Digital Poster
DTI & DWI II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3780.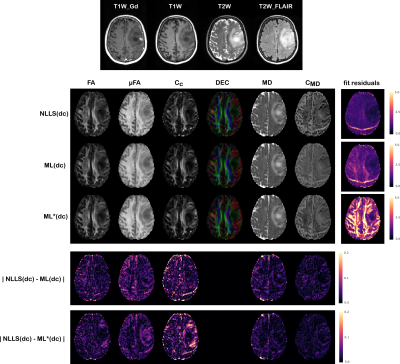 |
21 |
Q-space trajectory imaging with positivity constraints: a
machine learning approach
Deneb Boito1,2 and
Evren Özarslan1,2
1Biomedical Engineering, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2Center for Medical Image Science and Visualization, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden Keywords: Data Processing, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Q-space trajectory imaging (QTI) is a diffusion MRI framework which access features of the microstructure through the statistical moments of the diffusion tensor distribution. To overcome unreliable estimates obtained with standard fitting methods, a constrained estimation framework named QTI+ was recently proposed. Constrained optimization however typically requires sophisticated fitting routines which introduce a heavy computational burden. In this work we thus explore the possibility of speeding up the QTI parameter estimation, while retaining strict positivity constraints, using artificial intelligence. Results are shown on synthetic datasets as well as for healthy subjects and data from brain tumor patients. |
|
3781.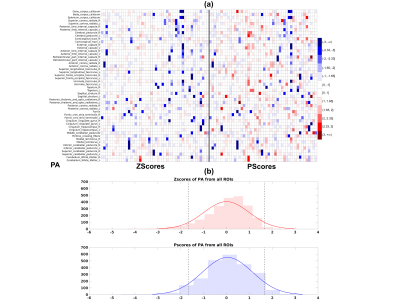 |
22 |
Using ‘P-scores’: a novel percentile-based normalization method
to accurately assess individual deviation in heavily skewed
neuroimaging data
Rakibul Hafiz1,
Amritha Nayak1,2,
M. Okan Irfanoglu1,
Leighton Chan3,
and Carlo Pierpaoli1
1National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, United States, 2Henry Jackson Foundation for Advancement of Military Medicine, Bethesda, MD, United States, 3Rehabilitation Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, United States Keywords: Data Analysis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Quantitative Medical Imaging We propose a novel quantity to correctly assess the extent individuals deviate from the median of a heavy-tailed distribution. We compute a percentile-based score, we call ‘P-score’, which normalizes the deviation of an individual from the sample median by incorporating the individual’s position in the left/right tail of the sample distribution and the corresponding length between the sample median and the 5th/95th percentile edge values of the sample distribution, respectively. We demonstrate the skewness present in diffusion MRI data and the bias introduced when Z-scores are used and further show the control of this bias using the proposed ‘P-scores’ approach. |
|
3782.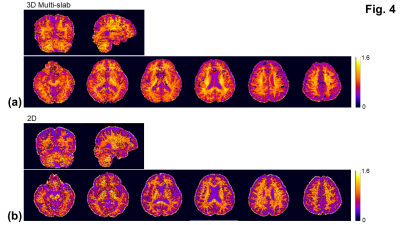 |
23 |
Fast mean kurtosis measurements using navigator-free 3D
multi-slab DWI
Chu-Yu Lee1 and
Merry Mani1
1Department of Radiology, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Kurtosis; Multi-slab; 3D The fast mean kurtosis measurements using 2D DWI has reduced the scan time substantially but remains subject to low SNR, particularly at b-value = 2500 s/mm2. A larger voxel (≥ 2 mm3) is normally used to increase SNR. This study presents the navigator-free 3D multi-slab DWI for fast mean kurtosis measurements with a resolution of 1.5 mm3. By using a short TR of 2.5 sec, the work demonstrates the promise of using the navigator-free 3D multi-slab DWI for whole-brain fast mean kurtosis measurements with an improved SNR efficiency. |
|
3783.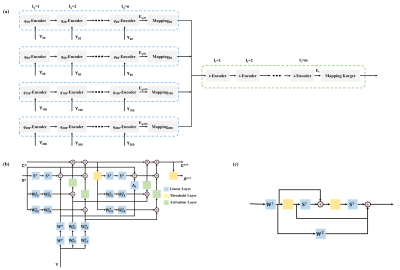 |
24 |
tDKI-Net: a joint q-t space learning network for
