Weekend Course
MRI of Moving Targets & Maturation
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Optimizing the Patient Experience in Clinical MRI I | |||
| 08:00 | Strategies for Alleviating Anxiety & Minimizing Anesthesia in Pediatric MRI
Maddy Artunduaga
|
||
| 08:30 | Short & Sweet: Technical Solutions to Minimizing Motion
Michael Gee
Motion is a common cause of image quality degradation in pediatric MRI and comes from a variety of sources. Motion artifacts can lead to difficulty visualizing small structures, incorrect apparent diffusion coefficient calculations on DWI, ghosting and blurring artifacts, and the need to repeat individual sequences or an entire exam. This talk will review current techniques to decrease patient motion, including fast imaging techniques, motion-robust sequences, indications for anesthesia/sedation, and motion correction technology. These strategies can all help reduce motion degradation and improve image quality during pediatric MRI.
|
||
| Optimizing the Patient Experience in Clinical MRI II | |||
| 09:00 | An Holistic Approach to Improving the Patient Experience: Low-Cost Solutions
Nancy Beluk
|
||
| 09:30 |  |
Out-of-This-World Solutions (VR/AR) for Improving Education & Patient Care
Jesse Courtier
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) tools for radiology are starting to make a difference in real-world educational and clinical applications. This talk provides examples of real educational and clinical applications in the field of radiology with discussion of methods of implementation.
|
|
| 10:00 | Break & Meet the Teachers |
||
| Placental & Fetal MRI I | |||
| 10:20 | Placental MR: Structure & Function
Anne Sorensen, Ditte Hansen, David Peters, Marianne Sinding, Jens Frøkjær
Placental relaxometry provides quantitative characterization of placental tissue. Placental dysfunction is associated with placental hypoxia, which can be depicted by placental relaxometry. Thus, this method provides direct evidence of placental dysfunction during pregnancy, which has the potential to improve pregnancy outcome through optimal pregnancy monitoring and timely delivery. This session will cover a comparison of placental T1, T2 and T2* in the prediction placental dysfunction, a correlation between MR images and placental anatomy, and a summary of current pitfalls of placental relaxometry in terms of acquisition, processing, and interpretation.
|
||
| 10:40 | Abnormal Placentation: Case-Based Review
Priyanka Jha
Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder (PASD) is a life-threatening condition occuring in female patients who have previously undergone cesarean section or uterine instrumentation. In this condition, the placenta is strongly adherent to or invades the myometrium, without intervening decidua. It does not separate normally at the time of delivery, leading to catastrophic hemorrhage. Identifying the most frequent signs of PASD helps with diagnosis, including T2-dark intraplacental bands, placental/uterine bulge, loss of retroplacental T2-hypointense line, myometrial thinning and bladder wall interruption and focal exophytic mass and abnormal vascularization of placental bed. Presence of placental bulge is suggestive of higher grades of myoinvasion.
|
||
| Placental & Fetal MRI II | |||
| 11:00 | Emerging Patterns from Large-Scale MRI Studies of Human Placental & Fetal Development Video Unavailable |
||
| 11:20 | Fetal Post-Processing Analysis
Ali Gholipour-Baboli
Advances in in-vivo fetal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have driven a vastly improved analysis of prenatal brain development, in-utero. In this presentation, we review post-acquisition processing techniques for fetal MRI. Our journey begins with a review of motion-corrected super-resolution slice-to-volume reconstruction techniques that have been at the center of the advances in fetal MRI. We will then discuss the applications of these techniques, including the construction of normative, spatiotemporal MRI atlases of the fetal brain, and techniques for image segmentation and group analysis. This talk covers techniques for the analysis of T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted, and functional MRI of the fetal brain.
|
||
| 11:40 | 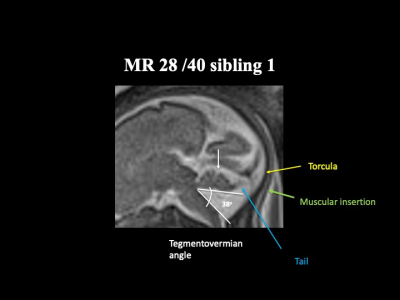 |
Fetal Neuroimaging in Practice: An evidence - based rationale to analysis of fetal malformations producing vermis rotation and posterior fossa expansion
Stacy Goergen
Risk - stratification of fetuses with an upwardly rotated cerebellar vermis will improve prenatal counselling.
|
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.