Digital Poster
Cardiomyopathy II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
4830.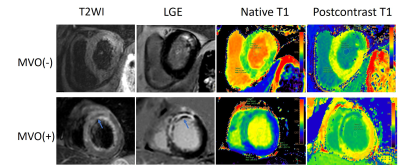 |
61 |
Predictive value of total ischemic time and T1 mapping after
emergency PCI in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial
infarction
Jiali Wang1,
Kai Xu1,
Chunfeng Hu1,
Yankai Meng1,
Shuguang Han1,
Yuan Lu1,
Peng Wu2,
Lu Han2,
and Yongzhou Xu3
1The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China Keywords: Myocardium, Ischemia, T1 mapping ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, effective risk stratification is crucial for the management of STEMI. This study sought to investigate the predictive value of total ischemic time (symptom onset to balloon, S2B), native T1 and extracellular volume (ECV) in STEMI patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). We found regardless of microvascular obstruction (MVO) or not, ECV in myocardial infarction (ECVMI) was significantly correlated with S2B time, while native T1 was not. In the 4-month follow-up, ECVMI was independently associated with final larger infarct size in multivariable regression analysis. |
|
4831.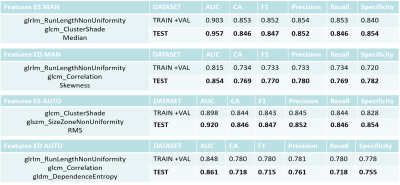 |
62 |
Radiomics of non-contrast bSSFP cine short axis images performs
better with end-systolic images in distinguishing infarct and
control subjects
Tom Dresselaers1,2,
Baptiste Vande Berg1,
Sofie Tilborghs3,4,
Alexandru Cernicanu5,
and Jan Bogaert1,2
1Radiology, UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2Dept. of Imaging and Pathology, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 3Department of Electrical Engineering (ESAT), KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 4Medical Imaging Research Center, UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 5Philips Benelux, Eindhoven, Netherlands Keywords: Heart, Radiomics Several studies suggest that radiomics of non-contrast cine balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) images allows to detect myocardial infarct patients. Relevant radiomic features vary however without clear knowledge of the underlying causes. Most studies rely on time consuming manual contouring on use end-diastolic images while it was shown that features vary through the heart cycle. In this study we show that radiomics of end-systolic images result in a higher classification accuracy than for end-diastolic images and produce the same result when relying on commercial automated contouring. |
|
| 4832. | 63 |
Fully automated 16- and 32-segmentation quantitative perfusion
CMR in detection of obstructive coronary artery disease
Sonia Borodzicz-Jazdzyk1,2,
Roel Hoek1,
Caitlin Vink1,
Luuk Hopman1,
Mark Hofman3,
Yvemarie Somsen1,
Ruben de Winter1,
Paul Knaapen1,
Mitchel Benovoy4,
and Marco Gotte1
1Department of Cardiology, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 21st Chair and Department of Cardiology,, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland, 3Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 4Area19 Medical Inc, Montreal, QC, Canada Keywords: Atherosclerosis, Perfusion Recently, a fully automated QP CMR workflow has been established, which provides measures of stress MBF according to a 32-segmentation model with subdivision into endo- and epicardial subsegments. We compared the diagnostic accuracy of QP CMR according to the standard AHA 16-segment model (16M-QP) and the newly developed automated 32-segment model (32M-QP) with conventional visual assessment in patients who underwent adenosine stress perfusion CMR imaging followed by invasive coronary angiography and/or coronary computed tomography angiography. Our preliminary data have not shown superiority of diagnostic accuracy of 16M-QP or 32M-QP in comparison to visual assessment of adenosine stress first-pass perfusion imaging. |
|
4833.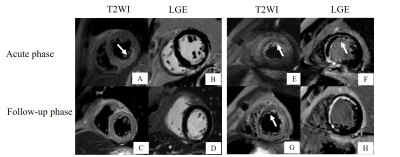 |
64 |
Delays in first medical contact to primary interventional
therapy and left ventricular remodeling in myocardial infarction
Jiali Wang1,
Kai Xu1,
Chunfeng Hu1,
Yankai Meng1,
Shuguang Han1,
Yuan Lu1,
Peng Wu2,
Lu Han2,
