Digital Poster
Higher Field, Higher Resolution & Faster Imaging II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
4226.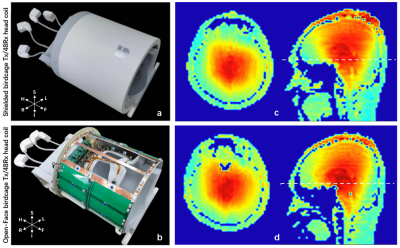 |
141 |
Design of an improved Open-Face birdcage for human whole brain
imaging at 5T
Zidong Wei1,2,3,
Qiaoyan Chen1,2,
Qiang He3,
Xiaoliang Zhang4,
Xin Liu1,2,
Hairong Zheng1,2,
and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, 3Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, New York, NY, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Brain The clinical experience, especially for subjects with claustrophobia, is not friendly when using the conventional shielded birdcage head coils on the ultra-high field. The closed structure also does not better support motion detection and motion correction, and other MRI functional applications. In this work, an optimized Open-Face birdcage head coil were designed based on EM simulations. The transmit efficiency, B1 uniformity, and SAR efficiency of the facial open-window birdcage coil with different configurations and a conventional shielded birdcage coil are compared. Finally, an optimized Open-Face birdcage head coil was built and evaluated on a whole body 5T MRI scanner. |
|
4227.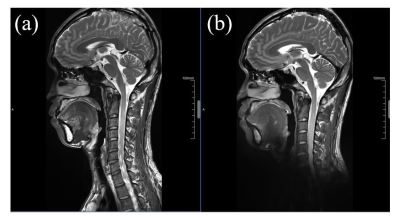 |
142 |
A 48-channel head and neck neurovascular coil for MR vessel wall
imaging at 5 T
Yingchao Tan1,2,3,
Qiaoyan Chen1,2,
Guangzu Xu3,
Lei Zhang1,2,
Na Zhang1,2,
Xiaoliang Zhang4,
Xin Liu1,2,
Hairong Zheng1,2,
and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, 3Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, New York, NY, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Head & Neck/ENT Ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been increasing in use for human brain imaging. However, due to the absence of a head and neck neurovascular coil, joint imaging of intracranial and extracranial arterial vessel wall has not been applied in current ultra-high field MRI. In this study, a 48-channel head and neck receiver neurovascular coil for joint imaging of intracranial and extracranial arterial vessel wall at 5T was developed. Simultaneous high-resolution imaging of intracranial and extracranial arterial walls with an isotropic spatial resolution of 0.5 mm has been achieved, which further expands the application of ultra-high field imaging. |
|
4228.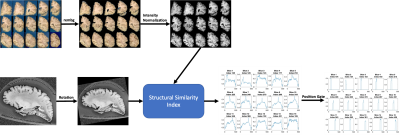 |
143 |
Automatic Alignment of Ex-vivo Brain Pathology to 7T structural
MRI
Jinghang Li1,
Nadim Farhat1,
Jacob P. Berardinelli1,
Joseph M. Mettenburg2,
Howard J. Aizenstein1,3,
Julia K. Kofler4,
and Tamer S. Ibrahim1,3
1Bioengineering, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Neuroradiology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 3Psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 4Pathology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Ex-Vivo Applications In this work, we present an image alignment pipeline that facilitates ongoing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) white matter pathology studies. Following our recently developed ex-vivo 7T cutting-guide container [1], in this work, we demonstrate a standardized alignment (between histopathology and ex-vivo 7T MRI) procedure that significantly reduces human effort and eliminate the need for manual alignment. |
|
4229.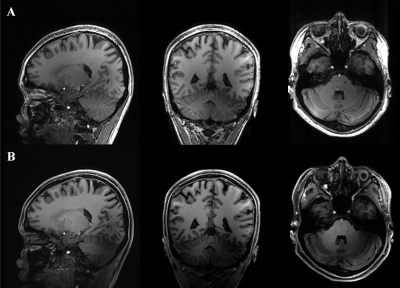 |
144 |
Improved visualization of whole-brain structures and pathology
at ultra-high field 7T MRI with parallel transmission universal
pulses
Caohui Duan1,
Xiangbing Bian1,
Kun Cheng1,
Song Wang1,
Linchang Liu1,
Jinhao Lyu1,
Jianxun Qu2,
Franck Mauconduit3,
and Xin Lou1
1Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China, 3CEA NeuroSpin, Paris, France Keywords: High-Field MRI, Parallel Transmit & Multiband Ultra-high field 7T MRI provides a significant increase in signal-to-noise ratio and contrast for noninvasively visualizing the brain, but is challenging to use for whole-brain imaging. In this study, we investigated the clinical potential of parallel transmission universal pulses (UP) for improving visualization of whole-brain structures and pathology. Our results show that UP enables remarkable signal contrast improvement throughout the brain, which is promising to improve lesion detection (e.g., brain metastases) and structures visualization over the whole brain. |
|
4230.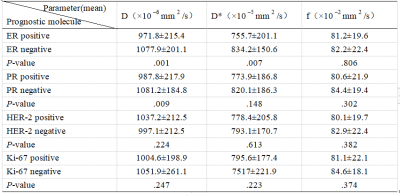 |
145 |
Predictive Value of Intrapixel Incoherent motion (IVIM) Imaging
For Prognostic Factors in Breast Cancer
Jian-mei Fu1,
Jing Chen1,
Gui-dong Dai1,
and Yun-zhu Wu2
1The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, LUZHOU, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Shanghai, China Keywords: High-Field MRI, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Intravoxel Incoherent MotionImaging The objective of this study was to estimate the true diffusion and motion of molecules in the capillary network using the VIM biexponential model without injection of contrast media, three parameters (d value, d * value and F value) were obtained to evaluate the expression of prognostic molecules (ER, PR, Her-2, Ki-67) in breast cancer, which can guide the treatment of breast cancer more precisely.
|
|
| 4231. | 146 |
GRAPPA acceleration of Cartesian magnetic resonance
fingerprinting (MRF) at 7T
Saba Shirvani1,
Belinda Ding2,
Iulius Dragonu2,
and Christopher T. Rodgers1
1Clinical Neurosciences, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2Research and Collaboration UK, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Frimley, United Kingdom Keywords: High-Field MRI, MR Fingerprinting, Quantitative Imaging, Tissue Characterization, Brain MR fingerprinting enables for robust simultaneous quantitative parametric mapping and is usually performed with spiral acquisitions. These are particularly sensitive to B1 inhomogeneities and hence more susceptible at ultra high-field. To mitigate B1 inhomogeneity effects, we implemented a Cartesian MRF approach. Cartesian 2D data collection time is somewhat slow, and we overcome this by demonstrating the feasibility of GRAPPA acceleration for applications in phantoms and in vivo. We present a fully sampled Cartesian data set in a phantom and in vivo, and we present the performance of increasing GRAPPA acceleration factors to reduce scan time significantly, without compromising image quality. |
|
4232.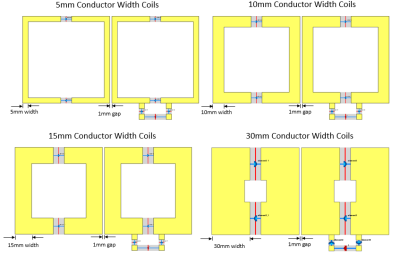 |
147 |
Effect of conductor width on coil array coupling
Yunkun Zhao1 and
Xiaoliang Zhang1
1Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides This study investigates the effect of conductor width of the RF coils to the EM coupling of an array. The results show that the wide conductor of the RF coils offers less EM coupling among resonant elements. |
|
4233.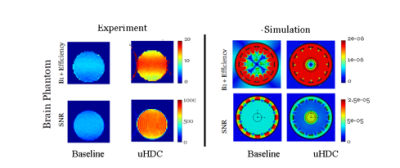 |
148 |
RF Field Enhancement with Ultrahigh Dielectric Constant Material
for Micro Imaging at 7T
Mohan Jayatilake1,
Christopher T Sica1,
Dhevin Karunanayaka1,
Anupa Ekanayaka2,
Biyar Ahmed1,
Rommy Elyan1,
and Prasanna Karunanayaka1
1Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States, 2Grodno State medical University, Grodno, Belarus Keywords: High-Field MRI, High-Field MRI In this study, we investigated the effects of ultra-high dielectric constant (uHDC) material for reducing noise and enhancing the B1 efficiency at 300 MHz for 1H nuclear applications at 7T. Using electromagnetic field simulations [CST Studio (2020) software] and imaging experiments, we estimated B1+ efficiency maps for a phantom mouse brain with and without uHDC material. Our results show significant enhancement of B1+ efficiency and Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) in the presence of the uHDC material. |
