Digital Poster
New Approaches in RF Coils I
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
5063.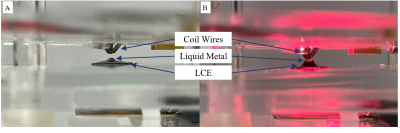 |
121 |
Low-Loss Switches for Multinuclear MRI/S Using
Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Materials
Edith Valle1,
Seelay Tasmim2,
Mary P. McDougall1,2,
and Taylor H. Ware2,3
1Electrical and Computer Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, United States, 2Biomedical Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, United States, 3Materials Science & Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, United States Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Hybrid & Novel Systems Technology The development of highly sensitive multinuclear RF coils for MRI/S is challenging because most current multi-tuning techniques involve the addition of lossy components. Although it is possible to optimize for a particular nucleus, usually non-1H, multinuclear coils have lower SNR than their single-tuned counterparts. We investigate a novel switching system that uses stimuli-responsive materials. The coils with the proposed switching method had a decrease of <26% in Q when compared to single-tuned coils. As a result, we demonstrated a promising alternative to traditional switching techniques. |
|
5064.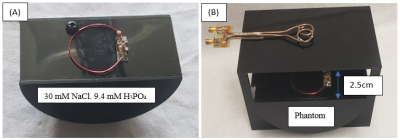 |
122 |
Investigation of Triple-Tuned Trap Designs
Joseph Busher1 and
Mary P. McDougall1,2
1Biomedical Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, United States, 2Electrical and Computer Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, United States Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides Multi-frequency coils are typically known to have substantial losses as compared to their single-tuned counterparts. Here we investigate sensitivity tradeoffs of triple-tuned (1H-23Na-31P) trap designs on receive coils in a tightly controlled experiment to isolate the sensitivity effects of the traps. Triple-tuned LCC traps were shown to have significant improvement in sensitivity for 23Na and 1H as compared to an LC trap design. The increase came at the expense of 31P sensitivity, however continued optimization of the trap design will likely further improve the final experimental SNR. |
|
5065.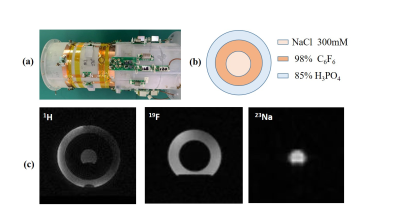 |
123 |
A Triple-nuclear four-channel RF coil for Simultaneous
acquisition of 1H/19F/23Na MR imaging at 3T
Nan Li1,2,
Feng Du1,2,
Xiaoliang Zhang3,
Xin Liu1,2,
Hairong Zheng1,2,
and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, United States, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems As the lower natural abundance of X-nuclei, it is important to enhance that the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the X-nuclei is as high as possible by designing a well-designed multiple-tuned coils. In this study, a new triple-tuned RF coil system capable of 1H / 19F / 23Na imaging was proposed. The performance of the triple-tuned coil was evaluated compared to their counterpart single-tuned coils by the numerical electromagnetic simulation. Imaging tests at 3T MRI were performed on the phantom by using the triple-tuned RF coil. |
|
5066.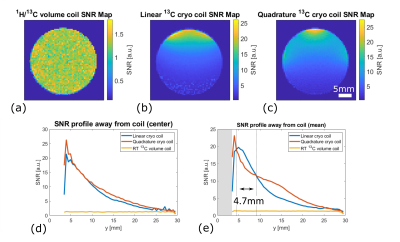 |
124 |
Signal-to-noise and B1 characterization of linear and quadrature
13C-cryocoils for preclinical MRSI
Luca Nagel1,
Geoffrey J. Topping1,
and Franz Schilling1