and Yongzhou Xu3
1The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China Keywords: Myocardium, Ischemia Early reperfusion and early evaluation of cardiac adverse left ventricular remodeling (ALVR) have become important aspects of treatment for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) post-percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The aim of this study was to investigate the predictive value of emergency medical service (EMS) delays on the severity of myocardial injury in STEMI patients after PCI. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) cine, myocardial strain, and scar characteristics were analyzed. The first medical contact to balloon (FMC2B) time was recorded. FMC2B time > 90 min led to poor recovery of cardiac function and was an independent predictor of ALVR. |
|
4834.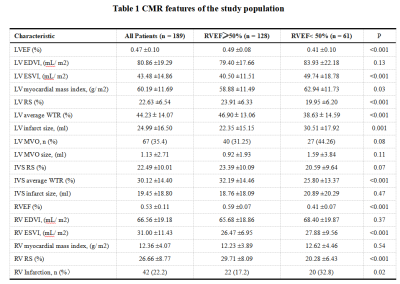 |
65 |
Based on cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging for
predicting right ventricular dysfunction in STEMI patients by
Machine learning
Yanan Zhao1,
Jianing Cui1,
Xiuzheng Yue2,
Sicong Huang2,
Yun Kang2,
and Tao Li1
1Department of Radiology, The First Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare(Beijing), Beijing, China Keywords: Heart, Heart, right ventricular dysfunction; machine learning techniques; ST-Segment-Elevation myocardial infarction In clinical work, right ventricular (RV) dysfunction has been ignored in acute ST-Segment-Elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients. And previous studies have shown the interaction between left ventricular (LV) and RV. The aim of this study was to assess RV function by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT) and to explore what factors affect RV dysfunction by machine learning techniques. The results showed that the incidence of RV dysfunction was 32.28% in STEMI patients and the occurrence of RV dysfunction was associated with RV end-systolic volume index, LV ejection fraction (EF), and interventricular septum radial strain by machine learning technique. |
|
4835. |
66 |
Non-enhanced Multi-contrast 3D Whole-heart MRI for Assessment of
Reperfusion Injury in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
Xin Liu1,
Lu Liang1,
Jing An2,
Chen Zhang3,
Karl-Philipp Kunze4,
Radhouene Neji4,
René M Botnar5,
Claudia Prieto5,
and Qi Yang1
1Radiology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 3China MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China, 4MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Limited, Camberley, United Kingdom, 5School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom Keywords: Myocardium, Myocardium Bright- and black-blood MRI sequences provide multi-contrast information for myocardial assessment in patients with acute ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). A free-breathing 3D whole-heart bright-blood and black-blood phase sensitive (BOOST) inversion recovery sequence has been recently proposed for a simultaneous multi-contrast high-quality depiction of cardiac and vascular structures without contrast agent injection. In this study, we applied this sequence to visualize reperfusion injury in 10 patients with STEMI. Good agreement in microvascular obstruction (MVO) and intramyocardial hemorrhage (IMH) visualization was observed between the proposed approach and traditional 2D imaging methods in patients, promising potential integration into clinical treatment workflow. |
|
4836.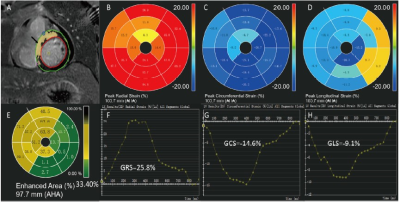 |
67 |
Predictive value of myocardial strain on myocardial infarction
size in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction with
preserved LVEF
Bin Li1,2,
Guohai Su1,2,
Qiang Wang1,
Jian Wang3,
Xiuzheng Yue4,
Yingjie Ma1,
Peng Wang1,
Yang Li1,
and Jing Tian1
