Digital Poster
Cardiac Inflammation
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 04-09 May 2024 • Singapore

| Computer # | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3519.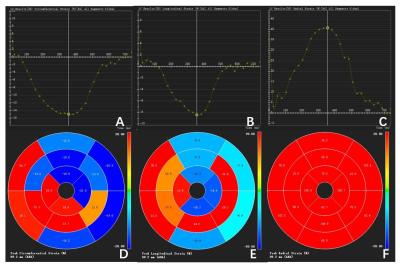 |
129 |
Evaluating Subclinical Myocardial Injury in Systemic Lupus
Erythematosus Patients Using CMR Feature Tracking
Lingling Huang1,
Xiaojuan Wang1,
Qi Lin1,
Peng Wu2,
and Yongzhou Xu3
1Longyan First Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Longyan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China Keywords: Myocardium, Myocardium, SLE Motivation: Early detection of myocardial injury in Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients is important. Goal(s): Find a clinical biomarker for preclinical myocardial injury in SLE patients. Approach: CMR-FT (Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking) technology and CVI 42 software were used to measure cardiac functional parameters and myocardial strain parameters for SLE patients with/without subclinical myocardial injury and healthy controls. Results: Compared to the control group, the circumferential strain (CS) and longitudinal strain (LS) were found to be reduced in patients with subclinical myocardial injury in SLE. The CMR-FT technology was able to detect changes in myocardial strain before a decrease in ejection fraction occurred. Impact: Early detection of myocardial injury in SLE patients and proactive treatment are important for improving patient outcomes. This study found that CMR-FT quantitative technique can identify subclinical myocardial damage in patients with SLE. |
|
3520.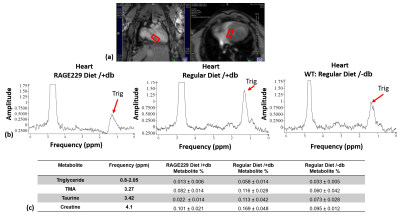 |
130 |
Assessment of RAGE-DIAPH1 interaction agonist induced changes to
cardiac and muscle metabolites in a murine model of Type-1
Diabetes
Rajiv G Menon1,2,
Syed Hasan3,
Ann Marie Schmidt3,
Ravichandran Ramasamy3,
and Ravinder R Regatte1,2
1Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research (CAI2R), Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 3Department of Endocrinology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States Keywords: Endocrine, Diabetes Motivation: Diabetes Mellitus causes systemic changes in lipids of multiple organs. Previous studies have shown that receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and its tail binding partner diaphanous 1 (Diaph1) are key mediators of metabolic changes in T1D mice. Goal(s): To use 1H-MRS and CSE-MRI to investigate the metabolic effects of the RAGE-DIAPH1 interaction antagonist, RAGE229, in T1D murine hearts and hind limb. Approach: 18 mice were divided into 3 cohorts (Rage229/+db, RegDiet/+db, RegDiet/-db) and scanned using 1H-MRS and CSE-MRI. Results: Inhibition of RAGE-DIAPH1 interaction by RAGE229 leads to significant reduction in triglyceride levels in hearts and hind limb of T1D mice. Impact: The results of this study set the stage for further testing of RAGE229 as potential therapeutic adjuncts in alleviating metabolic dysfunction in T1D. |
|
3521.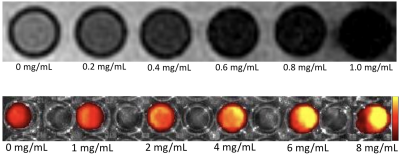 |
131 |
MRI and fluorescence imaging of perfluorohexane loaded
nanoparticles targeting atherosclerosis and their effects on
activated macrophages
Man Ye1
1Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China Keywords: Atherosclerosis, Molecular Imaging Motivation: Cardiovascular disease is the main cause and disease of morbidity and mortality in the world, and atherosclerosis causes more than 90% of cardiovascular diseases. Goal(s): Early diagnosis and timely treatment of atherosclerosis to reduce the morbidity and mortality of residents. Approach: In the development of atherosclerosis, reducing the content of macrophages which derived foam cells can reverse the formation of atherosclerotic plaque. Results: The dextran sulfate in the nanoparticles can target SR-A of activated macrophages in atherosclerosis, and then the nanoparticles undergo phase transformation in macrophages to induce apoptosis. Impact: The nanoparticles have multi-mode molecular imaging capabilities, and have excellent targeting performance. Under LIFU, it can undergo phase transformation and induce apoptosis of macrophages, providing a promising strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerotic plaque in the future. |
