Digital Poster
Hyperpolarized 129Xe MR
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
4495.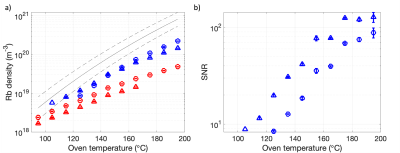 |
61 |
Investigating Rb vapor density and temperature distributions in
a high throughput 129Xe-Rb polarizer
James E. Ball1,
Jim M. Wild1,
and Graham Norquay1
1University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Hyperpolarized MR (Gas) Accurate knowledge of the Rb vapor density, [Rb], is essential for optimizing 129Xe polarization (PXe) and production rates in clinical-scale 129Xe-Rb SEOP hyperpolarizers, used for hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI. We used atomic absorption spectroscopy to measure [Rb] for multiple Rb transitions to assess [Rb] measurement accuracy and extend [Rb] measurement range sensitivity. It was shown that [Rb] is significantly lower than saturation [Rb] and that [Rb] homogeneity was improved by implementing a larger Rb source distribution or a presaturator. The 129Xe-Rb spin-exchange cross section, $$$\gamma^\prime$$$, was determined to be $$$\gamma^\prime$$$= (1.2± 0.1) ×10−21m3s−1 for our operating conditions. |
|
4496.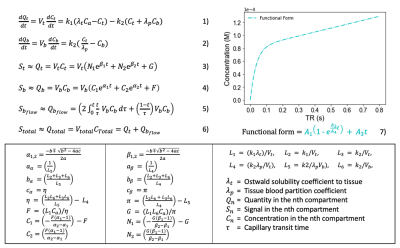 |
62 |
A novel compartmental model of 129Xe gas exchange using blind
estimation of blood concentration
Yohn Taylor1,
Geoffrey J. M. Parker1,2,
Mina Kim1,
and Pilar Jimenez-royo3
1Centre for Medical Image Computing, Quantitative Imaging Group, Department of Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Bioxydyn Limited, Manchester, United Kingdom, 3GlaxoSmithKline, Stevenege, United Kingdom Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Modelling, Blind deconvolution Preclinical to clinical translation of pulmonary gas exchange measurements utilising hyperpolarised 129Xe MRI is limited by the overlapping spectral peaks of dissolved 129Xe MR red blood cell (RBC) and tissue compartments in some preclinical species. We present a novel kinetic model of 129Xe exchange (KMXE) in conjunction with blind estimation techniques to evaluate 129Xe exchange between pulmonary tissue and blood without needing an explicit measurement of RBC signals. Using simulations, we show that kinetic parameter estimates are comparable to those estimated using conventional methods, demonstrating feasibility for evaluating gas exchange kinetics when no distinct RBC spectral peak can be measured. |
|
4497.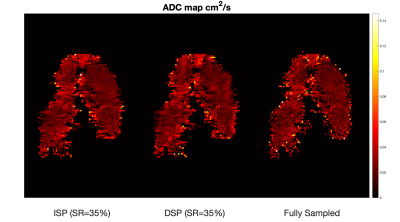 |
63 |
The effect of variable compressed sense (CS) undersampling
patterns in hyperpolarized Xenon (129Xe) diffusion-weighted MRI
Mitra Tavakkoli1,2,
Sarah Svenningsen3,4,
Yonni Friedlander4,
Norm Konyer5,
Parameswaran Nair3,4,
and Michael D Noseworthy1,5,6,7
1Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2Imaging Research Centre, St. Joseph's Healthcare, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 3Department of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 4Firestone Institute for Respiratory Health, St Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 5Imaging Research Centre, St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 6Biomedical Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 7Department of Radiology, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Sparse & Low-Rank Models, Compressed Sensing, Lung, 129Xenon Compressed sensing is a fast-imaging technique capable of making high quality images with undersampled data. However, its application in hyperpolarized 129Xe diffusion-weighted MRI needs to be optimized. In this study, diffusion weighted images undersampled identically and differently, were compared with SNR, SSIM, mean ADC using repeated measures ANOVA. The application of different undersampling patterns for both diffusion-weighted and baseline images can result in ADC maps with higher quality, as compared to fully sampled equivalent parametric images. Thus, the baseline and diffusion-weighted images do not necessarily have the same optimum undersampling pattern, and optimization of each needs investigation separately. |