1Department of Cardiology, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China, 2Research Center of Translational Medicine, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China, 3Department of Radiology, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, Beijing, China Keywords: Myocardium, Cardiovascular, Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction With the development of the emergency system, we can see more and more acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.the predictive value of myocardial strain as determined by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) for myocardial infarct size could not been clarified by previous investigations in STEMI patients with preserved LVEF. The present study reveals incremental value of global circumferential strain (GCS), determined by CMR, for the prediction of infarction size after STEMI, above and beyond LVEF as well as global longitudinal strains. The findings of this study suggest that GCS may represents a potential marker of infarct size and may be used to better guide drug therapy. It may be beneficial to use GCS to determine the infarct size and prognosis of post-MI patients who do not qualify for contrast imaging. |
|
4837. |
68 |
Imaging reactive oxygen species and tissue iron in
ischemia-reperfusion injury in swine with multimodal
[18F]ROStrace PET/CT and QSM
Sophia Swago1,
Elizabeth W. Thompson1,
Annefleur Loth2,
Abhijit Bhattaru3,
Brianna F. Moon1,
Giovanni Ferrari4,
Estibaliz Castillero4,
Victor A. Ferrari5,
Robert Gorman6,
Cory Tschabrunn7,
Robert Mach3,
Joel Karp3,
Walter R. Witschey3,
and Paco Bravo3
1Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Amsterdam Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam (AMC-UvA), Amsterdam, Netherlands, 3Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 4Department of Surgery, Columbia University, New York City, NY, United States, 5Department of Medicine and Penn Cardiovascular Institute, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 6Department of Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 7Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States Keywords: Myocardium, Ischemia Additional myocardial injury can occur after reestablishing blood flow post ischemia. We use a multimodal protocol of sequential quantitative susceptibility mapping and positron emission tomography to directly image reactive oxygen species (ROS) and tissue iron in vivo in pig hearts after ischemic injury. We found that ROS was increased in infarct compared to remote regions of the myocardium in all animals. In an animal with microvascular obstruction, we observed an increase in susceptibility measured by QSM in the infarct region, indicating increased tissue iron, but no increased susceptibility was seen in the animals without microvascular obstruction. |
|
4838.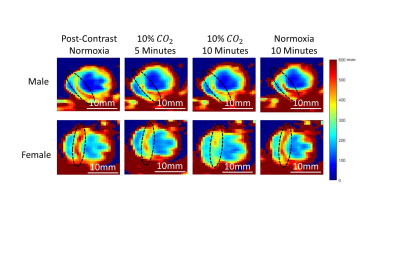 |
69 |
Assessing Myocardial Microvascular Reactivity with a Novel MRI
Blood-Pool Imaging Approach
Sadi Loai1,2,
Beiping Qiang3,
Michael A. Laflamme3,4,5,
and Hai-Ling Margaret Cheng1,2,6
1Institute of Biomedical Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2Translational Biology & Engineering Program, Ted Rogers Centre for Heart Research, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3McEwen Stem Cell Institute, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Laboratory of Medicine and Pathobiology, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada Keywords: Vessels, Perfusion Coronary microvascular dysfunction is driven by vascular inflammation and can go undetected for years. Current imaging diagnostics lack the ability to quantify microvascular vasomodulation, a potential biomarker for cardiac diseases dominated by microvascular disease. We propose a novel MRI approach that utilizes elevated carbon dioxide and a blood-pool contrast agent to quantify changes in microvascular blood volume. Our results confirmed hypercapnia caused strong vasodilation within female myocardium but no response in males. Transitioning from hypercapnia to room air elicited strong vasoconstriction in both sexes. This technology will be valuable for early detection of microvascular dysfunction in various diseases.
|
|
4839.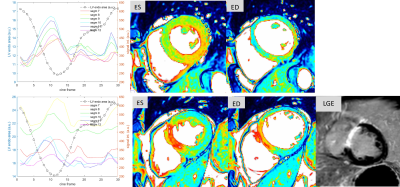 |
70 |
Do myocardial balanced steady-state free precession signal
intensity curves allow to distinguish infarct patients from
healthy subjects?