diffusion-time-dependent kurtosis imaging and Karger’s model
fitting
Tianshu Zheng1,
Ruicheng Ba1,
Xiaoli Wang2,
Xizhen Wang3,
Chuyang Ye4,
and Dan Wu1
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Biomedical Engineering & Instrument Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, Hangzhou, China, 2School of Medical Imaging, Weifang Medical University, Weifang, Shandong, China, Weifang, China, 3Medical imaging center, Affiliated hospital of Weifang Medical University, Weifang, Shandong, China, Weifang, China, 4School of Integrated Circuits and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, Beijing, China Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Time-dependent diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (TDDMRI) is useful for non-invasive characterization of tissue microstructure. The TDDMRI models require both densely sampled q-space (b-value and diffusion direction) and t-space (diffusion time) data for microstructural fitting, leading to very time-consuming acquisition protocols. In this work, we presented a tDKI-Net to estimate diffusion kurtosis at multiple diffusion times, which was fed into the Karger model to obtain K0 and transmembrane exchange time, using downsampled q-space and t-space data. We tested the proposed network in the normal rat brains, as well as those in a rat model of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. |
|
3784.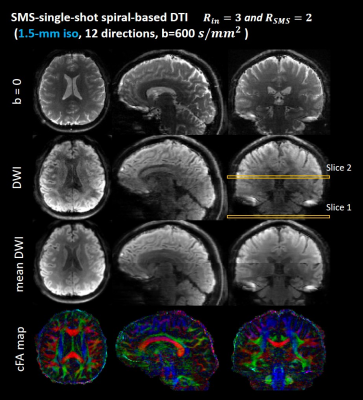 |
25 |
Simultaneous Multi-slice Single-shot Spiral Acquisitions for
Accelerated Diffusion-weighted Imaging
Guangqi Li1,
Yuancheng Jiang1,
and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion Tensor Imaging Single-shot acquisition techniques are commonly used to acquire diffusion-weighted images due to their high sampling efficiency. Single-shot uniform-density spiral sampling combined with in-plane under-sampling has been used to achieve diffusion imaging. In this study, we investigated simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) -accelerated single-shot spiral imaging (SMS-SSH-Spiral) to further improve the scan efficiency of DWI. The in vivo results demonstrate the feasibility of SMS-SSH-Spiral acquisitions for diffusion tensor imaging with 2-fold slice acceleration and 3-fold in-plane acceleration. Diffusion data with 1.5mm isotropic resolution is acquired using our multi-band single-shot acquisition strategy. |
|
3785.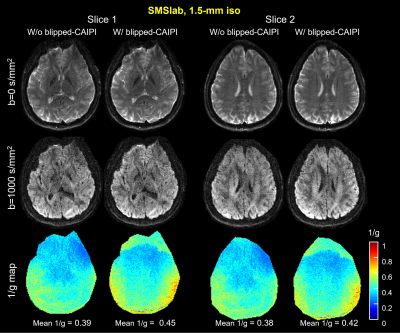 |
26 |
Hybrid-space reconstruction for simultaneous multi-slab DWI with
blipped-CAIPI
Jieying Zhang1,
Simin Liu1,
and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion Tensor Imaging 3D simultaneous multi-slab imaging (SMSlab) can achieve high-resolution DWI with high SNR efficiency. Multi-band acceleration can also achieve less SNR reduction. Recently, we integrated SMSlab DWI with blipped-CAIPI gradients to reduce the g-factor penalty and proposed a 4D k-space framework (kx-ky-kz-km) to model the signal encoding, with km representing the multi-band encoding. Because the blipped-CAIPI gradients are applied along the slice direction, they introduce kz deviations from the nominal k-space location. This study proposed a hybrid-space reconstruction algorithm, REACH, to solve the phase interferences introduced by the blipped-CAIPI gradients. |
|
3786.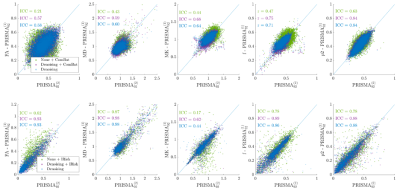 |
27 |
Should We Harmonize or Denoise in Diffusion MRI?