|
4498.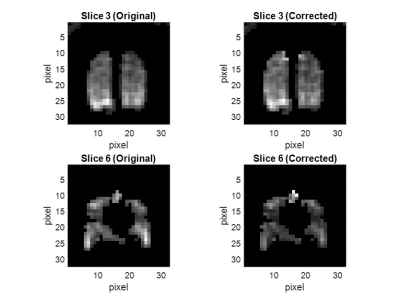 |
64 |
Mapping transmit and receive B1 using variable flip angle
acquisition on a person-by-person basis for hyperpolarized
Carbon-13 and Xenon-129 MRI
Kylie Yeung1,2,3,
Zack Ravetz1,4,
Kher Lik Ng2,5,
Gabriele AbuEid2,
William Hickes2,
Kenneth Jacob2,
Mitchel Danisa2,
Marianne Durrant2,
Rebecca Mills1,
Ayaka Shinozaki1,6,
Jordan McGing1,
Aaron Axford1,
Sarah Birkhoelzer1,
Rolf F Schulte7,
Oliver Rider1,
Anthony McIntyre2,
Emily Fraser5,
Damian J Tyler1,6,
Fergus Gleeson2,8,
and James T Grist1,2,6,9
1Oxford Centre for Clinical Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2Department of Radiology, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3Department of Oncology, Univeristy of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 4RRPPS, University Hospitals Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 5Oxford Respiratory Service, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Oxford, United Kingdom, 6Department of Physiology, Anatomy and Genetics, Univeristy of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 7GE Global Research, Munich, Germany, 8Department of Oncology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 9Alama Mater Studorium, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Hyperpolarized MR (Non-Gas), Xenon-129, Carbon-13 Hyperpolarized MRI allows the imaging of processes such as gas exchange and metabolism. Calibration of transmit and receive (Tx/Rx) B1 is required to account for coil inhomogeneities in reconstruction. A variable flip angle (VFA) method, which is fast and readily implemented, allows for a simultaneous B1/T1 measurement. In this study, a mathematical model of VFA calibration was developed, tested, validated in a hyperpolarized Carbon-13 (13C) phantom and in vivo with hyperpolarized Xenon-129 imaging of human lungs. |
|
4499.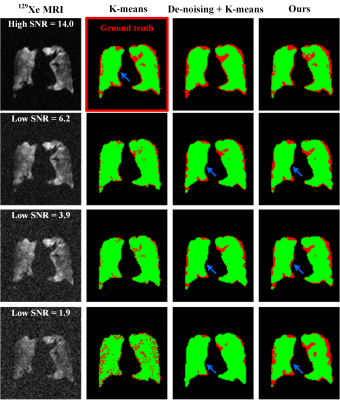 |
65 |
Hybrid segmentation of ventilation defect regions in low
signal-to-noise ratio hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI
Cheng Wang1,2,
Sa Xiao1,2,
Zimeng Li1,2,
Haidong Li1,2,
and Xin Zhou1,2
1State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences - Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan, China, 2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Lung Ventilation defect percentage (VDP) generated from hyperpolarized gas (3He or 129Xe) MRI is a sensitive indicator of lung disease. However, the commonly used K-means method for the calculation of VDP is not suitable for low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) images. In this work, we proposed a hybrid segmentation method to segment the ventilation defect regions and calculate VDP values under low SNR conditions. The results show that the proposed method has improved both the accuracy of segmenting VDP map and calculating VDP value. |
|
4500.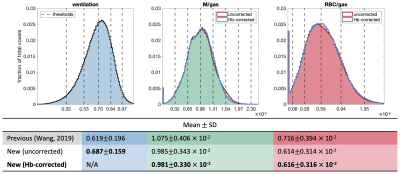 |
66 |
Healthy reference distributions for 129Xe gas exchange MRI with
consideration of sex and hemoglobin
Aryil Bechtel1,
David Mummy1,
Junlan Lu2,
Suphachart Leewiwatwong3,
Joseph Mammarappallil1,
Sakib Kabir1,
and Bastiaan Driehuys1,2,3
1Radiology, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 2Medical Physics, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 3Biomedical Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Lung 129Xe gas exchange MRI is commonly quantified by binning images of ventilation, membrane uptake (M/gas), and red blood cell transfer (RBC/gas) according to thresholds established using healthy reference distributions. To date, reference values have been based on small samples and do not account for hemoglobin concentration (Hb), which is known to vary by sex. We apply a Hb correction to data from 15 young, healthy volunteers (age=25.2±3.3 yrs., 6 female). After correction, there was no significant difference in individual mean M/gas and RBC/gas between males and females. The resulting reference distributions have less dispersion and skew than previously established distributions. |