Tom Dresselaers1,2,
Baptiste Vande Berg1,
Sofie Tilborghs3,4,
Alexandru Cernicanu5,
and Jan Bogaert1,2
1Radiology, UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2Dept. of Imaging and Pathology, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 3Department of Electrical Engineering (ESAT), KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 4Medical Imaging Research Center, UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 5Philips Benelux, Eindhoven, Netherlands Keywords: Myocardium, Cardiomyopathy, infarction Pre-contrast balanced steady-state free precession (bssfp) cine images seem to contain sufficient information to identify patients with an acute or chronic myocardial infarction using radiomics or deep learning methods. The reason remains however to be elucidated. It is also unclear if the cardiac phase should be considered although radiomics features vary through the heart cycle. In this study we show that the known global myocardial bssfp signal intensity variations observed in healthy subject are in fact segment dependent and have a reproducible three peak profile. In patients with acute myocardial infarct these profiles shows segment dependent alterations vs. controls. |
|
4840.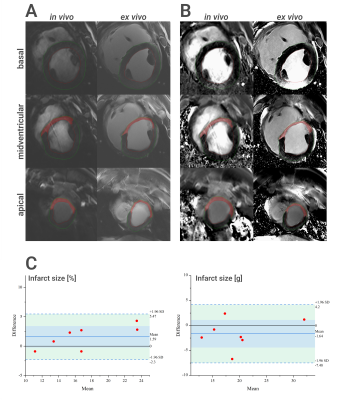 |
71 |
Semi-automatic scar size quantification in late gadolinium
enhancement of acute to chronic myocardial infarction in a
porcine model scanned at 7T
Alena Kollmann1,
David Lohr1,
Maya Bille1,
Maxim Terekhov1,
Michael Hock1,
Ibrahim Elabyad1,
Florian Schnitter2,
Wolfgang Bauer1,2,
Ulrich Hofmann2,
and Laura Maria Schreiber1
1Chair of Molecular and Cellular Imaging, Comprehensive Heart Failure Center (CHFC), University Hospital Wuerzburg, Wuerzburg, Germany, 2Department of Internal Medicine I, University Hospital Wuerzburg, Wuerzburg, Germany Keywords: Myocardium, Ischemia Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) is considered the gold standard for the quantification of scar size. We tested in a large animal model of acute and chronic infarction if clinically used methods for the assessment of infarct size (manual planimetry and several semi-automatic approaches) in LGE images are applicable to preclinical 7T LGE imaging of porcine hearts. We found excellent intra-observer reproducibility for all methods. The tested semi-automatic methods performed differently on magnitude (MAG) and phase-sensitive inversion recovery (PSIR) images. Overall, infarct sizes measured in in vivo scans showed good correlation to ex vivo LGE measurements. |
|
4841.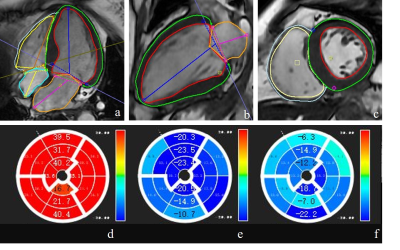 |
72 |
Strain may reflect cardiac segments with high coronary artery
calcium score and the risk of myocadiac ischemia
Xuefang Lu1,
Weiyin Vivian Liu2,
Guangnan Quan3,
Changsheng Liu1,
Yuchen Yan1,
Wei Gong1,
Yilin Zhao1,
Zhoufeng Peng1,
and Yunfei Zha1
1Department of Radiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Myocardium, Ischemia, strain Preclinical disease is primarily assessed through the coronary artery calcium score (CACS) and used for risk assessment. Our study demonstrated that the moderate correlation of the CACS and strain, suggesting atrial or ventricular myocardium and vascular changes influence each other. In addition, there were statistically different strain values between CAD and non-CAD patients. Strain analysis for cine CMR can add functional information such as chamber wall movement on early prediction of myocardium abnormities like myocadiac ischemia and be beneficial to patients who receive one-stop check-ups for less imaging time, no contrast, and radiation-free screening. |
|
4842.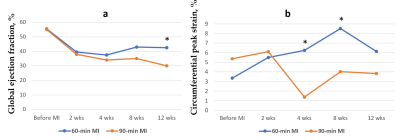 |
73 |
New Tagging MRI Method is More Sensitive than Ejection Fraction
for Assessment of Contractile Function Recovery in Infarcted Pig
Hearts
Anna V Naumova1 and
William S Kerwin1
1Radiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States Keywords: Myocardium, Heart, myocardial infarction A new tagging method has been proved as a sensitive approach for assessment of regional deformation in the infarcted pig’s heart. The linear tags were placed in 60-degree pattern offsets and aligned with the AHA segments. The tagging analysis algorithm uses local Fourier transformation of the isolated spectral peaks. We have shown the temporal changes in circumferential strain of the infarcted segments of myocardium and faster recovery of myocardial strain followed by 60-min ischemia-reperfusion injury in comparison with 90-min. Circumferential strain was a more sensitive parameter for earlier detection of regional contractile dysfunction in comparison with ejection fraction. |
|
4843.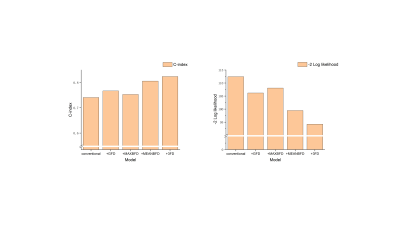 |
74 |
Fractal Analysis of Left Ventricular Trabeculae in HFpEF
Patients with Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease
Zi-Yi Gu1,
Wei-Bo Chen2,
Yong-Yi Wang1,
and Lian-Ming Wu3
1Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Affiliated Renji Hospital, Shanghai, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Department of Radiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Affiliated Renji Hospital, Shanghai, China Keywords: Heart, Heart, HFpEF HFpEF patients with multivessel CAD have changes in myocardial trabecular complexity. The left ventricular FD obtained with fractal analysis can reflect the complexity of myocardial trabecular and has an independent predictive value for the diagnosis of HFpEF in patients with multivessel CAD. Including FD into the diagnostic model can help improve the diagnosis. |
|
4844.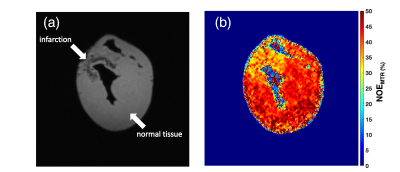 |
75 |
Tracking lipid and macromolecular changes in Ex-vivo hearts
using NOEMTR and rNOE at 7T
Blake Benyard1,
Sophia Swago 1,
Neil E. Wilson1,
Paul S. Jacobs1,
Walter Witschey1,
Mohammed Harris1,
and Ravinder Reddy1
1Center for Advanced Metabolic Imaging in Precision Medicine (CAMIPM), Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States Keywords: Myocardium, Heart, CEST & MT Two ex-vivo animal hearts were scanned at 7T to track lipid and macromolecular changes using NOEMTR and rNOE. Data was acquired on a fresh lamb heart and a healthy Yorkshire swine with an anteroseptal infarct by occlusion of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery. After performing a multi-pool analysis, it is demonstrated that the NOEMTR and rNOE signal decreases in the infarcted region of the swine heart compared to the normal tissue and lamb heart. |
|
4845.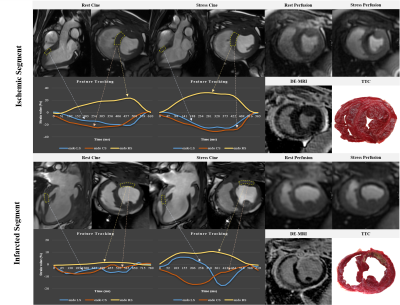 |
76 |
Vasodilator Stress Myocardial Strain in Coronary Artery
Disease:An Animal Study With Histological Validation
Jing Xu1,
Zhao Shihua1,
and Minjie Lu1
1Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College Fuwai Hospital, Beijing, China Keywords: Myocardium, Heart ATP can cause a pronounced positive inotropic effect on human heart. CMR-FT even at rest provides an excellent negative predictive value for myocardial ischemia and infarction in patients with CAD. CMR-FT is easy to perform without the need for dedicated acquisition and complex post-processing which can be applied to standard CMR cine sequences. Rest myocardial strain might be a noninvasive option serving as an additional gatekeeper for CAD patients with a needle-free test. Human studies are needed to validate these findings in a multicenter setting and to test whether CMR-FT can be incorporated into clinical guidelines. |
|
4846.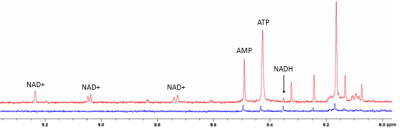 |
77 |
1H NMR of downfield metabolites in swine heart after myocardial
infarction
Sophia Swago1,
Jacob Smothers2,
Neil E. Wilson3,
Mark A. Elliott3,
Ravi Prakash Reddy Nanga3,
Robert Gorman4,
Cory Tschabrunn5,
Arjun Sengupta6,
Aalim Weljie6,
Ravinder Reddy3,
and Walter R. Witschey3
1Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Department of Chemistry, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, United States, 3Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 4Department of Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 5Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 6School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States Keywords: Myocardium, Spectroscopy Growing interest into in vivo 1H MRS of downfield metabolites (>4.7 ppm) has necessitated greater understanding of the metabolite contributions of peaks found in the downfield. 1H NMR provides high-SNR, high-spectral resolution data that can aid in the identification of metabolite resonances. We collected downfield NMR spectra at 700 MHz from infarct and remote myocardium extract of pig hearts after myocardial infarction. We were able to assign peaks to NAD+, NADH, ATP, and AMP in the downfield region and quantified these metabolites in infarct and remote myocardium. |
|
4847.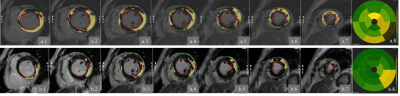 |
78 |
A clinical application of deep learning reconstructed LGE
combined with coronary calcification scoring in coronary artery
disease
Xuefang Lu1,
Yuchen Yan1,
Weiyin Vivian Liu2,
Changsheng Liu1,
Wei Gong1,
Yan Wang1,
Zhoufeng Peng1,
Guangnan Quan3,
and Yunfei Zha1
1Department of Radiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, 3General Electric Medical (China) Co, Beijing, China Keywords: Myocardium, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, late gadolinum enhancement Preclinical disease is primarily assessed through the coronary artery calcium score (CACS) and used for risk assessment, screening CACS is a reliable indicator for the assessment of coronary artery disease in our study, FWHM analysis of PSMDEDL and PSMDEO showed moderate correlation between the percentage of enhancement area and CACS, beneficial for check-up with less imaging time and low radiation screening. This finding should be further validated in a larger sample size. Moreover, threshold techniques such as 2SD to 5SD were sensitive to signal intensity and should be concerned for analysis on deep-learning reconstructed images, especially missing detection rate. |
|
4848.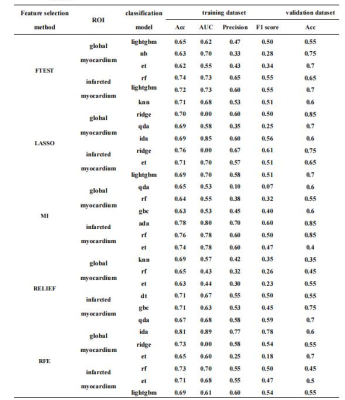 |
79 |
Comparison of 17 machine-learning models derived from LGE-MRI
for predicting reverse LV remodeling in patients with STEMI
Jianing Cui1,
Tao Li1,
Xiuzheng Yue2,
Sicong Huang2,
Yun Kang2,
and Fei Yan1
1Radiology, the First Medical center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Heart, Heart, reverse left ventricular remodeling Radiomics is an emerging quantitative imaging method that could extract mineable high-dimensional data from medical images. We investigate the suitable models and significant radiomics features of LGE images in participants with STEMI and assess their value in predicting r-LVR. We chose 17 classification models to analyze all the adiomics features of LGE images in participants with STEMI. Our study found that the model of extra tree classifier was manifested relatively high AUC value in predicting r-LVR. The wavelet-HHH_gldm_SmallDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis was relatively strong predictor of r-LVR. |
|
4849.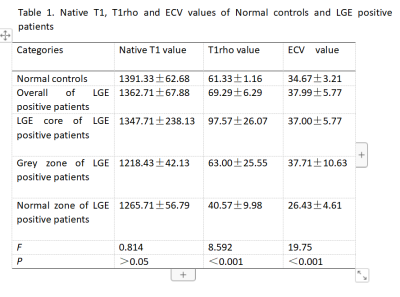 |
80 |
T1rho was used to monitor myocardial changes in patients with
CAD
Yanbing Yang1,
Xiuzheng YUE2,
Fang Wang3,
and Yishi Wang2
1People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, yinchuan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, beijing, China, 3People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, yinchaung, China Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Cardiomyopathy The current reference standard for detection of myocardial scar tissue is late gadolinium enhancement(LGE). Cardiac magnetic resonance T 1 mapping is a technique that enables quantification of extracellular volume fraction (ECV). Calculating ECV mapping need to inject gadolinium contrast agent, which may be contraindicated in some patients. For those patients, T1rho contrast may help them find the changes in myocardial because T1rho MRI has been used to detect early myocardial infraction in swine model. In this study, we used T1rho to assess myocardial changes in patients with early CHD with a view to finding Grey zone of LGE positive patients. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.