Digital Poster
IVIM Clinical Applications
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 04-09 May 2024 • Singapore

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
2872.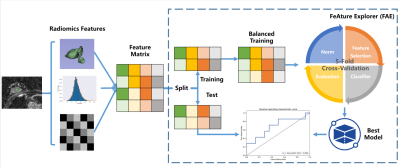 |
97 |
IVIM-DWI prediction of pCR before neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
breast cancer
Muzhen He1 and
Yang Song2
1Fujian Provincial Hospital,China, Fuzhou,Fujian, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers, City, China, China, China Keywords: IVIM, Breast Motivation: A nomogram incorporated radiomics and morphology was developed to predict pCR. Goal(s): This study developed a predictive model using baseline imaging of morphology and radiomics for the purpose of predicting the pCR to NACT. Approach: Radiomics and conventional magnetic resonance imaging signs analysis were performed. To build a nomogram model that integrates the radiomics signature and conventional imaging, a logistic regression method was employed. Results: The nomogram showed good performance and was a valuable tool in clinic. Impact: Through the validation process, the nomogram developed in this study showed good performance, effectively predicting pCR in breast cancer. Hence, it serves as a valuable tool for informing individualized treatment decision-making for breast cancer patients. |
|
2873.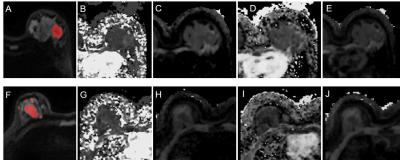 |
98 |
Prediction of Pathological Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
in Breast Cancer Using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Histogram
Parameters
Yanbo Li1,
Yuchen Xue2,
Jinxia Guo3,
Lizhi Xie3,
and Hong Lu1
1Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin, China, 2Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China Keywords: IVIM, Breast Motivation: The motivation behind this study lies in the need for accurate prediction of pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in breast cancer. Goal(s): Our goal was to assess the potential of IVIM-derived histogram parameters as predictive markers before NAC in breast cancer patients. Approach: We conducted a comprehensive analysis of 287 breast cancer cases, utilizing IVIM model-based parameters and multivariate logistic regression. The study included voxel-wise analysis. Results: The prediction model, combining the selected IVIM parameters and PR status, exhibited strong discriminative power. Additionally, we identified the minimum of D, Skewness of D* and D as significant volumetric predictors associated with pCR. Impact: The impact of this study is significant, as it enhances breast cancer treatment by providing a reliable predictive model for neoadjuvant chemotherapy response, potentially improving patient outcomes and treatment strategies. |
|
2874.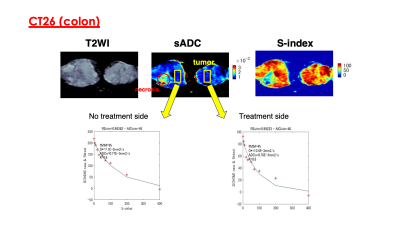 |
99 |
Effectiveness of IVIM/DWI MRI parameters in evaluating anti-PD-1
antibody treatment response in xenograft models in vivo
Sawako Hayami1,
Mami Iima2,3,
Tomomi Nobashi2,
Yuko Someya2,4,
Hirohiko Imai5,
Denis Le Bihan6,7,
and Yuji Nakamoto2
1Faculty of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto City, Kyoto, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto City, Kyoto, Japan, 3iACT, Kyoto University Hospital, Kyoto City, Kyoto, Japan, 4Department of Radiology, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, Kobe City, Hyogo, Japan, 5Department of Systems Science, Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University, Kyoto City, Kyoto, Japan, 6Human Brain Research Center, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto City, Kyoto, Japan, 7NeuroSpin, CEA Paris-Saclay Center, Gif-sur-Yvette, Essonne, France Keywords: IVIM, Cancer Motivation: Although intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameters are garnering attention as a DWI analytical method, their effectiveness in evaluating the immunotherapy efficacy is still largely unvalued. Goal(s): Our goal was to assess if IVIM/DWI parameters reflect tissue changes subsequent to anti-PD-1 antibody treatment in vivo. Approach: Colon (CT26) and breast (4T1) cancer xenograft murine models received the treatment and afterward MR study. Results: fIVIM (flowing blood volume fraction) was significantly lower in the treated tissue in the CT26 model, while no change was observed in the 4T1 model. Also, there was no difference in the lesion size in both models. Impact: The difference of fIVIM (flowing blood volume fraction) parameter and lesion size between two anti-PD-1 antibody-treated xenograft models might reflect a different level of treatment efficacy, which may indicate the IVIM potential to observe tissue heterogeneity. |
