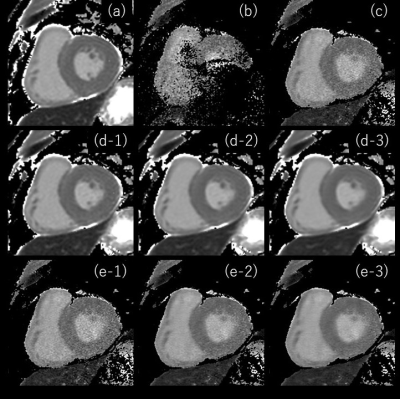 |
15 | High resolution myocardial T1mapping with a deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE reconstruction Video Permission Withheld
Takashige Yoshida1, Kohei Yuda2, Masami Yoneyama3, Jihun Kwon3, and Marc Van Cauteren4
1radiology, Tokyo metropolitan police hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 2Tokyo metropolitan police hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands
High-resolution imaging and T1 mapping is needed to achieve useful clinical information optimally in cardiac MRI. However, prolonged acquisition time can lead to poor or non-diagnostic image quality. In this study, we investigated the use of a deep learning-based reconstruction algorithm to highly accelerate T1map acquisition for cardiac MRI. Adaptive-CS-Net, a deep neural network previously introduced at the 2019 fastMRI challenge, was expanded and integrated into the Compressed-SENSE Artificial Intelligence (CS-AI) reconstruction. The purpose of this study was to compare the image quality of high-resolution T1map between reference and accelerated methods: SENSE, Compressed-SENSE, and CS-AI.
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.