Weekend Course
Artifacts & Correction Strategies
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| 07:45 |
 |
Basic Artifacts
Martin Graves
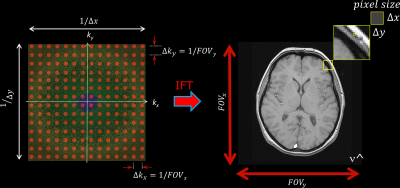
Keywords: Image acquisition: Artefacts Image artifacts can arise from one or more of the following: MR physics, MR system hardware, and the patient. Given the wide range of possible MR artifacts this presentation will be limited to the main relationships between data corruptions during image acquisition, i.e., in raw data or k-space, and their appearance in the reconstructed image after Fourier transformation. The cause and effect of artifacts including Gibbs ringing, phase encode direction aliasing/foldover, zippers, spikes and motion during image acquisition will be discussed, together with failures in fat suppression and the effect of receiver bandwidth on chemical shift artifact. |
| 08:15 |
 |
B0-Related Artifacts
Catherine Morgan
Keywords: Image acquisition: Artefacts, Physics & Engineering: Physics Inhomogeneity of the main magnetic field, B0, can cause a number of artefacts. In this educational session, causes of B0 inhomogeneity will be described, with a focus on magnetic susceptibility related artefacts. For example at air-tissue interfaces or around metal implants. The effects on different sequences e.g. spin-echo, gradient-echo and echo-planar imaging will be described. Lastly correction strategies for B0 artefacts will be presented, grouped by approach: acquisition, specialised sequences and post-processing. |
| 08:45 | B1-Related Artifacts Laura Schreiber | |
| 09:15 |
Gradient-Related Artifacts
Corey Baron
Keywords: Image acquisition: Artefacts This educational session will describe the mechanisms behind artifacts that stem from gradient non-linearity, eddy currents, and concomitant gradient fields. Attendees will learn to identify each type of gradient-related artifact, and will learn about methods to mitigate, correct, or avoid them. Distinction will be made between artifacts stemming from gradients used for contrast generation and gradients used for image encoding. For example, diffusion MRI is especially sensitive to gradient-related artefacts due to the use of extremely large gradient amplitudes to sensitize the signal to diffusion. |
|
| 09:45 |
Break & Meet the Teachers |
|
| 10:15 |
Flow-Related Artifacts
Julio Garcia Flores
Keywords: Cardiovascular: Blood, Cardiovascular: Hemodynamics, Image acquisition: Artefacts This educational session will introduce most common technique to measure flow. In particular phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging and its applications. Blood flow acquisition and quantification can be affected by image artifacts from multiple sources. This lecture will discuss the most common sources of artifacts impacting blood flow measurements in 2D and 4D and strategies to correct them. |
|
| 10:45 |
Image Reconstruction Artifacts
Gastao Cruz
Keywords: Image acquisition: Reconstruction Artifacts arise in MR reconstruction from a variety of sources: the discrete (and band-limited) sampling of the signal, noise amplification, parallel imaging, regularization strategies like compressed sensing, motion, and many others. In this talk we'll look at some of the underlying mechanics that cause these artifacts, and how they can impact clinical images. |
|
| 11:15 |
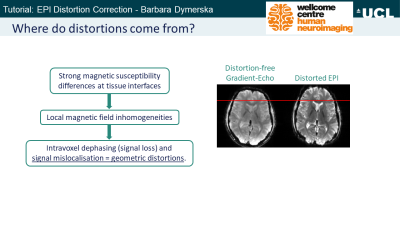 |
Tutorial: EPI Distortion Correction
Barbara Dymerska
Keywords: Image acquisition: Artefacts, Contrast mechanisms: fMRI, Neuro: Brain EPI is sensitive to inhomogeneities in the static magnetic field that arise from the interfaces between tissues with different magnetic susceptibilities. Field inhomogeneities cause geometric distortions in EPI in the phase-encoding direction leading to mislocalization of activation and difficulty coregistering functional results to anatomical scans. We will learn how to correct distortions using a field map calculated from the phase change between images acquired at different echo times. A single field map does not capture dynamic field changes occurring due to motion or respiration. We will thus also expand our capabilities to perform dynamic distortion correction. |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.