|
2875.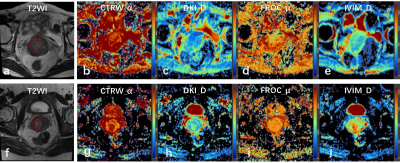 |
100 |
A comparison of four non-Gaussian diffusion models combined with
whole-tumor histogram analysis for evaluating cervical cancer
Lu Yang1,
Xiaohui Duan1,
Mengzhu Wang2,
Haodong Qin3,
Zhao Chen3,
Huijun Hu1,
Zhuoheng Yan1,
and Xu Yan2
1Department of Radiology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, No. 107 Yanjiang Roa, GuangZhou, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China, 3MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers, Guangzhou, China Keywords: DWI/DTI/DKI, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Motivation: Non-Gaussian diffusion models can effectively characterize the microstructure of tissues. Goal(s): To investigate the potential predictive value of multiple non-Gaussian diffusion models for assessing cervical cancer (CC). Approach: Diffusion parameters derived from continuous-time random-walk (CTRW), diffusion-kurtosis imaging (DKI), fractional order calculus (FROC) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) were calculated. The most significant histogram features selected by univariate analysis and multivariate logistic regression were used to establish predictive models. The predictive performance was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses. Results: The combination of multiple non-Gaussian diffusion models and whole-tumor histogram analysis could distinguish pathological types and differentiation degree in CC. Impact: Predicting pathological types and differentiation degree of cervical cancer is crucial for appropriate treatment and prognosis. The use of multiple non-Gaussian diffusion models combined with whole-tumor histogram analysis offers a precise and non-invasive solution to this clinical issue. |
|
2876.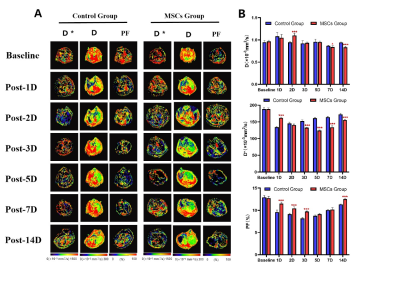 |
101 |
Assessment of mesenchymal stromal cells promoting liver
regeneration via intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted
imaging
Xu yang Wang1,
Shuang shuang Xie1,
and Wen Shen1
1Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tian Jin, China Keywords: fMRI Analysis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, intravoxel incoherent motion Motivation: Scholars are proposing the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to promote liver regeneration and prevent postoperative liver function failure; however, no method currently exists for evaluating their effectiveness in vivo. Goal(s): We assessed whether intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) could be used to assess changes in liver regeneration in rats after partial hepatectomy. Approach: Rats undergoing stem cell therapy underwent imaging examinations at baseline and postoperative days 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, and 14, and were compared with untreated rats. Results: Liver D, D*, and PF differed significantly between control rats and those receiving MSCs at all time points. Impact: Mesenchymal stem cells can promote liver regeneration by inducing cell hypertrophy and extending the proliferation period of liver cells. IVIM parameters enable monitoring changes in liver blood perfusion after mesenchymal stem cell therapy and show correlations with pathological indicators. |
|
2877.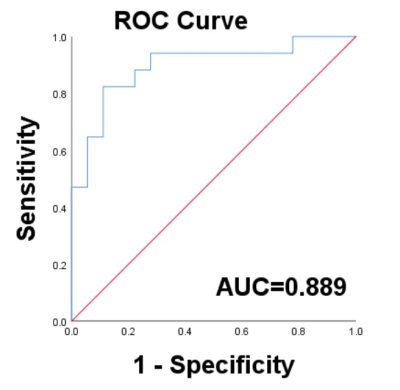 |
102 |
The value of IVIM-based tumor habitats in predicting the lymph
node metastasis of breast cancer
Haifa Liu1,
Yingmin Zhai1,
Hui Liu1,
Mengzhu Wang2,
Yang Song2,
Chengxiu Zhang3,
Guang Yang3,
and Robert Grimm4
