Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain:
Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Vikas Gulani, M.D., Ph.D., Fernando Calamante, Ph.D., Frank G. Shellock, Ph.D., Emanuel Kanal, M.D., Scott B. Reeder, M.D., Ph.D.
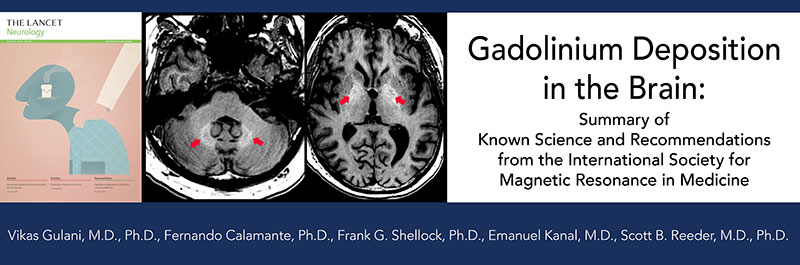
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) announces the publication of clinical and research guidelines regarding gadolinium deposition on the brain, published in The Lancet Neurology on 13 June 2017. Gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCAs) are widely used as an essential component of many diagnostic MRI exams. GBCAs have a proven track record for accurate diagnosis and treatment monitoring of a large number of diseases including cancer, neurological pathology, heart disease, liver disease, and many other important conditions afflicting adults and children. GBCAs have also had an outstanding safety profile with over 300 million administered doses over the past 30 years with relatively uncommon, well-defined side effects and toxicities. Recently, reports of deposition of small quantities of gadolinium in certain regions of the brain have been reported, raising concerns of possible toxicity. In this article, the authors, representing a panel of international experts on the ISMRM Safety Committee, provide a review of current knowledge of the gadolinium deposition phenomenon, and based on this knowledge, provide recommendations on the use of GBCAs for clinical care and research.
Read the whole article for free in The Lancet
Note: Requires free registration to access the full article.