|
4501.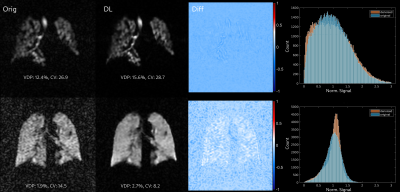 |
67 |
Improving Xenon-129 Lung Ventilation Image Quality with a
Commercial Deep-Learning Based Image Reconstruction
Neil J Stewart1,
Jose de Arcos2,
Alberto M Biancardi1,
Jemima H Pilgrim-Morris1,
Oliver I Rodgers1,
Ryan S Munro1,
Guilhem J Collier1,
Graham Norquay1,
Helen Marshall1,
Anja Brau3,
Marc Lebel4,
and Jim M Wild1
1The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom, 2GE Healthcare, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 3GE Healthcare, San Francisco, CA, United States, 4GE Healthcare, Calgary, AB, Canada Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Hyperpolarized MR (Gas) The utility of a deep learning based reconstruction tool for improving the quality of hyperpolarized 129Xe lung ventilation images was assessed. DL-reconstructed 129Xe ventilation image quality and SNR was improved compared with conventionally reconstructed images. In a cohort of patients with asthma and/or COPD, a small bias towards increased ventilation defect percentage, and a bias towards decreased coefficient of variation, in DL-reconstructed vs. conventionally-reconstructed images, was observed. Initial feasibility of utilising this tool for reduced-cost 129Xe ventilation imaging using natural-abundance xenon, and improved spatial resolution imaging with 129-enriched xenon, is demonstrated. |
|
4502.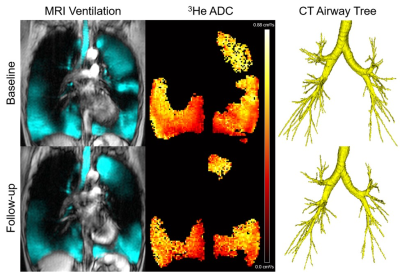 |
68 |
Terminal Airspace Enlargement Measured Using Pulmonary
Functional MRI Predicts CT Airway Loss in COPD
Paulina Victoria Wyszkiewicz1,2,
Maksym Sharma1,2,
Harkiran K Kooner1,2,
David G McCormack3,
Miranda Kirby4,
and Grace Parraga1,2,3,5
1Department of Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Robarts Research Institute, London, ON, Canada, 3Division of Respirology, Department of Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 4Department of Physics, Toronto Metropolitan University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5School of Biomedical Engineering, Western University, London, ON, Canada Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Lung The onset and progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is currently believed to initiate in the small-airways and progresses to emphysema or terminal airspace (alveolar) enlargement and destruction. MRI apparent-diffusion-coefficient (ADC) provides a way to measure subclinical emphysematous destruction in patients. Here we investigated the relationship between pulmonary functional MRI measurements of terminal airspace enlargement using 3He MRI-ADC and CT airway changes in ex-smokers with COPD. MRI-ADC values at baseline were uniquely predictive of worsening CT total-airway-count and airway wall-area after three-years. MRI captures evidence of mild or subclinical emphysema and its relationship with terminal airway obliteration in COPD. |
|
4503.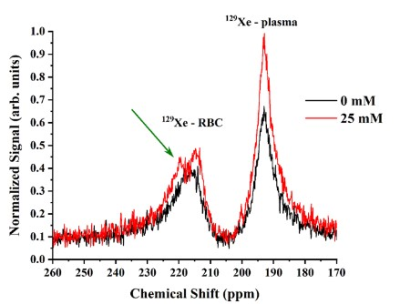 |
69 |
Effect of glucose on the HP 129Xe dissolved phase blood
resonances
Lutoslawa Mikowska1,
Vira Grynko2,3,
Yurii Shepelytskyi3,4,
Iullian Constantin Ruset5,
Joseph Deschamps6,
Hannah Aalto6,
Marta Targosz-Korecka1,
Hubert Harańczyk1,
Dilip Balamore7,
and Mitchell Albert3,4,8
1Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Applied Computer Science, Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland, 2Chemistry and Material Science Program, Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON, Canada, 3Thunder Bay Regional Health Research Institute, Thunder Bay, ON, Canada, 4Chemistry Department, Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON, Canada, 5Xemed LLC, Durham, NH, United States, 6Applied Life Sciences Program, Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON, Canada, 7Department of Engineering/Physics/Technology, Nassau Community College, Garden City, NY, United States, 8Northern Ontario School of Medicine, Sudbury, ON, Canada Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Spectroscopy, blood, hemoglobin, dissolved phase imaging We examined the impact of elevated glucose levels on the chemical shift and T2* relaxation of hyperpolarized 129Xe dissolved in sheep blood. The addition of glucose did not affect the 129Xe-plasma resonance. For the first time, however, we have observed an additional 129Xe dissolved phase resonance attributed to 129Xe bound to glycated hemoglobin. A glucose-related linear downfield shift of the 129Xe resonance frequency was observed for 129Xe bound to native hemoglobin, whereas the T2* relaxation of 129Xe bound to glycated hemoglobin increased non-linearly with increasing glucose concentration. |
|
4504.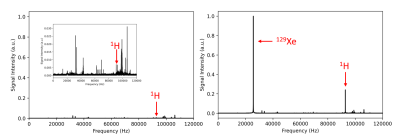 |
70 |
Direct detection of polarization transfer from hyperpolarized
129Xe to thermally polarized 1H at 2 mT
Michele Kelley1,
Nicholas Bryden1,
Sebastian William Atalla1,
and Rosa Tamara Branca1
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, United States Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Hyperpolarized MR (Gas) We present a simple protocol for polarizing 1H at ultra-low field. By simply bubbling hyperpolarized Xe gas in a solution containing thermally polarized 1H spins, the proton thermal polarization can be enhanced by more than 100-fold. This enhancement is clearly observed, even in absence of saturation pulses, at ultra-low field where thermal polarization is close to background noise levels. Simultaneous detection of 1H and 129Xe magnetizations shows that the transfer of polarization from 129Xe to 1H spins is a continuous process that lasts until the dissolved-phase 129Xe polarization is relaxed back to thermal equilibrium. |
|
4505.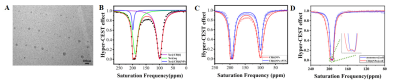 |
71 |
Hyperpolarized 129Xe Magnetic Resonance Dual Signal Probe Based
on CB[6] Nanoparticles for Precise Drug Delivery Monitoring
Chenlu Yuan1,
Qianni Guo1,
Qingbin Zeng1,
Yaping Yuan1,
Weiping Jiang1,
Chaohui Ye1,
and Xin Zhou1
1Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences – Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan 430071, P. R. China, WUHAN, China Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), 129Xe,Hyper-CEST We synthesized an ultrasensitive 129Xe NMR probe with dual signals. It is a hollow nanoparticle composed of water-soluble CB[6]. It has two different hydrophobic cavities. Two 129Xe NMR signals with different chemical shifts can appear in a single detection, effectively avoiding the occurrence of false positive and false negative in complex biological environment detection, improving the accuracy and sensitivity of single detection, and has broad application prospects. |
|
4506.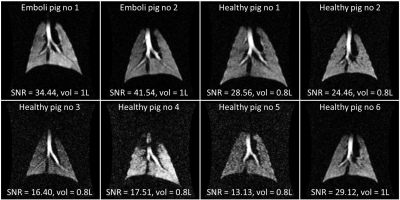 |
72 |
Batch-mode production of hyperpolarised xenon gas with a
continuous-flow polariser for preclinical and clinical human
lung ventilation images
Michael Vaeggemose1,2,
Graham Norquay 3,
Esben Søvsø Szocska Hansen1,
Neil J. Stewart3,
Oliver I. Rodgers3,
Ryan S. Munro3,
Rolf F. Schulte4,
Guilhem J. Collier 3,
Christoffer Laustsen1,
and Jim M. Wild3
1MR Research Centre, Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus N, Denmark, 2GE Healthcare, Brøndby, Denmark, 3POLARIS group, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom, 4GE Healthcare, Munich, Germany Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Lung ventilation imaging Hyperpolarised 129Xe gas was accumulated using spin-exchange optical pumping (SEOP) by continuous-flow of xenon gas directly from the cell without the use of cryogenic separation. 3D ventilation images were acquired in human and porcine models to determine clinical diagnostic image quality. Xenon ventilation image quality indicates that on demand batch production of xenon is feasible for both preclinical and clinical lung ventilation imaging examinations. |