1Department of Radiology, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China, 3East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 4MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthineers AG, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: IVIM, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, IVIM,MRI, breast tumor, Lymph node metastasis, habitats Motivation: Biopsy is usually used to diagnose lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Our study evaluated the clinical significance of a non-invasive method. Goal(s): Our aim was to explore the performance of a prediction model using tumor habitats. It predicted lymph node metastasis in patients with malignant breast cancer. Approach: We developed a predictive model of tumor habitats. It used the data of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) and diagnosed lymph node metastasis. Results: The IVIM indicators can segment whole tumor into four subregions, which were related to hypoxic condition. The model can effectively predict lymph node metastasis of breast cancer patients. Impact: The predictive model elucidates the features of habitats. Its performance is good for the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer, helping clinicians make better decisions and recommend appropriate treatment options. Thus, patient outcomes are improved. |
|
2878.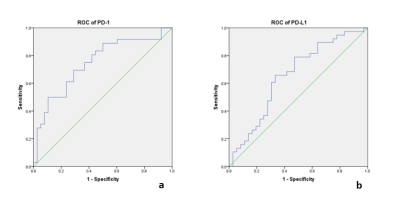 |
103 |
Evaluation of PD-1/PD-L1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion: A Diagnostic Perspective
Qianjuan Chen1,
Liling Long1,
Huiting Zhang2,
and Alto Stemmer3
1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University,, Naning, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Wuhan, China, 3MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany Keywords: IVIM, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, PD-1/PD-L1 Motivation: In clinical practice of hepatocellular carcinoma, there are lacking in preoperative and pre-medication results regarding immunosuppressive checkpoint inhibitors PD-1 and PD-L1. Goal(s): This study aimed to evaluate the expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) before surgery and immunotherapy. Approach: Immunohistochemistry staining was performed on liver cancer tissue to analyze the correlation between immunohistochemistry results and derived parameters (D, D*, and f) from IVIM and ADC, allowing for the assessment of their diagnostic value. Results: The parameters D and D* from IVIM had statistically significant differences between the expression of PD-1 and PD-L1. Impact: The results of this study may have an impact on clinical decision-making in the future and demonstrate a favorable outcome for scientific research in the immune microenvironment. |
|
2879.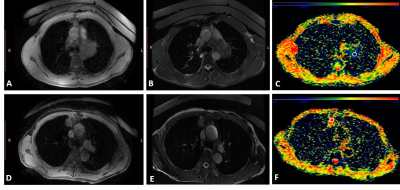 |
104 |
Potential Diagnostic Efficiency of Intravoxel Incoherent
Motion-based Virtual Magnetic Resonance Elastography in
Pulmonary Neoplasms
Shuo Zhang1,
Yonghao Du1,
Ting Liang1,
Xuyin Zhang1,
Yinxia Guo1,
Jian Yang1,
Xianjun Li1,
and Gang Niu1
1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China Keywords: IVIM, Cancer, Stiffness Motivation: Exploring non-invasive techniques with the potential of replacing invasive pathological analysis of pulmonary neoplasms remains urgent. Goal(s): To investigate the feasibility of IVIM-based vMRE to provide quantitative estimates of tissue stiffness in pulmonary neoplasms and to verify the diagnostic performance in distinguishing neoplasm property. Approach: sADC and virtual stiffness values of neoplasm were extracted, and the diagnostic performance of vMRE in distinguishing benign and malignant and detailed pathological type were explored. Results: Virtual stiffness values of malignant neoplasms were significantly higher than benign ones. Subsequent sub-type analyses showed adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma were mostly stiffer than non-specific benign neoplasms. Impact: IVIM-based vMRE has good feasibility in reflecting stiffness of pulmonary neoplasms. Virtual stiffness and sADC values showed significant difference between malignant and benign lesions.The application of non-invasive vMRE is promising as a new method for clinical diagnosis. |