1School of Medicine, Klinikum rechts der Isar, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Technical University of Munich (TUM),, Munich, Germany Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems Cryogenically-cooled 13C radiofrequency (RF) coils (cryocoils) improve SNR by reducing thermal coil noise compared to room-temperature coils. Coil geometry impacts B1 patterns, which impact experiment design and must be characterized. The sensitivity profiles of a linear and a quadrature coil were characterized with varied RF powers, which is complicated by transmit B1 variation with position and resulting excitation variations. The sensitivity was compared to a room-temperature volume resonator. The quadrature cryocoil configuration offers better B1 uniformity but lower SNR closest to the coil compared to the linear configuration, both have an overall better SNR performance compared to the volume resonator. |
|
5067.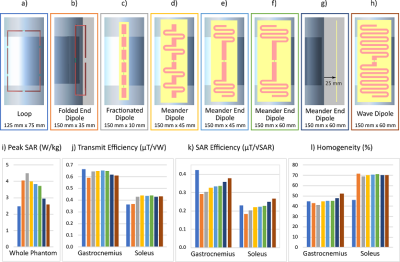 |
125 |
Investigating Dipole Antennas as 1H Transmit Elements for a
1H/31P Calf Coil at 7 T
Veronika Cap1,
Martin Meyerspeer1,
Sigrun Roat1,
Elmar Laistler1,
and Roberta Frass-Kriegl1
1Division MR Physics, Center for Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems, dipoles, simulation Different dipole antenna types as 1H transmit elements for metabolic 1H/31P MRS studies of the human calf were investigated. In simulations, the dipole elements and a loop coil were compared in terms of transmit efficiency and SAR. A three-element array of the best-performing design was simulated and constructed, and its transmit performance was found to be comparable to a four-element loop array. Investigating the interaction between a dipole transmit element and a receive-only loop placed underneath, efficient geometric decoupling was observed. This can be exploited to improve the receive sensitivity (homogeneity, depth) by using transceiver dipoles together with receive-only loops. |
|
5068.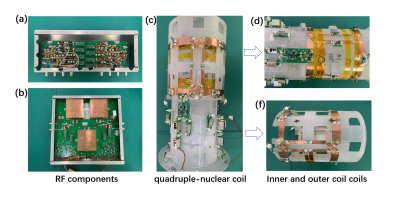 |
126 |
Design and Construction of a quadruple-nuclear transceiver coil
array for 1H/19F/23Na/31P MRI at 3T
Feng Du1,2,
Nan Li1,2,
Xiaoliang Zhang3,
Xin Liu1,2,
Hairong Zheng1,2,
and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen 518055, Guang Dong, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, United States, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, New Devices Multinuclear MRI has been demonstrated as a crucial tool for comprehensively characterizing tumor pathology and monitoring tumor treatment response as it can provide biochemical, physical, and functional as well as structural information. The objective of this work is to develop a quadruple-nuclear transceiver coil array for 1H/19F/23Na/31P MRI at 3T to simultaneously detect multinucleal signals. The phantom studies were performed on self-developed 3T MRI system to verify the performance. These results proved that uniform excitation and highly sensitive acquisition in the region of interest were achieved by utilizing the proposed RF coil and indicated the fesibility for multinuclear MRI applications. |
|
5069.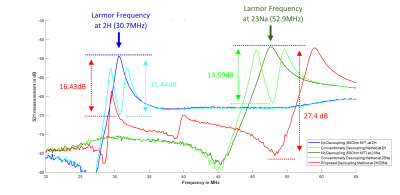 |
127 |
A Low-complexity Approach to Decouple Dual-tuned RF Coil
Elements in Multinuclear Receive Array Coils
Chenhao Sun1,
Courtney Bauer1,
Jue Hou1,
and Steven M. Wright1
1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems, Multi-Nuclei, multinuclear, decoupling This study proposes a novel low-complexity decoupling approach for multi-nuclei receive array coil design. Instead of using narrowband LC networks and isolation preamplifiers, a preamplifier with high input impedance can be used to decouple receive coils while maintaining most SNR. A broadband impedance matching network consist of LCC multi-tuned circuit and transformer was developed to interface the coil with a high Z preamplifier. The proposed setup has achieved more than 15dB of decoupling over a range of 25MHz. The prototype simultaneously yielded 73.6% and 91.9% of SNR at 2H and 23Na when compared to the conventional single-tuned preamplifier decoupling methods. |