|
4507.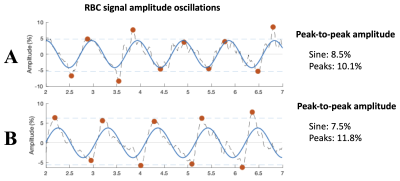 |
73 |
Repeatability of pulmonary 129Xe static spectroscopy and dynamic
spectroscopy fit methods: a reader study
Aryil Bechtel1,
Anna Costelle2,
Elianna Bier3,
Junlan Lu2,
Joseph Mammarappallil1,
Sakib Kabir1,
David Mummy1,
and Bastiaan Driehuys1,2,3
1Radiology, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 2Medical Physics, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 3Biomedical Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Heart, Lung 129Xe MRS measures static and dynamic spectral parameters from 129Xe signal in airspaces, membrane tissues, and red blood cells (RBC) and has the potential to characterize cardiopulmonary diseases. However, a better understanding of measurement repeatability is needed, and different approaches to quantifying cardiogenic oscillations have been proposed. Here, we compare quantification of oscillations using sine-fitting and a peak-finding algorithm and use reader ratings to identify acceptable study quality. Across a range of cardiopulmonary disease groups, measurements of static parameters showed good intra-session repeatability while the peak-finding algorithm generally yielded higher repeatability than sine fits for most dynamic parameters. |
|
4508.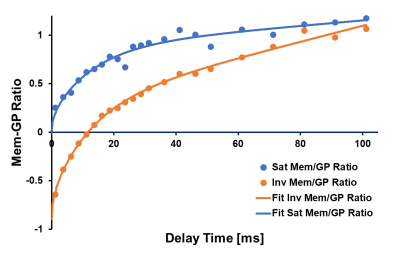 |
74 |
Chemical Shift Inversion Recovery (CSIR) spectroscopy with
hyperpolarized xenon-129 MRI: A comparison with CSSR
spectroscopy
Kai Ruppert1,
Luis Loza1,
Faraz Amzajerdian1,
Hooman Hamedani1,
Mostafa K Ismail1,
Ryan J Baron1,
Ian F Duncan1,
Harrilla Profka1,
Stephen Kadlecek1,
and Rahim R Rizi1
1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Pulse Sequence Design Chemical shift saturation recovery (CSSR) MR spectroscopy using hyperpolarized xenon-129 provides metrics of pulmonary physiology by saturating the xenon dissolved-phase magnetization in the lung with a 90° RF pulse and measuring the subsequent signal recovery via gas exchange. Our measurements in a rat demonstrate that chemical shift inversion recovery (CSIR) spectroscopy, which replaces the saturation with an inversion pulse, produces equivalent results to CSSR but with greater robustness with respect to both low signal amplitudes at short delay times and incomplete saturation. |
|
4509.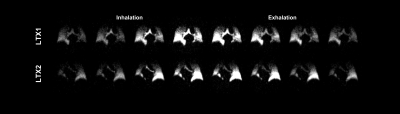 |
75 |
Assessing Ventilation Dynamics of Lung Transplantation with
Free-Breathing Hyperpolarized Xenon-129
Faraz Amzajerdian1,
Hooman Hamedani1,
Ryan Baron1,
Mostafa Ismail1,
Luis Loza1,
Kai Ruppert1,
Stephen Kadlecek1,
and Rahim Rizi1
1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Lung Regional quantification of ventilation dynamics can provide valuable insights into the functional changes associated with both unilateral and bilateral lung transplantation, potentially improving diagnostic monitoring and providing a better understanding of underlying pathophysiology. By imaging hyperpolarized xenon-129 (HXe) continuously over an extended period of time, ventilation dynamics more representative of steady-state, physiological breathing were derived and used to assess differences between unilateral and bilateral transplant patients. |
|
4510.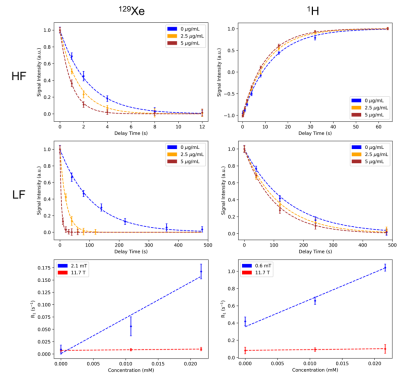 |
76 |
Enhanced 129Xe T1 relaxation in blood and in presence of SPIONs
at low field strengths
Nicholas Bryden1,
Sebastian William Atalla1,
Michele Kelley1,
Leah R Holmes1,
and Rosa Tamara Branca1
1Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, United States Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Non-Gas), Relaxometry We demonstrate enhanced T1 relaxation of hyperpolarized 129Xe spins in blood and in the presence of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) at low field strengths. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.