Weekend Course
Spectroscopy: From NMR Tubes to Humans
Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB & ISMRT 31st Annual Meeting • 07-12 May 2022 • London, UK

| Principles: NMR | |||
| 07:45 | Basic Principles of NMR
Hao Lei
This talk introduces the basic principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). It starts with explaining the interaction between nuclear momentum and static magnetic field, and how such interaction lead to alignment of nuclear spins and energy level degeneration. The principles underlying NMR signal excitation and reception are then discussed. This is followed by introduction of some basic concepts in NMR, such as Larmor frequency, chemical shift and relaxation. The presentation ends with some discussions on how NMR measurements can be used in practical applications to yield chemical/biological information of interest.
|
||
| 08:10 | From in vitro, ex vivo and in situ NMR to MRS metabolomics imaging
Leo Cheng
NMR theory forms the base of MRI that are widely used in various fields with particular interests in medical clinics. While MRI observes only water molecules, NMR, or MRS, can measure vast amounts of molecules other than water. This lecture will walk the audience from the concept of magnetic moment through various aspects of NMR/MRS physics principles and practices to in vitro, ex vivo, and in situ NMR. Recognizing the under-used capability of MRS and with the opportunity to incorporate them into clinical MRI, MRS can contribute imaging by combining molecular evaluations and high resolution anatomic imaging through metabolomics imaging.
|
||
| MRS & Alternatives | |||
| 08:35 | Fundamentals of MRS in vivo data acquisition
Caroline Rae
Fundamentals of MR spectroscopy in vivo. We deconstruct single voxel spectroscopy to see how alterations in acquisition methods and parameters can impact spectra, including an in depth dive into the PRESS sequence.
|
||
| 09:00 | Increasing the Specificity : Physics of MT, CEST, paraCEST & APT
Seth Smith
This presentation is intended to provide an understanding of exchange-mediated contrasts commonly explored in MRI. Specifically we will focus on MT, CEST, and ParaCEST; what are the physics of the contrast mechanisms, what biochemical interactions give rise to the observed phenomena, how to exploit the contrasts with standard acquisition and analysis methods, as well as explore the sensitivity and specificity of each in tissue. Lastly, we will present some specific applications of each, such as MTR and qMT, APT-CEST.
|
||
| 09:25 | Break & Meet the Teachers |
||
| Simulations & Processing | |||
| 09:50 |  |
Simulating Spectra
Jamie Near
The goal of this lecture is to describe how to perform MR spectroscopy simulations using the density matrix formalism. The following questions will be addressed:
-What is a density matrix and how is it constructed? -What is a Hamiltonian operator and how is it constructed? -How does the density matrix evolve under the influence of Hamiltonian operators? -How is a simple spin-echo simulation pulses performed?-How are shaped RF waveforms simulated? -What are spatially-resolved simulations and how are they performed? -What is the projection method and how does it work? -What is coherence order filtering and how does it work? |
|
| 10:15 | MRS Data Processing
Brian Soher
|
||
| MRS Implementation | |||
| 10:40 | 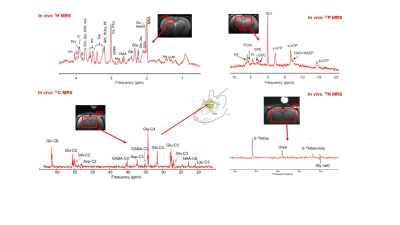 |
Preclinical MRS: Advances, Challenges & Strategies
Cristina Cudalbu
Preclinical in vivo MRS has undergone an enormous evolution from the first unlocalized experiments to the robust technique which is today: advancements in localization, spectral resolution, water and outer volume suppression, minimization of the static B0 magnetic field variations, artifact suppression, spectral editing, number of detected metabolites, spectral fitting and quantification precision. SVS 1H MRS in nowadays widely used while MRSI, X-nuclei MRS and diffusion weighted MRS are more complex MRS techniques with several challenges.
|
|
| 11:05 | Human MRS: Advances, Challenges & Strategies
Itamar Ronen
Educational lecture on proton and non-proton MRS in humans
|
||
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.