|
5070.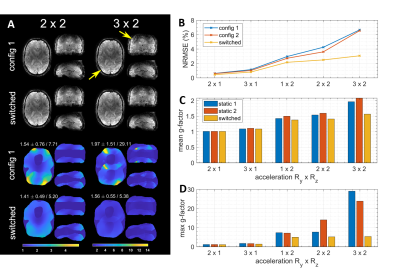 |
128 |
Reconfigurable Coaxial Receive Dipoles for Dynamic Parallel
Imaging of Human Brain at 9.4T
Georgiy Alekseevich Solomakha1,
Felix Glang1,
Theodor Steffen2,
Klaus Scheffler1,3,
and Nikolai Ivanovich Avdievich 1
1High-field Magnetic Resonance, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tuebingen, Germany, 2Electronical Workshop, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tuebingen, Germany, 3Department for Biomedical Magnetic Resonance, University of Tübingen, Tuebingen, Germany Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems Recently developed dynamic parallel imaging, i.e. rapid modulation of element's sensitivities during acquisition, greatly improved the performance of the method. In this work, sensitivity profiles of dipole elements were electronically reconfigured by varying impedances of lumped element circuits connected in series with the dipoles . This required a large number of DC wires directly connected to the dipoles. In the present work, we developed, constructed, and evaluated a dynamically reconfigurable 8-element coaxial dipole array for brain imaging at 9.4T. Our design eliminates the DC wires directly connected to the dipoles and, hence, substantially simplifies further increasing the number of receive channels. |
|
5071.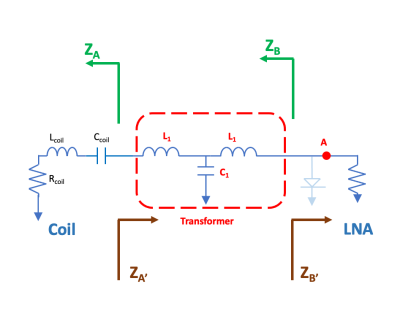 |
129 |
A high impedance radio-frequency system improves the decoupling
between receiving coils in MRI
Yu-Lung Tang1,
Hsin-Ju Lee2,3,
and Fa-Hsuan Lin2,3
1Timwave Technologies Company Limited, Taipei, Taiwan, 2Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems The decoupling between coils significantly impacts the amount of independent information between channels in a receiver coil array. Using a pre-amplifier with a low input impedance is limited by the technology in achieving the lowest possible impedance, typically around a few ohms. Here we propose a strategy to improve the decoupling between coil elements in a receiver array by increasing the impedance of the coil system. Simulations and bench measurements show that increasing the impedance from a typical 50 ohm to around 1,000 ohm can increase the decoupling by 25 dB. |
|
5072.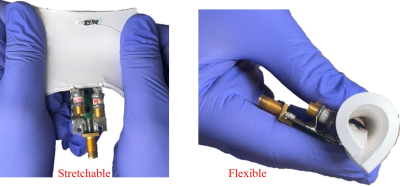 |
130 |
Dielectric Loaded Stretchable and Flexible Surface RF Coil
Seyedamin Hashemi1,
Sri Kirthi Kandala1,
and Sung-Min Sohn1
1School of Biological and Health Systems Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, Phantoms, Receive coil, flexible coil, loaded coil This study presents a novel receive radiofrequency coil that enhances the signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) and field-of-view (FOV) in magnetic resonance images. The fabricated coil is loaded by a mixture of dielectric material (TiO2) and an elastomer offering stretchability and flexibility. The functionality of the coil compared to a typical surface coil was assessed using phantom imaging at 7T. The SNR (in dB), signal intensity, and uniformity are improved by 14.75%, 25%, and 87.76% by using a TiO2-loaded coil, respectively. This design method will be invaluable for uneven sample shapes and a very close place to a subject. |
|
| 5073. | 131 |
Helmet RF Applicator for Enhancing Focal RF Power Deposition in
Thermal Magnetic Resonance of the Brain at 7T