Benjamin Ades-Aron1,
Santiago Coelho1,
Jelle Veraart1,
Timothy M. Shepherd1,
Dmitry S. Novikov1,
and Els Fieremans1
1Radiology, Center for biomedical imaging, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States Keywords: Data Processing, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Harmonization Denoising To address the ongoing reproducibility crisis in quantitative diffusion MRI (dMRI), efforts are underway to harmonize and improve precision of diffusion parameter estimation. Using inter- and intra-scanner test-retest higher order dMRI, we compare the reproducibility of two popular harmonization methods, ComBat and linear-RISH, to that of denoising using MPPCA on complex-valued dMRI. We find that denoising combined with harmonization improves voxel-wise test-retest ICC by up to 60% compared to harmonization alone. Using dMRI at different voxel sizes, we find that denoising reduces the bias due to varying noise floors more accurately than harmonization. Denoising appears essential to harmonize dMRI datasets. |
|
3787.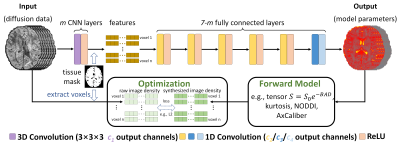 |
28 |
DIMOND:DIffusion Model OptimizatioN with Deep learning
Zihan Li1,
Berkin Bilgic2,3,
Hong-Hsi Lee2,3,
Kui Ying4,
Hongen Liao1,
Susie Huang2,3,
and Qiyuan Tian2,3
1Department of biomedical engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 3Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 4Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques The accurate estimation of diffusion model parameter values using non-linear optimization is time-consuming. Supervised learning methods using neural networks (NNs) are faster and more accurate but require external ground-truth data for training. A unified and self-supervised learning-based diffusion model estimation method DIMOND is proposed. DIMOND maps diffusion data to model parameter values using NNs, synthesizes the input data from the predictions using the forward model, and minimizes the difference between the raw and synthetic data. DIMOND outperforms conventional ordinary least square regression (OLS) and has a high potential to improve and accelerate data fitting for more complicated diffusion models. |
|
3788.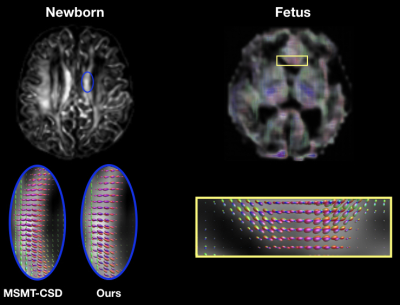 |
29 |
Learning diffusion MRI fiber orientation distribution functions
of the developing human brain
Hamza Kebiri1,2,
Ali Gholipour2,
Davood Karimi2,
and Meritxell Bach Cuadra1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging & Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Harvard Medical School & Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Fiber Orientation Distribution functions Diffusion MRI of fetal and newborn brains is constrained by short scanning time allowing only a small number of diffusion measurements to be acquired. Methods going beyond the diffusion tensor model require multi-shell and multiple gradient directions in order to unveil more accurate white matter properties. We propose a learning based framework to reconstruct fiber orientation distribution functions from only six diffusion measurements by leveraging existing high-quality datasets. Quantitative evaluation on 15 newborn subjects show that our framework achieves competitive results with state-of-the-art methods. Qualitative evaluation on a fetus shows the model ability to translate to this challenging population. |
|
3789.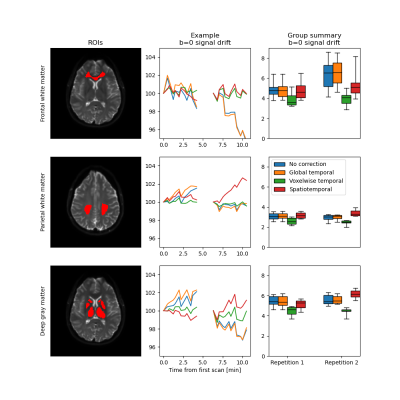 |
30 |
Spatiotemporal signal drift in diffusion MRI of the brain and
ways to correct for it: effects on estimates of ADC and IVIM f
Oscar Jalnefjord1,2,
Amina Warsame1,
and Louise Rosenqvist1
1Department of Medical Sciences, Institute of Clinical Sciences, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden Keywords: Data Processing, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Signal drift has been identified as a confounding factor in diffusion MRI (dMRI), causing increases variance and potential bias in derived parameter maps. In this work, we show that temporal signal drift is spatially dependent in human brain images for dMRI, thus calling for spatiotemporal corrections. We also show that signal drift can have a substantial effect on short-term repeatability of ADC and IVIM f obtained from data acquired with a protocol ordered by b-value as is commonly done in clinical practice. |