|
2880.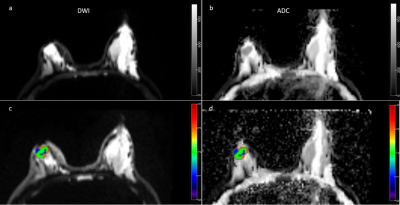 |
105 |
Predicting estrogen receptor factor expression based on tumor
habitats in patients with malignant breast cancer: a feasibility
study
Mengting Duan1,
Yingmin Zhai1,
Mengzhu Wang2,
Yang Song2,
Chengxiu Zhang3,
Guang Yang3,
Haifa Liu1,
and Hui Liu1
1Department of Radiology, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China, 3East China Normal University, Shanghai, China Keywords: IVIM, Radiomics, IVIM, MRI, habitats, breast tumor, estrogen receptor Motivation: Immunohistochemistry remains the gold standard for diagnosing the estrogen receptor (ER) factor in breast cancer. However, the non-invasive IVIM radiomics method offers a meaningful alternative for predicting ER expression. Goal(s): The objective of this study is to assess the feasibility and performance of a prediction model based on tumors habitats in predicting ER expression in malignant breast cancer patients. Approach: We developed and evaluated a predictive model that utilizes tumors habitats to diagnose ER expression. Results: The IVIM indicators can be employed for tumor subregions’ segmentation to hypoxia. The model demonstrates effective prediction capabilities for determining the probability of ER-positive in breast cancer. Impact: Our research highlights the excellent performance of the predictive model based on tumors habitats in predicting ER expression in breast cancer. The model can aid clinicians in making more informed treatment decisions and subsequently improve patient outcomes. |
|
2881.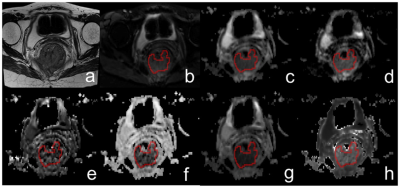 |
106 |
Assessment of pathological prognostic factors in rectal cancer:
comparison of DWI, IVIM, and DKI
Mi Zhou1,
Meining Chen2,
Qin Zhang3,
and Hongyun Huang1
1Department of Radiology, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers, Chengdu, China, 3MRI clinical application, Customer Service Department, Siemens Digital Medical Technology Co., LTD, Shanghai, China Keywords: IVIM, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Motivation: The prognosis of rectal cancer (RC), depends on pathological prognostic factors. Despite the contributions of MRI, accurate preoperative prediction of these factors remains challenging. Goal(s): Evaluate the values of DWI, IVIM, and DKI in predicting RC’s pathological prognostic factors. Approach: In 162 rectal cancer patients, we compared DWI, IVIM, and DKI MRI techniques to predict EMVI, LNM, and histological differentiation, analyzing correlations with histological data. Results: MK was identified as a powerful predictor, especially for histological differentiation and LNM. The combine of MK+MD exhibited robust potential to predict EMVI, highlighting the diagnostic values of these models for rectal cancer prognosis. Impact: This research enhances MRI's predictive capabilities for critical rectal cancer prognostic factors, potentially refining treatment planning and improving the prognosis of patients. |
|
2882.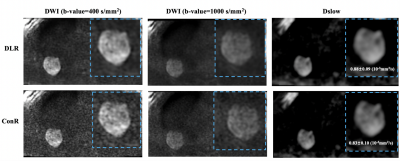 |
107 |
The impact of deep learning based image reconstruction on
IVIM for benign and malignant pulmonary lesion discrimination
Li Fan1,
Jie Li1,2,
Yi Xia1,
Jiankun Dai3,
Jie Shi3,
Guangyuan Sun4,
Meiling Xu1,
Xiaoqing Lin1,2,
and Shiyuan Liu1
1Department of Radiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China, 2College of Health Sciences and Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai, China, 3MR Research,GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China Keywords: IVIM, Lung, Deep learning reconstruction; Lung cancer; Magnetic resonance imaging; Diffusion weighted imaging; Intravoxel incoherent motion. Motivation: DWI-based IVIM model provides information about tumor microenvironment and is reported useful in discriminating pulmonary lesions. However, lung DWI suffers low SNR and substantial susceptibility artifacts. Recently, a vendor-provided deep-learning reconstruction (DLR), relative to