Faezeh Rahimi1,2,
Thomas Wilhelm Eigentler1,3,
Jason M. Millward1,4,
Pirus Ghadjar5,
and Thoralf Niendorf1,4,6
1Berlin Ultrahigh Field Facility, Max-Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association, Berlin, Germany, 2Theoretische Elektrotechnik Institut Hochfrequenz- und Halbleiter-Systemtechnologien, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 3Chair of Medical Engineering, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 4a joint cooperation between the Charité Medical Faculty and the Max-Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine, Berlin, Germany, 5Clinic for Radiation Oncology, Charite’ Universitätsmedizin, Berlin, Germany, 6MRI.TOOLS GmbH, Berlin, Germany Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, Interventional Devices, SAR distribution, Focal Heating, Hyperthermia, Brain Thermal MR at 7T Thermal Magnetic Resonance (ThermalMR) uses an RF-applicator to add a thermal intervention dimension to a diagnostic imaging device. Optimizing the performance of RF applicator configurations can eventually improve the performance of ThemalMR. This work examines the feasibility of multi-channel RF applicators using broadband Self-Grounded Bow-Tie (SGBT) antenna building blocks. The focus is on enhancing focal RF power deposition in a target volume by using a multi-channel helmet RF array configuration versus conventional annular RF arrays. Our preliminary findings obtained for the human head voxel model Duke show improved target coverage of high SAR10g and high temperature for the helmet configuration. |
|
5074.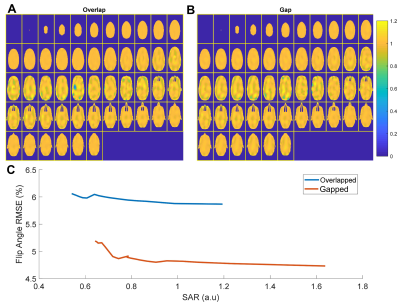 |
132 |
Overlapped or gapped multi-row self-decoupled transmit array:
which is better?
Ming Lu1,
Zhipeng Cao2,3,
and Xinqiang Yan2,3
1College of Nuclear Equipment and Nuclear Engineering, Yantai University, Yantai, China, 2Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 3Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States Keywords: Parallel Transmit & Multiband, High-Field MRI This work is aiming to answer which multi-row self-decoupled array outperforms in parallel transmission to generate a uniform transmit RF field (B1+). |
|
5075.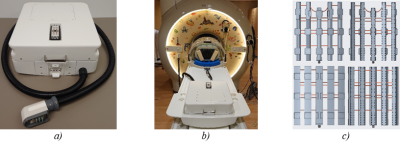 |
133 |
Xenon-129 Platform for Operating a T/R Coil and Phased Array at
3T
Wolfgang Loew1,
Virginia Van Horne2,
Peter van der Meulen3,
and Charles Dumoulin1
1Department of Radiology, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, United States, 2Innovation Ventures, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, United States, 3Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands Keywords: Whole Body, New Devices A platform was developed for 129Xe applications allowing the use of an insertable whole-body transmit/receive coil by itself or in combination with a 129Xe phased array coil. Experiments were performed in a 3T MRI scanner without modification of the scanner’s 1H body coil. 129Xe imaging was performed with a loader phantom and a xenon Boltzmann phantom in both configurations. |
|
5076.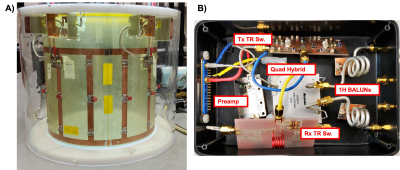 |
134 |
The Lord of the EndRings: A roadmap for the design and
construction of a Tx/Rx 31P birdcage head coil and feed network
at 3 Tesla
Peter Truong1,
Helmut Stark2,
Agessandro Abraham3,4,
Lorne Zinman3,5,
and Jamie Near1,6