|
3790.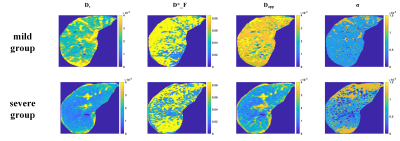 |
31 |
Chronic liver disease: The role of multiple diffusion-weighted
models using the Bayesian shrinkage method for liver fibrosis
assessment
Jiqing Huang1,
Benjamin Leporq1,
Olivier Beuf1,
and Hélène Ratiney1
1Univ Lyon, INSA Lyon, CNRS, Inserm, CREATIS UMR 5220, U1206, F-69621, Lyon, Villeurbanne, France Keywords: Data Processing, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Liver fibrosis is one of the leading features in chronic liver disease (CLD) since it conditions the prognosis and guides the treatment strategy. In this work, estimated parameters from various diffusion-weighted MRI models fitted by the Bayesian method were analyzed for the relationship with liver fibrosis through spearman’s correlation and t-test. Four parameters (Ds, σ, D*_F, Dapp) were selected for fibrosis classification and achieved the best result based on the decision tree. Our result suggested that the statistical model and a hybrid IVIM-DKI model are promising models and confirmed the confounding effect of fat for diffusivity to assess liver fibrosis. |
|
3791.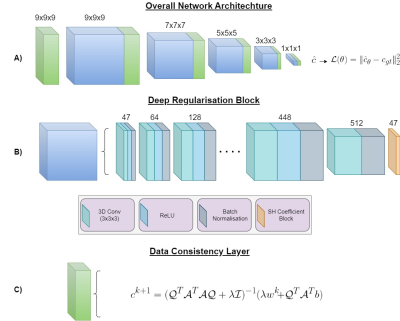 |
32 |
Recovering high quality FODs from reduced number of diffusion
weighted images using a model-driven deep learning architecture
Joseph Bartlett1,2,3,
Catherine Davey1,2,
Leigh Johnston1,2,
and Jinming Duan3,4
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 2Melbourne Brain Centre Imaging Unit, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 3School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 4Alan Turing Institute, London, United Kingdom Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques SDNet utilises the learning ability of deep neural networks with the robustness of model-based approaches to produce high quality fibre orientation distributions (FODs) from a reduced set of multi-shell diffusion weighted images (DWI). The cascaded architecture, with data consistency layers throughout, makes use of model based prior knowledge and spatial correlations within the DWI signal to achieve state-of-the-art performance in both sum of squared errors and angular correlation coefficient. Our model also shows competitive results with respect to apparent fibre density error and peak amplitude error over a range of regions of interest. |
|
3792.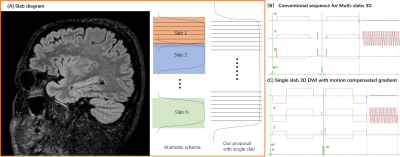 |
33 |
3D Isotropic and high resolution whole brain DWI with single
slab and single shot EPI utilizing motion compensated diffusion
gradients
Zhigang Wu1,
Yajing Zhang2,
Gilbert Guillaume3,
Wengu Su4,
Yan Zhao5,
and Jiazheng Wang6
1Philips Healthcare, Shenzhen, Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 2Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 3MR Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Mississauga, ON, Canada, 4BU MR Application, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 5BU MR R&D, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 6Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Pulse Sequence Design, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Pulse Sequence Design, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Diffusion, 3D 3D Diffusion imaging (3D DWI) has showed great potential in probing tissue microstructure and brain structural connectivity. However, motion-induced phase errors introduced by diffusion gradients will cause severe artifacts in 3D DWI. Multi-slab can be used to overcome this limitation, but it will introduce slab boundary artifacts. We propose a method which utilizes motion-compensated diffusion gradients for 3D DWI to mitigate the phase error between shots. Results from in vivo data demonstrate the proposed method can improve image quality and realize an isotropic high resolution and whole brain 3D DWI in a single slab. |