|
3522.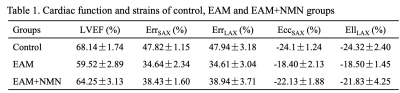 |
132 |
7.0T CMR-TT evaluate quantitatively the effect of nicotinamide
mononucleotide on experimental autoimmune myocarditis via
ferroptosis
Chunhua Wang1,
Zhetao Wang2,
Jing Zhu3,
Peng Zhou1,
and Fabao Gao2
1Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chenggdu, China, 2West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chenggdu, China, 3Chengdu Medical College the First Affiliated Hospital, Chenggdu, China Keywords: Inflammation, Infiltration, Myocardium Motivation: To evaluate the diagnosis and follow-up value of CMR-TT in myocarditis. To explore more treatment strategies for myocarditis and the potential mechanism. Goal(s): Using 7.0T CMR-TT to evaluate the effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) for experimental autoimmune myocarditis and exploring the potential mechanism. Approach: Lewis rats were induced to be autoimmune myocarditis by porcine cardiac myosin and treated by NMN. The strains of rats were detected by 7.0T CMR-TT. Histopathology, biochemistry and ELISA were used for myocardial damage and ferroptosis. Results: Strains reduction in EAM was alleviated by NMN. The changes of cardiac and ferroptosis biomarkers were relieved by NMN. Impact: CMR-TT can provide the imaging evidence for the diagnosis and follow-up of myocarditis. The study will provide more options and targets for clinicians to treat myocarditis. |
|
3523.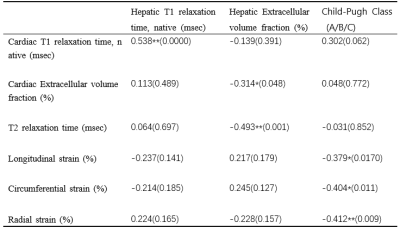 |
133 |
Using cardiac MRI quantification in identifying subtle cardiac
structural and functional changes in patients with liver
cirrhosis.
Yu Zhang1,
Yiming Yang2,
Zhiyuan Chen2,
Dongjing Zhou2,
Shuping Zhang2,
Ruhang Huang2,
Haodong Qin3,
and Yupin Liu2
1Second Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou,China, China, 2Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, Guangzhou, China, China, 3MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou, China, China Keywords: Inflammation, Infiltration, Quantitative Imaging Motivation: Patients with liver cirrhosis often have heart-related physiological and pathological changes. Goal(s): The aim of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of using multiple parameters for cardiac MRI quantification in identifying subtle cardiac structural and functional changes in patients with liver cirrhosis. Approach: Cardiac MRI methods were employed, along with Mann-Whitney U tests and Spearman correlation analyses for Statistical analyses. Results: Our results indicated that MRI showed an increase in myocardial fibrosis parameters, and there was a positive correlation between liver T1 relaxation time and myocardial T1 relaxation time. Impact: This study could lead to improved understanding of heart diseases associated with cirrhosis, helping to create better diagnostic and treatment plans, ultimately improving patients' quality of life. |
|
3524.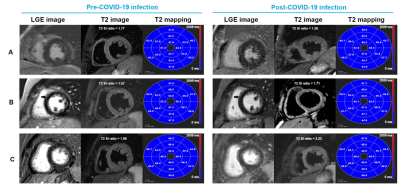 |
134 |
Multiparametric Cardiovascular MR in Non-hospitalized COVID-19
Infection Subjects: An Intra-individual Comparison Study
Song Luo1 and
Wei Qiang Dou2
1Diagnostic Radiology, Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2MR Research, GE Healthcare, Bei Jing, China Keywords: Inflammation, Infiltration, Heart Motivation: To evaluate the prevalence of cardiac involvement in mild, non-hospitalized, recovered COVID-19 patients Goal(s): investigate the changes of cardiac structure and function by comparing multiparametrical cardiac MR Approach: This prospective study enrolled 39 unhospitalized COVID-19 patients. Results: Four patients had the same late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) pattern at baseline and repeated CMR and 5 female patients had myocardial T2 ratio >2 but with normal T2 value in post-COVID-19 CMR. All other CMR parameters were in normal ranges before and after COVID-19 infection. Impact: This knowledge has an important role in can help alleviate wide social concern on COVID-19 related myocarditis. |
|
3525.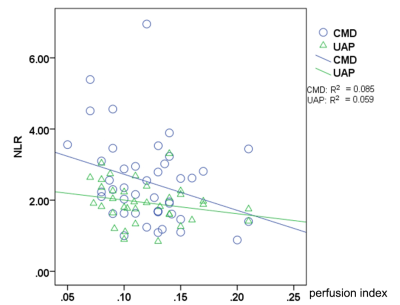 |
135 |
Association between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and MR