conventional reconstruction (ConR), is provided to improve image quality. Goal(s): Investigate the impact of DLR on IVIM parameters for distinguishing malignant from benign pulmonary lesion. Approach: DWI was acquired using FOCUS-MUSE to alleviate susceptibility artifacts and was reconstructed with DLR and ConR, separately. SNR and diagnostic performance of IVIM were compared. Results: DLR significantly increased DWI image SNR and improved diagnostic performance of IVIM parameters for pulmonary lesion discrimination. Impact: The application DLR would be beneficial for lung DWI in term of image quality and the performance of IVIM quantitative parameters for distinguishing benign from malignant pulmonary lesion. |
|
2883.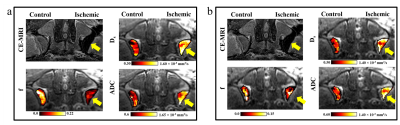 |
108 |
Sensitivity of IVIM in Detecting Acute Femoral Head Ischemia: A
Comparison Between RESOLVE and Single Shot EPI Using An In Vivo
Piglet Model
Erick O Buko1,2,
Suhail P Parvaze1,2,
Ferenc Tóth1,
and Casey P Johnson1,2
1Veterinary Clinical Sciences, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN, United States, 2Center for Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States Keywords: IVIM, Ischemia, perfusion, bone Motivation: Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) is a promising noninvasive technique to measure tissue diffusion and perfusion using a single multi-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) acquisition. Goal(s): To determine whether IVIM is sensitive to acute femoral head ischemia in the piglet model using RESOLVE and single-shot EPI. Approach: 24 piglets underwent bilateral hip imaging using a 3T MRI before and after surgical induction of unilateral femoral head ischemia. IVIM and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values were compared between the pre- and post-operative scans. Results: IVIM is sensitive in detecting ischemia and subsequent injury to the femoral head. RESOLVE outperforms ssEPI in detecting changes in perfusion. Impact: IVIM may be a clinically useful non-contrast-enhanced alternative to CE-MRI to measure femoral head ischemia and perfusion changes for detecting, staging, and monitoring LCPD and other forms of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. |
|
2884.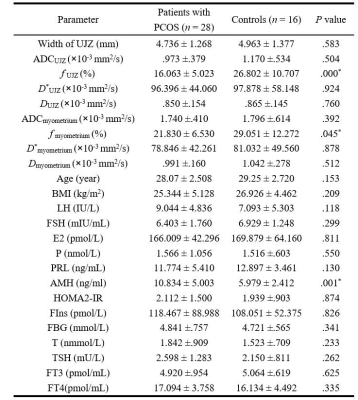 |
109 |
Value of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI in
evaluating endometrial receptivity in women with polycystic
ovary syndrome
Wenhui Shao1,
Yuwei Cao1,
Feifei Qu2,
Feiyun Wu1,
and Ting Chen1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, 300 Guangzhou Road, Nanjing, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China Keywords: IVIM, Reproductive, polycystic ovary syndrome, vessels, hormonal levels Motivation: This study evaluated endometrial receptivity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) impacting embryo implantation and pregnancy outcomes. Goal(s): The primary objectives were to evaluate endometrial receptivity by measuring uterine junctional zone (UJZ) and myometrium parameters and to explore the correlation between these imaging parameters and hormonal levels. Approach: Using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM), the study measured the quantitative parameters of the UJZ and myometrium in women with PCOS. Results: Patients with PCOS had lower UJZ and myometrium f values than controls, indicating reduced perfusion affecting embryo implantation. A positive correlation with free thyroxine levels was observed. Impact: Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging is vital in assessing endometrial receptivity. Patients with polycystic ovary syndrome had lower f values of the uterine junctional zone and myometrium than controls, suggesting less blood perfusion, which might be associated with poor pregnancy outcomes. |
|
2885.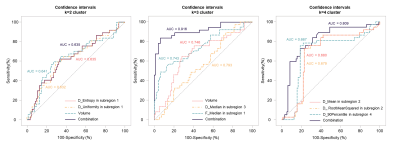 |
110 |
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) - based tumor subregions
features associates with HER2 expression in breast cancer
Mingyue Yang1,
Siyao Du1,
Ruimeng Zhao1,
Yueluan Jiang2,
Yang Song3,
and Lina Zhang1