|
3793.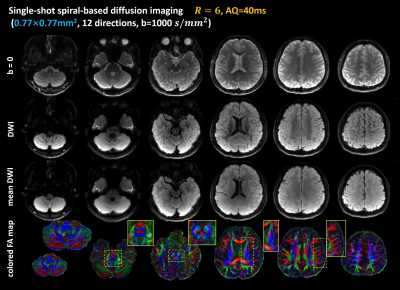 |
34 |
Sub-millimeter Diffusion Tensor Imaging using Single-Shot Spiral
Acquisitions with a Large Acceleration Factor
Guangqi Li1,
Xinyu Ye1,
Yuan Lian1,
Yajing Zhang2,
and Hua Guo1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2MR Clinical Science, Philips Health Technology (China), Beijing, China Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion Tensor Imaging Single-shot spiral acquisitions allow shorter TE, thus provide higher SNR compared to EPI acquisitions for DWI. However, spiral acquisitions are sensitive to field inhomogeneity. Parallel imaging techniques can be used to alleviate static B0 off-resonance effects. In this study, single-shot spiral acquisitions with a large acceleration factor of 5 or 6 were used to achieve sub-millimeter diffusion tensor imaging at 3T. The in vivo results demonstrate that the single-shot spiral sampling strategy can be adopted to achieve whole-brain diffusion tensor imaging with an in-plane resolution of 0.77×0.77mm2. |
|
3794.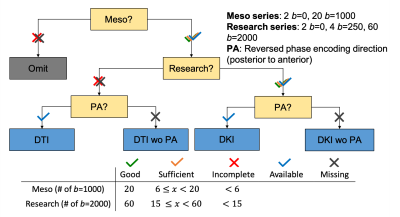 |
35 |
Higher-order diffusion MRI data acquired in clinical settings:
what are the pitfalls, and how to correct them?
Jenny Chen1,
Benjamin Ades-Aron1,
Saurabh Maithani1,
Yvonne Lui1,
Dmitry S. Novikov1,
Jelle Veraart1,
and Els Fieremans1
1New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Clinical Translation, DKI Multi-shell diffusion MRI (dMRI) opens up the opportunity for microstructure mapping, but is not routinely acquired in clinics. This study retrospectively analyzed a large diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) dataset (N=7984) acquired as multi-series in the clinic and proposes a workflow to inspect the data before preprocessing. Automated analysis of dicom headers shows about 36% with incomplete acquisition, likely due to time constraints and patient discomfort, and 32% with image discrepancies. Finally, we show that signal variations between series occur and need to be corrected for in preprocessing. Our results indicate higher-order dMRI in the clinical setting is feasible. |
|
3795.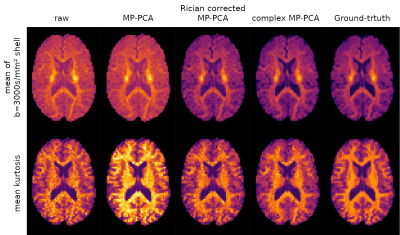 |
36 |
Iterative model-based Rician bias correction and its application
to denoising in diffusion MRI
J-Donald Tournier1,2,
Ben Jeurissen3,4,
and Daan Christiaens5,6
1Biomedical Engineering, School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Centre for the Developing Brain, School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 3imec-Vision Lab, Department of Physics, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium, 4Lab for Equilibrium Investigations and Aerospace, Department of Physics, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium, 5Medical Imaging Research Center, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 6Department of Electrical Engineering, ESAT/PSI, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Keywords: Data Analysis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Rician bias is a long-standing problem in diffusion MRI. We propose a simple iterative strategy to mitigate the problem when a voxel-wise model of the signal is available, and demonstrate its efficacy when fitting spherical harmonics and when included in a denoising strategy. |
|
3796.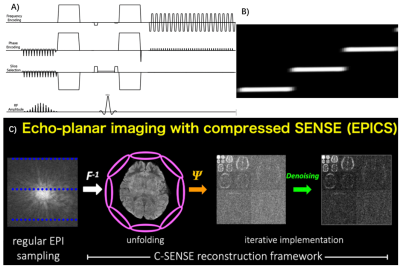 |
37 |
Noise and distortion reduction for Reduced FOV diffusion
utilizing Compressed SENSE framework for single shot EPI (EPICS)
Zhigang Wu1,
Yajing Zhang2,
Wengu Su3,
Masami Yoneyama4,
Peng Sun5,
Jing Zhang6,
Yan Zhao7,
and Jiazheng Wang5