myocardial first pass perfusion in patient with coronary
microvascular dysfunction
Gang Zhang1,
Wei Xing1,
Junjing He1,
Zhiwei Shen2,
Jiemei Sun1,
and Geli Zhou1
1First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Inflammation, Infiltration, Inflammation Motivation: The study on correlation between blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and cardiac magnetic resonance perfusion imaging (CMRI) quantitative indexes in patients with cardiac syndrome X (CSX) is few. Goal(s): To investigate the relationship between the blood neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the mean value and coefficient of variation of the magnetic resonance myocardial first pass perfusion parameters in patients with cardiac syndrome X. Approach: A total of 53 patients with CSX and 43 patients with unstable angina pectoris (UAP) were evaluated using MR myocardial perfusion and blood routine examination. Results: A negative correlation was observed between the myocardial perfusion index in CSX and blood NLR. Impact: It is provided further evidence for the potential utility of NLR as a diagnostic marker for CSX. |
|
3526.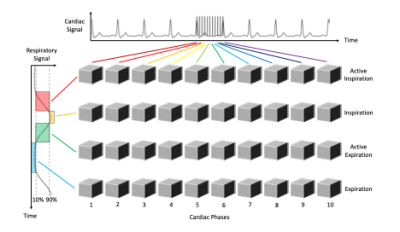 |
136 |
A 5D MRI Framework for Cardiac Motion Characterization in
Radiation Therapy
Tarun Naren1,
Chase Ruff1,2,
Kevin M Johnson1,3,
Carri Glide-Hurst2,
and Oliver Wieben1,3
1Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Human Oncology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States Keywords: Hematology, Oncology, Radiotherapy, 5D, cardiac
Motivation: Current radiotherapy treatment planning
does not account for cardiac substructure motion during the
respiratory and cardiac cycle, thus leading to suboptimal
treatment plans.
Goal(s): To develop a free breathing 5D MRI framework
to characterize cardiac and respiratory motion of the heart
for use in radiotherapy treatment planning.
Approach: A double gated (cardiac and respiratory)
radial bSSFP acquisition and constrained reconstruction
pipeline were implemented and motion and tested in five
volunteers.
Results: Left ventricle centroid analysis showed 5D
images provided significant motion characterization.
Advanced reconstruction allows <5 min scan time. Impact: The primary impact of this work will be on patients receiving thoracic radiotherapy. More accurate treatment planning and sparing of sensitive cardiac substructures will improve patient outcomes and reduce long term cardiotoxicities. |
|
3527.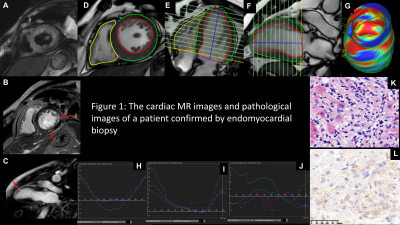 |
137 |
Value of feature-tracking myocardial strain analysis in
evaluation patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)
associated myocarditis
Kai Zhao1,
Jia Liu1,
Wei Li1,
Jianxiu Lian2,
and Jianxing Qiu1
1Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Myocardium, Heart, Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Myocarditis; Cardiac magnetic resonance; Feature-tracking; Strain Motivation: Myocarditis is a potentially fatal complication of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI). More diagnostic tools are needed beside enzymes. Goal(s): Data on CMR characteristics of ICI myocarditis is limited, especially the new strain analysis. Approach: The study compared the cardiac functional and stain parameters between patients with ICI associated myocarditis and controls. The parameters included LVEF, CO, CI, EDV/BSA, ESV/BSA, and SV/BSA, incidence rate of myocardial edema and LGE, LS, CS, RS (global and segmental). Results: For patients with ICI associated myocarditis, LVEF, ESV/BSA, CS (basal, mid, apical and global) and LS (mid, apical and global) may be effective parameters to identify myocardial injury. Impact: Some CMR strain parameters and cardiac function indicators significantly impaired, which may be helpful for early detection and to evaluate treatment effectiveness of ICI associated myocarditis. |
|
3528.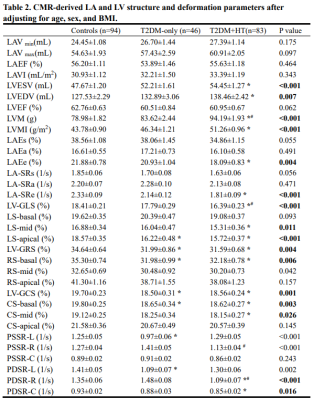 |
138 |
Exploring the additive effects of hypertension on left cardiac
structure and deformation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
using CMR-FT
Miaomiao Bai1,
Chen Zhang2,
Jianbo Lyu1,
Endong Zhao1,
Jiahui Zhang1,
and Xiaofeng Qu1