1The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China, 2research Collaboration Team, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China, 3research Collaboration Team, Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China Keywords: IVIM, Cancer Motivation: Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) analysis gives information on diffusion and perfusion and may have a potential for tumor tissue characterization and distinguish the HER2 expression. Goal(s): This work aims to cluster tumor subregions based on IVIM parameter maps and assess the optimal number of clusters and parameter of tumor subregions related to HER2 expression. Approach: we used kmeans method to split the ROI into different sub-regions based on IVIM maps, and imaging features to diagnose HER-2 expression. Results: We found the optimal number of clusters was 3, and F_Median in subregion 1, D_Median and F_Volume in subregion 2 strongly associated with HER2 expression. Impact: These subregions features are expected as a non-invasive way to obtain diffusion and perfusion information, leading to the discovery of reliable imaging biomarkers for guiding precision cancer therapy. |
|
2886.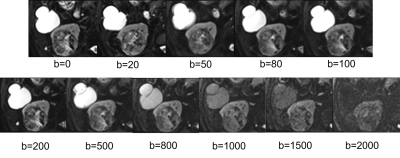 |
111 |
Value of multi-parametric diffusion-weighted imaging in
pathological grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Shichao Li1,
Ting Yin2,
and Zhen Li1
1Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2MR Research Collaboration Team, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Chengdu, China Keywords: Diffusion Modeling, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques Motivation: Accurate preoperative grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is essential for treatment decisions, particularly in patients with comorbidities. Goal(s): This study aims to investigate the utility of various diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) models, including mono-exponential, intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM), diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), and continuous time random walk (CTRW), in preoperative ccRCC grading to facilitate personalized treatment strategies. Approach: We conducted MRI scans on 105 ccRCC patients with multi-b value DWI and employed machine learning for model construction for ccRCC grading. Results: This study demonstrates the protential of multi-parametric DWI models for accurate ccRCC grading, yield an AUC of 0.861. Impact: This study has the potential to reshape the landscape of preoperative ccRCC grading, promote objectivity in treatment planning. |
|
2887.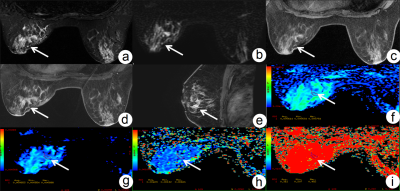 |
112 |
IVIM Combined with DCE-MRI Characterize Architectural Distortion
Detected on Mammography: A Pilot Study
deshuo dong1,
anliang chen1,
lina zhang1,
ailian liu1,
qingwei song1,
jie yang2,
haonan guan3,
and lizhi xie3
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 3GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, Dalian, China Keywords: fMRI Analysis, Breast Motivation: Breast adenosis (AD) detection is crucial for early breast cancer diagnosis. Traditional mammography has limitations. Goal(s): To enhance AD diagnosis using MRI and evaluate MRI's diagnostic value for AD detected in mammography. Assess the combined potential of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) sequences. Approach: Collected data from AD-diagnosed patients who underwent breast MRI. Analyzed DCE-MRI and IVIM parameters, compared benign and malignant AD, and assessed their combined diagnostic efficiency. Results: MRI exhibited high sensitivity (100%) and NPV (100%) for malignancy exclusion. DCE-MRI and IVIM combined yielded superior results with an AUC of 0.984. Impact: This study demonstrates that combining DCE-MRI and IVIM significantly enhances the diagnostic accuracy of AD changes. It offers a non-invasive approach to differentiate benign from malignant lesions, reducing unnecessary invasive procedures and improving breast cancer management. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.