1Philips Healthcare, Shenzhen, Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 2Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 3BU MR Application, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 4BU MR Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan, 5Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 6MR Clinical Application, Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 7BU MR R&D, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Reduced FOV, Compressed SENSE DWI is very important for MRI examination, but it has limited resolution due to distortion, blurring, and signal loss caused by B0 inhomogeneity. Reduced FOV imaging could decrease these impacts. However, due to the coil geometry penalty, it’s hard to combine it with parallel imaging to further improve the image quality, it will suffer from noise breakthrough issues and unfolding artifacts. We propose a framework that combines reduced FOV imaging, Compressed SENSE framework simultaneously to overcome these issues. This framework allows a new solution for reduced FOV based diffusion imaging with high resolution, low distortion, and without noise breakthrough issue. |
|
3797.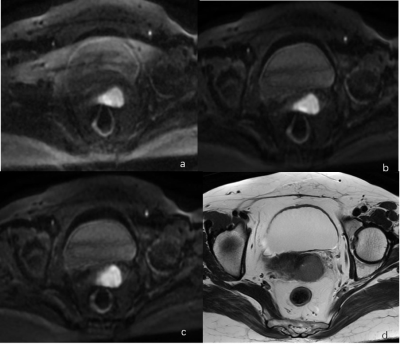 |
38 |
Value of Reversed Polarity Gradients and Multiplexed Sensitivity
Encoding in improving diffusion weighted imaging quality of
uterus
Wenjuan Wang1,
Wenjing Zhao1,
and Dmytro Pylypenko2
1Department of Radiology, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, China, 2MR Research China, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Artifacts, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, multiplexed sensitivity encoding, reversed polarity gradients The aim of this study is to investigate the application of multiplexed sensitivity encoding diffusion weighted imaging with reversed polarity gradients in improving the image quality of uterine tumors. 10 patients with uterine lesions in our hospital were enrolled. Conventional SS-EPI DWI, MUSE DWI, and RPG-MUSE DWI sequences were employed. The subjective image quality assessment and objective data measurement of uterine lesions scanned by different DWI sequence was evaluated by three radiologists using double-blind method. The results of this study showed that RPG-MUSE DWI can greatly improve the image quality of the uterus. |
|
3798.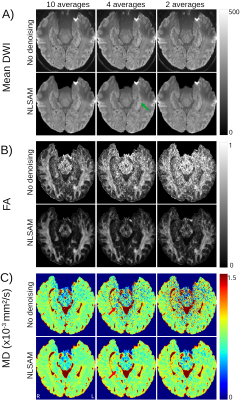 |
39 |
Denoising Enables Faster 1 mm Isotropic Diffusion Tensor Imaging
of the Human Hippocampus at 3T
Pablo Stack-Sanchez1,
Donald Gross2,
and Christian Beaulieu1
1Biomedical Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2Neurology, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada Keywords: Data Processing, Diffusion Tensor Imaging A hippocampus-focused, 1 mm isotropic, diffusion tensor imaging 5.5 minutes 3T protocol has yielded high-quality diffusion images and maps. Post-processing with denoising can potentially reduce the scan time considerably. Compared to the previously used 10 direction/10 average protocol, denoising enabled the use of 4 averages for a scan time of only 2.2 minutes to yield acceptable 1 mm isotropic diffusion image quality and mean diffusivity maps (MD) of the whole hippocampus in healthy controls. This rapid protocol was then able to delineate focal and small hippocampal lesions with elevated MD in temporal lobe epilepsy patients. |
|
3799.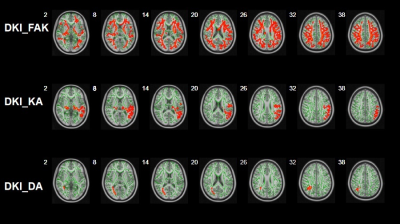 |
40 |
Application of machine learning with Tract-Based Spatial
Statistics in the diagnosis of pediatric autism
Xiongpeng He1,
Xiaoan Zhang1,
Xin Zhao1,
Yongbin Sun2,
Pengfei Geng1,
and Kaiyu Wang3
1Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, zhengzhou, China, 2Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, zhengzhou, China, 3MR Research China, GE Healthcare, Beijing 100000, PR China, Beijing, China Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Tract-Based Spatial Statistics Early and accurate diagnosis of pediatric autism was difficult for clinicians, which hindered the timely treatment of patients.This study aimed to explore the applicability of machine learning models of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) based on Tract-Based Spatial Statistics to diagnose pediatric autism. Results showed that DKI parameter was potential for differentiating early autism from the normal. And the machine learning models can be used for early detection of pediatric autism with high accuracy and sensitivity.
|
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.