1Physical Sciences Research Platform, Hurvitz Brain Sciences Program, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2Stark Contrast, Erlangden, Germany, 3Evaluative Clinical Sciences, Hurvitz Brain Sciences Research Program, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Department of Medicine (Neurology), Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre and University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5Institute of Medical Science and Rehabilitation Sciences Institute, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Challenges Join us as we take you on a journey in the development of a Tx/Rx 31P birdcage head coil. Even though there is a wealth of available knowledge explaining the theory of MRI RF coil design, there are many unforeseen situations one will encounter in practice. The road for coil development is filled with many valuable lessons. We hope to provide a practical guide for new builders by describing our experiences in coil design, construction, and troubleshooting. |
|
5077.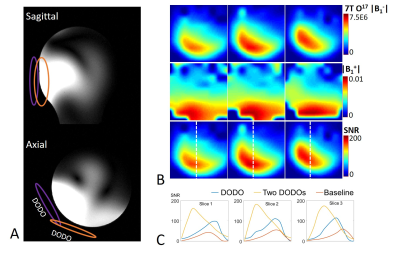 |
135 |
DOuble tuned and DOuble matched large-size loop coil (DODO)
design and evaluation for 17O MRSI and 1H MRI application at 7T
Xin Li1,
Guangle Zhang1,
Wei Zhu1,
Xiaoliang Zhang2,
Xiao-Hong Zhu1,
and Wei Chen1
1Department of Radiology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States, 2School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, University of Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, RF Arrays & Systems Current state-of-the-art RF coils for X-nuclear MRS/MRI studies typically use two separate sets of RF coils operating at the X-nuclear and proton frequencies, respectively. Here, we introduce a new coil concept whereby large-size loop coil with split capacitors which can be simultaneously tuned and matched to 17O and 1H Larmor frequencies for 7T human imaging application. Importantly, this novel coil exhibits excellent performance in proton and X-nuclear imaging, therefore, it provides a simple RF coil solution, particularly for ultrahigh field (UHF) multinuclear brain MR imaging applications. |
|
5078.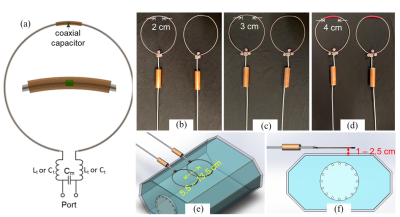 |
136 |
Wearable and stretchable RF coils using self-decoupling
technology
Shuyang Chai1,2,
John Gore1,2,
and Xinqiang Yan1,2
1Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 2Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems A novel flexible and stretchable coil based on the self-decoupling technology is proposed. It can be stretched and bent to match the shape of the human anatomy of interest, exhibiting high SNR. A 4 coil array was built and tested at different stretching (horizontally and vertically), and on different anatomies (torse, thigh, head), showing a strong robustness. |
|
5079.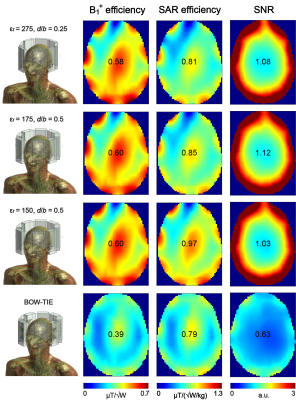 |
137 |
A multi-feed, loop-dipole approach to enhance performance of
multi-channel dielectric resonator antenna arrays for human
brain MRI at 7T
Daniel Wenz1,2 and
Thomas Dardano1,2
1CIBM Center for Biomedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Animal Imaging and Technology, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Dielectric resonator, loo-dipole The goal of this work was to demonstrate that performance of multi-channel dielectric resonator antenna arrays for brain MRI at 7T can be substantially improved using a novel multi-feed, loop-dipole coupling mechanism. Simulations were conducted for different rectangular DRA geometries and dielectric constants. Three RF feed types were investigated: loop-only, dipole-only and loop-dipole. 16-channel, loop-dipole rectangular DRA arrays provided significant gains in B1+, SAR efficiency and SNR vs. 8-channel bow-tie antenna array. The feasibility of multi-feed, loop-dipole approach was for a 24-channel DRA array was demonstrated. |
|
5080.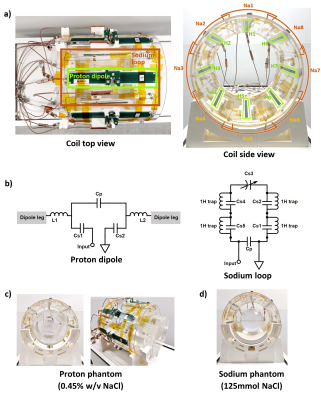 |
138 |