1Department of Radiology, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2MR Research Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare, Beijing, China Keywords: Myocardium, Cardiovascular, CMR-FT, Hypertension, T2DM Motivation: Hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)-related cardiac damage have a partial common pathological mechanism[1]. Goal(s): To investigate the effects of hypertension on left cardiac structure and deformation in patients with T2DM using cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking. Approach: The balanced steady-state free precession cine sequence and commercial software, cvi42, were used for image acquisition and post-processing. Covariance and multivariate linear regression were used for statistical analysis. Results: Hypertension has additive effects on left atrial and left ventricular geometry and strain in patients with diabetes. Impact: Our findings regarding the additive effect of hypertension in patients with diabetes provides a basis for clinical management and treatment of these comorbidities. |
|
3529.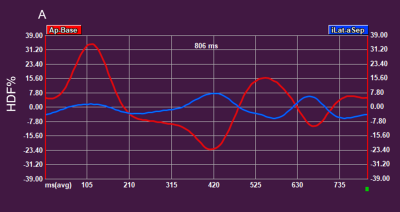 |
139 |
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance-derived left ventricular
hemodynamic force among patients with systemic lupus
erythematosus
Yangzhen Hou1,2,
Hui Zhou1,
Jing Luo1,
Ji Yang1,
Huiting Zhang3,
and Xiaoming Bi4
1Department of Radiology, Xiangya Hospital Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China., Changsha, China, 2Department of Radiology, Xiangya Hospital Central South University, Changsha, Hunan,, China., Changsha, China, 3Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Wuhan, China, Wuhan, China, 4MR Collabration, Siemens Healthineers, Los Angeles, USA, Los Angeles, CA, United States Keywords: Heart Failure, Cardiovascular Motivation: Cardiovascular involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients is common and serious; early and accurate identification of the cardiac dysfunction is crucial. Goal(s): Our goal was to investigate the potential role of hemodynamic force (HDF) in early recognizing impaired cardiac function in SLE. Approach: Left ventricular (LV) HDF and strain analysis were performed based on long-axis cine imaging using feature-tracking in 36 SLE patients and 34 healthy volunteers. Results: The force ratio between transverse and longitudinal direction was larger in SLE patients with no difference of strain analysis, indicating that the orientation of HDF altered in LV. Impact: This study demonstrated that HDF analysis can early detect systolic dysfunction in SLE in advance of significant decrease of LV EF, which may contribute to the early diagnosis of cardiac involvement and prognosis improvement of patients. |
|
3530.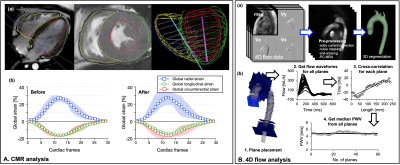 |
140 |
Impact of pegloticase on cardiovascular function in young-onset
Type 2 Diabetes
Sungho Park1,2,
Takashi Fujiwara1,
Ye Ji Choi3,
Callyn Rountree-Jablin3,
Laura Pyle3,
Petter Bjornstad3,
and Alex J Barker1,4
1Department of Radiology, Children's Hospital Colorado, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, CO, United States, 2Institute of Medical Devices, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea, Republic of, 3Department of Pediatrics, Division of Endocrinology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, United States, 4Department of Bioengineering, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, CO, United States Keywords: Myocardium, Safety, Youth-onset T2D, CMR, 4D flow MRI Motivation: Increasing prevalence of youth-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a global concern and characterized by a higher risk for hyperuricemia, a strong risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Goal(s): Studies have shown that serum uric acid (SUA) lowering in the general population may confer cardiovascular protection, but there have been no studies on its effectiveness in young adults with T2D. Approach: Here, we hypothesized aggressive SUA lowering using single intravenous infusion dose of the uricase, pegloticase, will attenuate cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) markers of CVD in young adults with T2D. Results: Unexpectedly, we documented impaired CMR-based global longitudinal strain after pegloticase infusion. Impact: Our study demonstrates the impacts of a drug therapy to reduce serum uric acid in youth-onset T2D and its impact on cardiovascular function using CMR. A comprehensive examination of the cardiovascular effects of the therapy is required for youth-onset T2D. |