|
4234.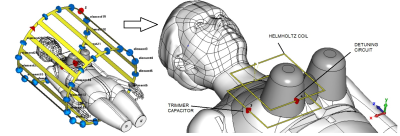 |
149 |
A wireless unilateral Rx-only RF coil for dedicated MRI of a
human breast at 1.5 T
Aleksander Fedotov1,
Pavel Tikhonov1,
Georgiy Solomakha1,
Victor Puchnin1,
Alena Shchelokova1,
and Anna Hurshkainen1
1Department of Physics, ITMO University, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation Keywords: High-Field MRI, RF Arrays & Systems Wireless dedicated radiofrequency coils have recently proven to be a good alternative to conventional cable-connected coils due to compatibility with the scanners of different vendors. Due to significant increase of B1+ with respect to body coil manual calibration procedure needed often for operation of wireless coils.The goal of this work is to develop the first Rx-only wireless coil for dedicated breast MRI to overcome the aforementioned drawback. For that the passive detuning structure inserted to wireless Helmholtz resonator was designed and studied. |
|
4235.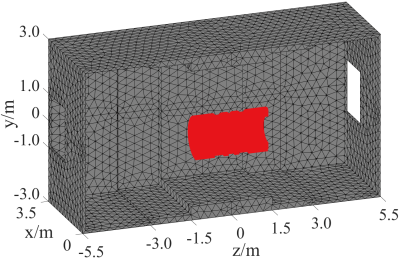 |
150 |
Passive shielding design for ultra-high field MRI
superconducting magnets using an integral operation with
nonlinear iteration
Yaohui Wang1,
Qiuliang Wang1,
Ming Yan1,
Weimin Wang2,
Zhifeng Chen3,
and Feng Liu4
1Institute of Electrical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2School of Electronics & Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Peking University & Shenzhen Graduate School, Beijing, China, 3Monash Biomedical Imaging, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 4School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia Keywords: Magnets (B0), Screening, Passive shielding Passive shielding is a feasible approach to constrain the strong magnetic fluxes in ultrahigh field MRI superconducting magnets. However, an in-depth investigation of the passive shielding design is not well discussed in the literature and notably lacks nonlinear optimization design/analysis methods for this practice. This work developed a computation algorithm for passive shielding design, which uses an integral operation with nonlinear iteration. An exemplification for shielding a 9.4T whole-body MRI superconducting magnet showed the significant advantages of the proposed method over commercial packages. The optimized passive shielding scheme will be used in our future magnet engineering projects. |
|
4236.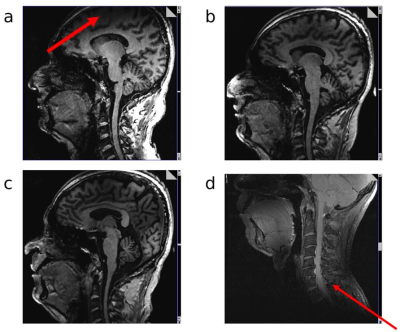 |
151 |
Development of Head and C-Spine coils for use at 7T
Jagjit Sidhu1,
Alexander Smerglia2,
Labros Petropoulos2,
Tsinghua Zheng2,
Xiaoyu Yang2,
Jami Tatulinski2,
Ken Sakaie1,
Paul Taylor 2,
and Mark Lowe1
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Quality Electrodynamics, Mayfield Heights, OH, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Spinal Cord MR imaging at 7T provides a greater signal intensity, which yields some combination of a greater signal-to-noise ratio, smaller voxel size, and/or faster scan times compared with lower field strengths. However, there remains room for improvement at 7T in terms of image homogeneity and a limited selection of coils. In this work, we summarize ongoing efforts to develop a single-transmit (STX) cervical spine (C-spine) and a parallel transmit (PTX) head coil. Both coils have a more open design with detachable anterior halves and larger physical dimensions. |
|
4237. |
152 |
Lumped inductors in RF resonators decrease the B1 fields in
samples at ultrahigh fields
Yunkun Zhao1 and
Xiaoliang Zhang1
1Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, RF Arrays & Systems This study investigates the effect of lumped inductors used in RF resonant circuits on the magnetic field strength generated by the radiofrequency (RF) coils. The results show that the lumped inductors can reduce B1 fields in samples. |
|
4238.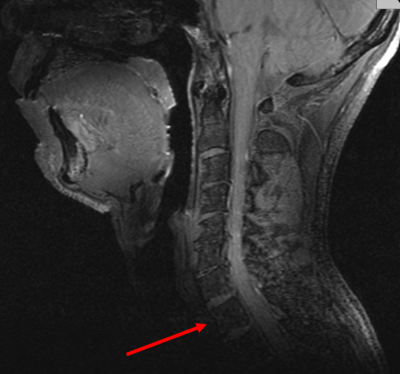 |
153 |
Improved Transmit Efficiency and Clinical Coverage using a
Cervical Spine Array with a Volumetric Transmitter at 7T
Alexander Smerglia1,
Labros Petropoulos1,
Jami Tatulinski1,
Tsinghua Zheng1,
Xiaoyu Yang1,
Jagjit Sidhu2,
Ken Sakaie2,
and Mark Lowe2
1Quality Electrodynamics (QED), Mayfield, OH, United States, 2Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Brain, Spine, Imaging, Cerebellum Several challenges are present when imaging the cervical spine in high-field MRI, such as achieving B1 coverage over the desired anatomy while maximizing efficiency of the transmitter. A cervical spine array coil with a volume transmit birdcage was built and tested on a system for improved transmit coverage and efficiency over previous prototypes. The coil consists of a partially shielded 22-rung birdcage transmitter and a 24 element receive RF array. A new mechanical design with larger eye windows improves the clinical experience. Improved transmit efficiency and complete B1 field coverage in the cervical spine region were confirmed through volunteer imaging. |
|
4239.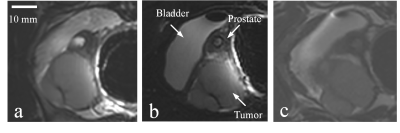 |
154 |
Comparing the imaging performance of a three-channel endorectal
coil for magnetic resonance imaging at 5T and 3T
Zhiguang Mo1,2,
Xiaoping Zhang3,
Huageng Liang3,
Changjun Tie1,2,
Wen Xiao3,
Qi Cao3,
Chenchen Liu3,
Xiaoliang Zhang4,
and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, NY, United States., Buffalo, NY, United Stats, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Prostate We made a three-channel endorectal coil for prostate imaging on the 5T magnetic resonance system and compared the imaging performance of the coils with the same structure on the 5T system and the 3T system. Prostate images at resolution of 0.78 mm × 0.78 mm × 2.5 mm were performed. In vivo prostate study shows that the endorectal coil works on the 5T system shows better image quality compared with the endorectal coil and surface coil array on the 3T system. |
|
4240.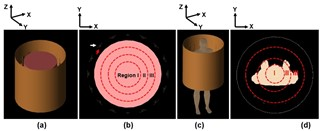 |
155 |
Uniformity Improvement of the 7T Body MR Images
Bu S Park1 and
Sunder Rajan2
1FDA, Silver Spring, MD, United States, 2Division of Biomedical Physics (DBP), FDA, Silver Spring, MD, United States Keywords: High-Field MRI, Electromagnetic Tissue Properties To optimize MR image quality of 7T Body, the image region is divided into multiple ROIs, which can be independently optimized using transmit array optimization techniques to improve image intensity. Compared to the results of quadrature driving method, mean and SD of |Mt| in the full image (inner diameter of 500 mm) were improved 47% (Mean) and 48% (SD), whereas 94% (Max) and 97% (Mean) improved in the unaveraged SAR using the proposed method. The proposed method using multiple independently optimized ROIs and numerical simulations significantly improved uniformity of |Mt| body images at 7T. Keywords: 7T Body, Uniformity, SAR |
|
4241.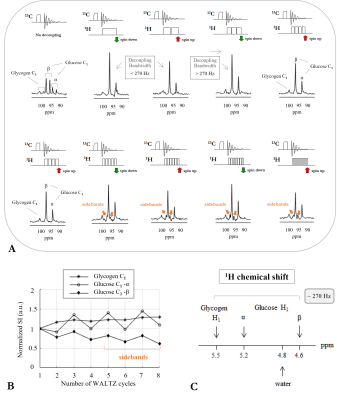 |
156 |
Towards high sensitivity 13C MRS of Human Brain Glycogen at 7T
Eulalia Serés Roig1
1Laboratory of Functional and Metabolic Imaging (LIFMET), Institute of Physics (IPHYS), School of Basic Sciences (SB), Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland Keywords: Phantoms, Non-Proton Largely neglected due to its low concentration, yet brain glycogen plays an active role in brain energy metabolism and may be involved in a variety of brain diseases. The application of 13C MRS along with 13C-glucose intravenous infusion is to date the forefront method for investigating brain glycogen metabolism in vivo. Notably, the C1-resonances of glycogen and glucose have been detected non-invasively in the conscious human brain by 13C MRS at 4T after 13C-glucose infusion labelled at the C1-carbon. In this study, we explore the potential of 13C MRS at 7T with broadband 1H-decoupling towards measuring glycogen and glucose C1-resonances. |