A 16-Channel Proton/Sodium Transmit/Receive Array Design for 7
Tesla Head Imaging
Menglu Wu1,2,
Jérémie Clément1,3,
Jules Vliem1,4,
David Leitão 1,
Raphael Tomi-Tricot1,2,5,
and Özlem Ipek1,2
1Biomedical Engineering, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2London Collaborative Ultra high field System (LoCUS), King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 3System Technologies, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 4Electrical Engineering, Technical University of Eindhoven, Eindhoven, Netherlands, 5MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthineers, Frimley, United Kingdom Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, Non-Proton 7T MRI has great potential to enhance the sensitivity to 23Na, allowing access to functional and anatomical information when combined with proton imaging. We introduce an RF coil design of a 16-channel Tx/Rx head array composed of eight proton dipoles and eight overlapping sodium loops for 7T. The initial results were acquired on phantoms with comparable performance for both nuclei, and a 40% B1+ gain was reported in sodium channels against the commercial coil. All elements were well-decoupled (-7.2dB to -36dB) without implementation of multiple layers or RF shield, paving the way for future simultaneous 1H/23Na MRI acquisition at 7T. |
|
5081.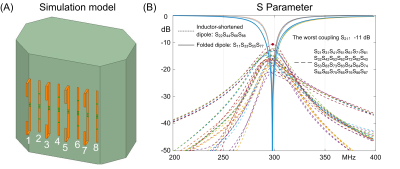 |
139 |
High-density dipole array for human lumbar spine cord imaging at
7T
Ming Lu1,
Shuyang Chai2,3,
and Xinqiang Yan2,3
1College of Nuclear Equipment and Nuclear Engineering, Yantai University, Yantai, China, 2Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 3Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, High-Field MRI The Dipole antenna, which has a long longitudinal coverage and deep penetration, has demonstrated a better transmit efficiency for spinal cord imaging compared to the standard loop coil. However, owing to the inevitable coupling, the number of dipoles is highly limited. In this work, we find that the number of dipoles could be doubled if they are be shortened in different ways and arranged to interleave. An 8-channel dipole array consisting of 4 inductor-shortened dipoles and 4 folded dipoles was designed and numerically investigated for 7T lumbar spinal cord imaging. |
|
5082.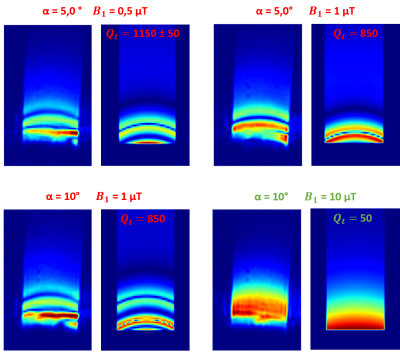 |
140 |
First MR Images acquisition with decoupled High Temperature
Superconducting surface coils
Camille Dubuc1,2,
Aimé Labbé1,
Sina Marhabaie1,
Clément Thibault3,4,
Jean-Christophe Ginefri1,
Javier Briatico5,
and Marie Poirier-Quinot1
1Université Paris-Saclay, BioMaps, ORSAY, France, 2Thales Research & Technology, Palaiseau, France, 3Université Paris-Saclay, CEA, CNRS, Inserm, BioMaps, Orsay, France, 4Université Paris-Saclay, CEA, CNRS, BAOBAB, NeuroSpin, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 5Unité Mixte de Physique, CNRS, Thales, Université Paris-Saclay, Palaiseau, France Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, Superconducting material, Decoupling A promising strategy to tackle the issue of decoupling High-Temperature Superconducting (HTS) surface coils during emission is to exploit nonlinearities of the HTS coil electromagnetic response. In this work, we present the first Magnetic Resonance Images acquired with a decoupled HTS surface coil and the required coil’s features to obtain these images. The change of the HTS coil Q-factor values leads to different decoupling levels (DL) of the HTS coil and the presence or absence of B1 artifacts on the images. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.