|
3531. |
141 |
Assessing different CKD stages by cardiac magnetic resonance
native T2 mapping and NT-pro BNP, a polit study
Yating Chen1,
Jingyu Zhang1,
Junjie Li1,
and Zhiyong Li1
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China Keywords: Myocardium, Kidney, chronic kidney disease, Cardiac magnetic resonance, T2 mapping, biomarkers, NT-pro BNP Motivation: We can use the positive correlation between natural T2 value and NT-pro BNP to achieve early clinical detection, diagnosis and treatment of myocardial abnormalities caused by chronic kidney disease, thereby improving the prognosis of patients with CKD. Goal(s): Our aim was to analyze the relationship between native T2 value and NT-pro BNP over stage progression. Approach: CMR is performed on a 3.0-T scanner. Cardiac data were assessed using CVI.42. Pearson, Spearman coefficients and ANOVA analysis were used to analyze the data. Results: There was a statistically significant difference in autologous T2 value between different CKD groups. and NT-pro BNP. Subgroups stratified by eGFR showed a significantly differential correlation between NT-pro BNP and native T2 value. Impact: We can use the positive correlation between natural T2 value and NT-pro BNP to achieve early clinical detection, diagnosis and treatment of myocardial abnormalities caused by chronic kidney disease, thereby improving the prognosis of patients with CKD. |
|
3532.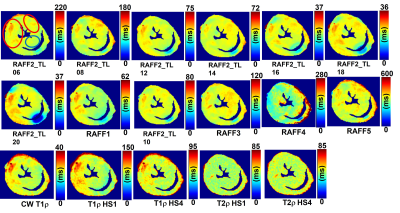 |
142 |
Effects of RAFF2 periodicity on contrast between infarct and
remote myocardium
Elias Ylä-Herttuala1,
Shalom Michaeli2,
and Timo Liimatainen3
1A.I. Virtanen Institute, Kuopio, Finland, 2University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States, 3University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland Keywords: Myocardium, Preclinical, RAFF2, Rotating frame relaxations, myocardial infarct Motivation: Current MRI techniques are insufficiently sensitive to determine specific physiological changes in the myocardium after infarction. Goal(s): To optimize sensitivity of RAFF2 technique to specific tissue changes of the myocardium after myocardial infarct (MI) by modulating the durations of P-packets of RAFF2 pulses. Approach: Mice hearts are imaged ex vivo 7 days after the factitious myocardial infarction by using different durations of P-packets of the RAFF2 along with other rotating frame relaxation techniques. Results: Duration of the RAFF2 pulse have an impact on relaxation maps and contrast of MI area compared to the remote area. Increased rotating frame relaxation times were also detected. Impact: This study presents novel application of RAFF2 technique for quantitative ex vivo assessment of mice myocardium after infarction. This method allows to study physiological changes in the myocardium with high sensitivity. |
|
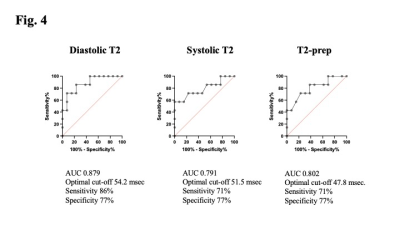 |
143143 |
Differentiation of cardiac inflammatory diseases by myocardial
cine T2 mapping
Mana Kato1,
Michinobu Nagao1,
Masami Yoneyama2,
Yasuhiro Goto1,
Isao Shiina1,
Kazuo Kodaira1,
and Shuji Sakai1
1Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan Keywords: Inflammation, Infiltration, Cardiomyopathy Motivation: Development of a non-contrast differential method for cardiac inflammatory disease Goal(s): Accurate identification of cardiac sarcoidosis and myocarditis Approach: Cardiac cine imaging to project T2 values using T2prep-based T2 mapping with dynamic multiple trigger-delay framework Results: Diastolic cine T2 values (54.2msec.) discriminated cardiac sarcoidosis from myocarditis with an AUC of 0.879, sensitivity of 86%, and specificity of 77%. Impact: This method is a new technique that captures changes in myocardial properties during the cardiac cycle without the use of contrast media. |
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.