|
4242.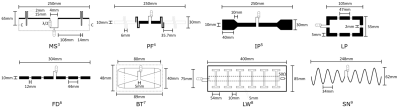 |
157 |
FAIR Benchmarking of 7T MRI Antennas – Case for a Standardized
Protocol for RF Transmit Element Performance Assessment
Max Joris Hubmann1,2,
Bilguun Nurzed3,
Thoralf Niendorf3,
Oliver Speck2,4,
and Holger Maune2
1Siemens Healthineers GmbH, Magdeburg, Germany, 2Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany, 3Berlin Ultra-High Field Facility, Max-Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association, Berlin, Germany, 4Research Campus STIMULATE, Magdeburg, Germany Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides This abstract proposes a standardized setup and four standardized metrics to increase 7T Tx RF antenna concept comparability and reproducibility, with the goal of a better technology transfer of antenna concepts across the MR community. Eight antenna concepts are evaluated based on power and SAR efficiency as well as mutual coupling and reliance on load changes using a rectangular phantom mimicking the average electromagnetic body properties. Based on the presented results, much information can be collected and deductions about each antenna's preferable ambits drawn. In conclusion, this work initiates a first standardized protocol for analyzing Tx RF antenna concepts. |
|
4243.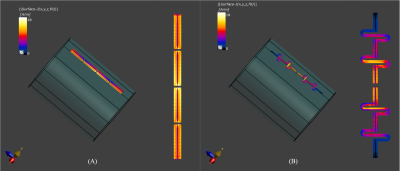 |
158 |
End-Grounded Dipole RF Element with Extended Coverage and
Minimized SAR at 7T MRI
Haiwei Chen1,
Lei Guo1,
Yang Gao2,
Zhiyan Quan3,
Xiaocui Tang3,
Sihong Pan3,
Feng Liu1,
and Xiaotong Zhang3
1the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2School of Electronic Engineering (National Key Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology) and Hangzhou Institute of Technology, Xidian University, Hangzhou, China, 3Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems Dipole RF coil suffers from high peak local SAR and limited imaging coverage. In this work, a novel dipole structure is proposed. Compared with the fractionated dipole, the proposed design achieves a substantially enlarged B1 field coverage and more than 25% SAR reduction by generating a uniform surface current on the coil. Experimental validations were conducted and agreed well with the simulation results. |
|
4244.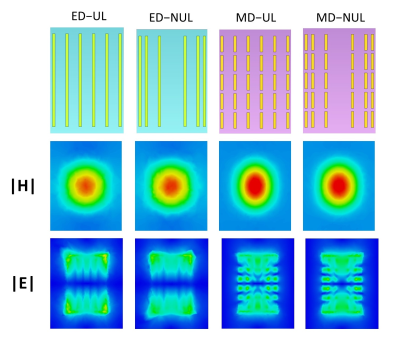 |
159 |
Characterization of the RF field for metamaterial-based
structures constructed of conducting strips and a dielectric at
7T MRI
Santosh Kumar Maurya1 and
Rita Schmidt2
1Brain Sciences, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel, 2Department of Brain Sciences, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel Keywords: New Devices, High-Field MRI Metamaterial-based structures constructed of conducting strips and a dielectric have already been used to locally increase the RF transmit field. In this study we characterize the RF field of such structures at 7T MRI. Configurations included either long strips (representing electric dipoles), or a matrix of short strips (representing magnetic dipoles). The RF field dependence on strip density and distribution was analyzed, providing insights useful for efficiency and coverage optimization. The configuration based on a matrix of short strips provides higher RF transmit efficiency, while the use of a non-uniform concave distribution of strips is useful to lower SAR. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.